Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pharmacokinetics and CSF penetration of tasidotin and metabolites in a nonhuman primate model.
Methods
Tasidotin 0.75 mg/kg was administered intravenously. The plasma and CSF concentrations of tasidotin and its metabolites were determined. Pharmacokinetic parameters were estimated using model-independent and model-dependent methods.
Results
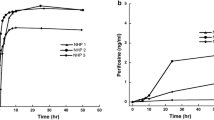
The mean (±SD) CSF:plasma AUC ratio for tasidotin was 1.1 ± 0.4. For tasidotin, tasidotin-C-carboxylate and desprolyl-tasidotin-C-carboxylate the plasma AUCs (mean ± SD) were 30 ± 10, 54 ± 19 and 12 ± 2 μM min, and apparent plasma half-lives were 27 ± 4, 229 ± 73 and 100 ± 29 min. The plasma clearance of tasidotin was 44 ± 14 ml/min/kg. The CSF AUC and half-life of tasidotin was 28 ± 10 μM min and 96 ± 40 min. The model-dependent plasma clearance was 35 ml/min/kg for tasidotin and 2 ml/min/kg for tasidotin-C-carboxylate.
Conclusions
Tasidotin penetrates into the CSF well and further evaluation of its activity in the treatment of central nervous system malignancies should be considered.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pellegrini F, Budman DR (2005) Review: tubulin function, action of antitubulin drugs, and new drug development. Cancer Invest 23:264–273
Kellie SJ, Barbaric D, Koopmans P, Earl J, Carr DJ, de Graaf SS (2002) Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of vincristine after bolus intravenous dosing: a surrogate marker of brain penetration. Cancer 94:1815–1820
Rice A, Michaelis ML, Georg G, Liu Y, Turunen B, Audus KL (2003) Overcoming the blood-brain barrier to taxane delivery for neurodegenerative diseases and brain tumors. J Mol Neurosci 20:339–343
Bai R, Friedman SJ, Pettit GR, Hamel E (1992) Dolastatin 15, a potent antimitotic depsipeptide derived from Dolabella auricularia. Interaction with tubulin and effects of cellular microtubules. Biochem Pharmacol 43:2637–2645
Jordan MA, Walker D, de Arruda M, Barlozzari T, Panda D (1998) Suppression of microtubule dynamics by binding of cemadotin to tubulin: possible mechanism for its antitumor action. Biochemistry 37:17571–17578
Bai R, Pettit GR, Hamel E (1990) Dolastatin 10, a powerful cytostatic peptide derived from a marine animal. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization mediated through the vinca alkaloid binding domain. Biochem Pharmacol 39:1941–1949
Stephenson K, Prasad V, Weitman S, Ludena RF (2004) ILX651 disrupts microtuble assembly by two mechanisms. AACR Meeting Abstracts 1297-c
Ray A, Okouneva T, Manna T, Miller HP, Schmid S, Arthaud L, Luduena R, Jordan MA, Wilson L (2007) Mechanism of action of the microtubule-targeted antimitotic depsipeptide tasidotin (formerly ILX651) and its major metabolite tasidotin C-carboxylate. Cancer Res 67:3767–3776
Cunningham C, Appleman LJ, Kirvan-Visovatti M, Ryan DP, Regan E, Vukelja S, Bonate PL, Ruvuna F, Fram RJ, Jekunen A, Weitman S, Hammond LA, Eder JP Jr (2005) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of the dolastatin-15 analogue tasidotin (ILX651) administered intravenously on days 1, 3, and 5 every 3 weeks in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 11:7825–7833
Ebbinghaus S, Rubin E, Hersh E, Cranmer LD, Bonate PL, Fram RJ, Jekunen A, Weitman S, Hammond LA (2005) A phase I study of the dolastatin-15 analogue tasidotin (ILX651) administered intravenously daily for 5 consecutive days every 3 weeks in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 11:7807–7816
McDermott DF, Hersh E, Weber J, Stephenson J, Cunningham CC, Ebbinghaus S, Thompson J, O’Day S, Weitman S, Hammond LA (2005) ILX651 administered daily for five days every 3 weeks (qdx5dq3w) in patients (pts) with inoperable locally advanced or metastatic melanoma:phase II experience. J Clin Oncol ASCO Annu Meet Proc 23:7556
Mita AC, Hammond LA, Bonate PL, Weiss G, McCreery H, Syed S, Garrison M, Chu QS, DeBono JS, Jones CB, Weitman S, Rowinsky EK (2006) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of tasidotin hydrochloride (ILX651), a third-generation dolastatin-15 analogue, administered weekly for 3 weeks every 28 days in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 12:5207–5215
Roth S, Krumbholz R, Arthaud L, Weitman S, Stephenson K (2004) In vivo and in vitro antitumor effects of ILX651, a pentapeptide with anovel mechanism of action. AACR Meet Abstr 488
Roth S, Krumbholz R, Schmid S, Arthaud L, Weitman S (2006) Tasidotin HCl (ILX651): in vivo antitumor effects after intravenous or oral administration. AACR Meet Abstr 66-c
Zhang WE, Kolb EA (2005) ILX651 inhibits growth of pediatric sarcoma lines in vitro and in vivo. AACR Meet Abstr 808
Herrington JD, Di Nunno L, Rinehart JJ (1998) Lack of CNS penetration of docetaxel in a patient with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Ann Pharmacother 32:611–612
McCully CL, Balis FM, Bacher J, Phillips J, Poplack DG (1990) A rhesus monkey model for continuous infusion of drugs into cerebrospinal fluid. Lab Anim Sci 40:520–525
Council NR (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy Press
Lewiston DEWA, Bonate PL et al (2004) Determination of ILX-651 (a synthetic analog of dolastatin-15) in human plasma by an LC/MS/MS method. Presented at American association of pharmaceutical scientists annual meeting M1012
YAe Shargel L (1999) Applied biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics. McGraw Hill, New York
Garg V, Zhang W, Gidwani P, Kim M, Kolb EA (2007) Preclinical analysis of tasidotin HCl in Ewing’s sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, synovial sarcoma, and osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:5446–5454
Glantz MJ, Choy H, Kearns CM, Mills PC, Wahlberg LU, Zuhowski EG, Calabresi P, Egorin MJ (1995) Paclitaxel disposition in plasma and central nervous systems of humans and rats with brain tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:1077–1081
Fellner S, Bauer B, Miller DS, Schaffrik M, Fankhanel M, Spruss T, Bernhardt G, Graeff C, Farber L, Gschaidmeier H, Buschauer A, Fricker G (2002) Transport of paclitaxel (Taxol) across the blood-brain barrier in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest 110:1309–1318
Heimans JJ, Vermorken JB, Wolbers JG, Eeltink CM, Meijer OW, Taphoorn MJ, Beijnen JH (1994) Paclitaxel (Taxol) concentrations in brain tumor tissue. Ann Oncol 5:951–953
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Genzyme Oncology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilburn, L.B., Bonate, P.L., Blaney, S.M. et al. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of tasidotin (ILX-651) and its metabolites in non-human primates. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 64, 335–340 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0875-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0875-7