Abstract
Purpose
Vinflunine ditartrate is a microtubule inhibitor belonging to the vinca alkaloid family. This phase I study was carried out to evaluate the maximal tolerated dose, the safety profile, the pharmacokinetics and the activity of oral vinflunine (VFL) given daily in patients with advanced/metastatic solid tumours and who have failed standard therapy.
Methods
Patients were treated with oral VFL administered once daily for 6 weeks followed by a two-week rest. Sequential dose-escalating cohorts of patients were enrolled into 5 dose levels: 20, 40, 60, 75 and 95 mg/day.
Results
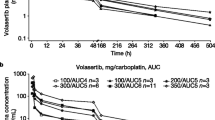
In total, 27 patients received 53 cycles. Dose-limiting toxicities (DLT) were observed from 60 mg/day. The dose levels 75 and 95 mg/day were both assessed as maximal tolerated dose. The most frequent dose-limiting toxicities were of haematological origin. The recommended dose was defined as 60 mg/day, dose at which 4 patients experienced long stabilizations (≥4 months) and also received longer treatment duration in comparison with the other dose levels. Blood exposure of VFL and its active metabolite 4-O-deacetyl vinflunine (DVFL) increased proportionally to the dose levels. The concentrations of VFL and DVFL reached a steady state at, respectively, 5 and 20 days and remained stable for the rest of the cycle. Increased incidence of DLT/SAE was consistent with the increase of VFL dose and drug exposure.
Conclusions
These results showed the feasibility of daily oral vinflunine administration on a 6-week treatment duration. This new schedule of administrations enabled sustained and stable blood concentrations of both VFL and DVFL. The recommended dose was defined at 60 mg/day, dose at which 4 patients experienced clinical benefit.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennouna J, Campone M, Delord JP, Pinel MC (2005) Vinflunine: a novel antitubulin agent in solid malignancies. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 14(10):1259–1267
Bennouna J, Delord JP, Campone M (2008) Vinflunine: a new microtubule inhibitor agent. Clin Cancer Res 14(6):1625–1632
Kruczynski A, Barret JM, Etievant C, Colpaert F, Fahy J, Hill BT (1998) Antimitotic and tubulin-interacting properties of vinflunine, a novel fluorinated Vinca alkaloid. Biochem Pharmacol 55(5):635–648
Bellmunt J, Theodore C, Demkov T, Komyakov B, Sengelov L, Daugaard G et al (2009) Phase III trial of vinflunine plus best supportive care compared with best supportive care alone after a platinum-containing regimen in patients with advanced transitional cell carcinoma of the urothelial tract. J Clin Oncol 27(27):4454–4461
Delord JP, Bennouna J, Favreau E, Brandely M, Puozzo C (2007) Absolute bioavailability of an oral form of vinflunine, a first phase I trial. AACR Meeting Abstracts 2007; (3_Molecular_Targets_Meeting):C145
Nguyen L, Petain A., Puozzo C (2009) Validation of neutropenia PK/PD model built from intravenous vinflunine and its application to design phase I trials with oral vinflunine. Abstracts of the Annual Meeting of the Population Approach Group in Europe 2009:18
Pasquier E, Kavallaris M, Andre N (2010) Metronomic chemotherapy: new rationale for new directions. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 7(8):455–465
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(3):205–216
Vermorken JB, Stupp R, Nguyen L (2003) Phase I study of IV vinflunine given on a weekly schedule in previously untreated patients with advanced solid tumours. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22:221 (Abstract 887) 2003
Zorza G, Van Heugen JC, De Graeve J, Puozzo C (2007) Development of a sensitive liquid chromatography method coupled with a tandem mass spectrometric detection for the clinical analysis of vinflunine and 4-O-deacetyl vinflunine in blood, urine and faeces. J Chromatogr B 853:294–302
Krzakowski M, Ramlau R, Jassem J, Szczesna A, Zatloukal P, Von Pawel J et al (2010) Phase III trial comparing vinflunine with docetaxel in second-line advanced non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-containing chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 28(13):2167–2173
Bennouna J, Fumoleau P, Armand JP, Raymond E, Campone M, Delgado FM et al (2003) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of the new vinca alkaloid vinflunine administered as a 10-min infusion every 3 weeks in patients with advanced solid tumours. Ann Oncol 14(4):630–637
Kerbel RS, Kamen BA (2004) The anti-angiogenic basis of metronomic chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 4(6):423–436
Pourroy B, Honore S, Pasquier E, Bourgarel-Rey V, Kruczynski A, Briand C et al (2006) Antiangiogenic concentrations of vinflunine increase the interphase microtubule dynamics and decrease the motility of endothelial cells. Cancer Res 66(6):3256–3263
Kruczynski A, Poli M, Dossi R, Chazottes E, Berrichon G, Ricome C et al (2006) Anti-angiogenic, vascular-disrupting and anti-metastatic activities of vinflunine, the latest vinca alkaloid in clinical development. Eur J Cancer 42(16):2821–2832
Briasoulis E, Pappas P, Puozzo C, Tolis C, Fountzilas G, Dafni U et al (2009) Dose-ranging study of metronomic oral vinorelbine in patients with advanced refractory cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(20):6454–6461
Addeo R, Sgambato A, Cennamo G, Montella L, Faiola V, Abbruzzese A et al (2010) Low-dose metronomic oral administration of vinorelbine in the first-line treatment of elderly patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 10(4):301–306
Sessa C, Guibal A, Del Conte G, Ruegg C (2008) Biomarkers of angiogenesis for the development of antiangiogenic therapies in oncology: tools or decorations? Nat Clin Pract Oncol 5(7):378–391
Jain RK, Duda DG, Willett CG, Sahani DV, Zhu AX, Loeffler JS et al (2009) Biomarkers of response and resistance to antiangiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(6):327–338
Maraveyas A, Lam T, Hetherington JW, Greenman J (2005) Can a rational design for metronomic chemotherapy dosing be devised? Br J Cancer 92(8):1588–1590
Acknowledgments
This study has been sponsored by Institut de Recherche Pierre Fabre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delord, J.P., Tourani, J.M., Lefresne, F. et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of oral vinflunine administered once daily for 6 weeks every 8 weeks in patients with advanced/metastatic solid tumours. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 71, 647–656 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-2051-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-2051-3