Abstract
Purpose
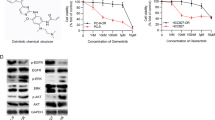
Perifosine has shown antitumor activity via inhibition of Akt phosphorylation in many advanced solid tumors. This study investigated the efficacy of perifosine alone and in combination with sorafenib in a transgenic mouse model of HCC.
Methods
The mouse model of HCC was generated by hydrodynamic injection of transposons encoding HrasG12V and short-hairpin RNA downregulating p53. The transgenic mice were treated with perifosine alone and in combination with sorafenib to evaluate efficacy of drugs on tumor growth and survival.
Results
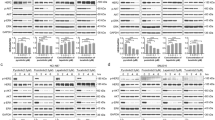
Treatment with perifosine for 5 weeks, alone and in combination with sorafenib, strongly inhibited tumor growth and increased survival. Perifosine inhibited HCC cell proliferation, induced apoptosis, and decreased tumor angiogenesis. Furthermore, its combination with sorafenib enhanced these effects. In addition, Akt phosphorylation was decreased by perifosine and further decreased by combination treatment. Although perifosine alone did not appear to activate the caspase pathway, combination treatment increased the cleavage of caspase-3, caspase-9, and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase.
Conclusions
The preclinical effect that current study showed represents a strong rationale for clinical trials using perifosine alone and in combination with sorafenib in the treatment of HCC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GEM:
-
Genetically engineered mouse
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MEK:
-
MAPK kinase
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- Shp53:
-
Short-hairpin RNA downregulating p53
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J (2012) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 379:1245–1255. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61347-0
Bruix J, Sherman M (2005) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 42:1208–1236. doi:10.1002/hep.20933
Chan SL, Mo FK, Johnson PJ, Liem GS, Chan TC, Poon MC, Ma BB, Leung TW, Lai PB, Chan AT, Mok TS, Yeo W (2011) Prospective validation of the Chinese University prognostic index and comparison with other staging systems for hepatocellular carcinoma in an Asian population. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:340–347. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06329.x
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:378–390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J, Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D, Guan Z (2009) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:25–34. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(08)70285-7
Bruix J, Sherman M (2011) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology 53:1020–1022. doi:10.1002/hep.24199
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501. doi:10.1038/nrc839
Patel V, Lahusen T, Sy T, Sausville EA, Gutkind JS, Senderowicz AM (2002) Perifosine, a novel alkylphospholipid, induces p21(WAF1) expression in squamous carcinoma cells through a p53-independent pathway, leading to loss in cyclin-dependent kinase activity and cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res 62:1401–1409
Chiarini F, Del Sole M, Mongiorgi S, Gaboardi GC, Cappellini A, Mantovani I, Follo MY, McCubrey JA, Martelli AM (2008) The novel Akt inhibitor, perifosine, induces caspase-dependent apoptosis and downregulates P-glycoprotein expression in multidrug-resistant human T-acute leukemia cells by a JNK-dependent mechanism. Leukemia 22:1106–1116. doi:10.1038/leu.2008.79
Leighl NB, Dent S, Clemons M, Vandenberg TA, Tozer R, Warr DG, Crump RM, Hedley D, Pond GR, Dancey JE, Moore MJ (2008) A Phase 2 study of perifosine in advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 108:87–92. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9584-x
Knowling M, Blackstein M, Tozer R, Bramwell V, Dancey J, Dore N, Matthews S, Eisenhauer E (2006) A phase II study of perifosine (D-21226) in patients with previously untreated metastatic or locally advanced soft tissue sarcoma: A National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group trial. Invest New Drugs 24:435–439. doi:10.1007/s10637-006-6406-7
Crul M, Rosing H, de Klerk GJ, Dubbelman R, Traiser M, Reichert S, Knebel NG, Schellens JH, Beijnen JH, ten Bokkel Huinink WW (2002) Phase I and pharmacological study of daily oral administration of perifosine (D-21266) in patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur J Cancer 38:1615–1621
Fei HR, Chen G, Wang JM, Wang FZ (2010) Perifosine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines by blockade of Akt phosphorylation. Cytotechnology 62:449–460. doi:10.1007/s10616-010-9299-4
Teachey DT, Grupp SA, Brown VI (2009) Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors and their potential role in therapy in leukaemia and other haematological malignancies. Br J Haematol 145:569–580. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.07657.x
LoPiccolo J, Blumenthal GM, Bernstein WB, Dennis PA (2008) Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: effective combinations and clinical considerations. Drug Resist Updat 11:32–50. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2007.11.003
Chen KF, Chen HL, Tai WT, Feng WC, Hsu CH, Chen PJ, Cheng AL (2011) Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway mediates acquired resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 337:155–161. doi:10.1124/jpet.110.175786
Zhai B, Hu F, Jiang X, Xu J, Zhao D, Liu B, Pan S, Dong X, Tan G, Wei Z, Qiao H, Jiang H, Sun X (2014) Inhibition of Akt reverses the acquired resistance to sorafenib by switching protective autophagy to autophagic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 13:1589–1598. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-13-1043
Ju HL, Ahn SH, Kim DY, Baek S, Chung SI, Seong J, Han KH, Ro SW (2013) Investigation of oncogenic cooperation in simple liver-specific transgenic mouse models using noninvasive in vivo imaging. PLoS One 8:e59869. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059869
Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Gorden A, Farina M, Conner EA, Lee JS, Factor VM, Thorgeirsson SS (2006) Ubiquitous activation of Ras and Jak/Stat pathways in human HCC. Gastroenterology 130:1117–1128. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.01.006
Villanueva A, Chiang DY, Newell P, Peix J, Thung S, Alsinet C, Tovar V, Roayaie S, Minguez B, Sole M, Battiston C, Van Laarhoven S, Fiel MI, Di Feo A, Hoshida Y, Yea S, Toffanin S, Ramos A, Martignetti JA, Mazzaferro V, Bruix J, Waxman S, Schwartz M, Meyerson M, Friedman SL, Llovet JM (2008) Pivotal role of mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 135:1972–1983. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.008
Wang C, Cigliano A, Delogu S, Armbruster J, Dombrowski F, Evert M, Chen X, Calvisi DF (2013) Functional crosstalk between AKT/mTOR and Ras/MAPK pathways in hepatocarcinogenesis: implications for the treatment of human liver cancer. Cell Cycle 12:1999–2010. doi:10.4161/cc.25099
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y, Mills GB (2005) Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:988–1004. doi:10.1038/nrd1902
Calvisi DF, Wang C, Ho C, Ladu S, Lee SA, Mattu S, Destefanis G, Delogu S, Zimmermann A, Ericsson J, Brozzetti S, Staniscia T, Chen X, Dombrowski F, Evert M (2011) Increased lipogenesis, induced by AKT-mTORC1-RPS6 signaling, promotes development of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 140:1071–1083. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.12.006
Chee KG, Longmate J, Quinn DI, Chatta G, Pinski J, Twardowski P, Pan CX, Cambio A, Evans CP, Gandara DR, Lara PN Jr (2007) The AKT inhibitor perifosine in biochemically recurrent prostate cancer: a phase II California/Pittsburgh cancer consortium trial. Clin Genitourin Cancer 5:433–437. doi:10.3816/CGC.2007.n.031
Posadas EM, Gulley J, Arlen PM, Trout A, Parnes HL, Wright J, Lee MJ, Chung EJ, Trepel JB, Sparreboom A, Chen C, Jones E, Steinberg SM, Daniels A, Figg WD, Dahut WL (2005) A phase II study of perifosine in androgen independent prostate cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 4:1133–1137
Dasmahapatra GP, Didolkar P, Alley MC, Ghosh S, Sausville EA, Roy KK (2004) In vitro combination treatment with perifosine and UCN-01 demonstrates synergism against prostate (PC-3) and lung (A549) epithelial adenocarcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 10:5242–5252. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-03-0534
Stommel JM, Kimmelman AC, Ying H, Nabioullin R, Ponugoti AH, Wiedemeyer R, Stegh AH, Bradner JE, Ligon KL, Brennan C, Chin L, DePinho RA (2007) Coactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases affects the response of tumor cells to targeted therapies. Science 318:287–290. doi:10.1126/science.1142946
De J, Brown RE (2010) Tissue-microarray based immunohistochemical analysis of survival pathways in nodular sclerosing classical Hodgkin lymphoma as compared with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int J Clin Exp Med 3:55–68
Llovet JM, Bruix J (2008) Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 48:1312–1327. doi:10.1002/hep.22506
Gedaly R, Angulo P, Hundley J, Daily MF, Chen C, Koch A, Evers BM (2010) PI-103 and sorafenib inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by blocking Ras/Raf/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. Anticancer Res 30:4951–4958
Huynh H, Ngo VC, Koong HN, Poon D, Choo SP, Thng CH, Chow P, Ong HS, Chung A, Soo KC (2009) Sorafenib and rapamycin induce growth suppression in mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 13:2673–2683. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00692.x
Manov I, Pollak Y, Broneshter R, Iancu TC (2011) Inhibition of doxorubicin-induced autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells by sorafenib—the role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase counteraction. FEBS J 278:3494–3507. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08271.x
Piguet AC, Saar B, Hlushchuk R, St-Pierre MV, McSheehy PM, Radojevic V, Afthinos M, Terracciano L, Djonov V, Dufour JF (2011) Everolimus augments the effects of sorafenib in a syngeneic orthotopic model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 10:1007–1017. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-10-0666
Strowski MZ, Cramer T, Schafer G, Juttner S, Walduck A, Schipani E, Kemmner W, Wessler S, Wunder C, Weber M, Meyer TF, Wiedenmann B, Jons T, Naumann M, Hocker M (2004) Helicobacter pylori stimulates host vascular endothelial growth factor-A (vegf-A) gene expression via MEK/ERK-dependent activation of Sp1 and Sp3. FASEB J 18:218–220. doi:10.1096/fj.03-0055fje
Chaparro M, Gonzalez Moreno L, Trapero-Marugan M, Medina J, Moreno-Otero R (2008) Review article: pharmacological therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with sorafenib and other oral agents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 28:1269–1277. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03857.x
Wilhelm S, Carter C, Lynch M, Lowinger T, Dumas J, Smith RA, Schwartz B, Simantov R, Kelley S (2006) Discovery and development of sorafenib: a multikinase inhibitor for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:835–844. doi:10.1038/nrd2130
Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Ottaviano Y, Davidson NE, Poirier GG (1993) Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: an early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 53:3976–3985
Guidetti A, Carlo-Stella C, Locatelli SL, Malorni W, Mortarini R, Viviani S, Russo D, Marchiano A, Sorasio R, Dodero A, Farina L, Giordano L, Di Nicola M, Anichini A, Corradini P, Gianni AM (2014) Phase II study of perifosine and sorafenib dual-targeted therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoproliferative diseases. Clin Cancer Res 20:5641–5651. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-0770
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the Korean Association for the Study of Liver and was supported by a faculty research grant of Yonsei University College of Medicine for 2013 (6-2013-0004). The authors are grateful to Dong-Su Jang (Medical Illustrator, Medical Research Support Section, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea) for his help with the figure.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.N., Ro, S.W., Kim, D.Y. et al. Efficacy of perifosine alone and in combination with sorafenib in an HrasG12V plus shp53 transgenic mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 76, 257–267 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2787-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2787-7