Abstract
Purpose
It has been reported that Th2 cytokines down-regulate antitumor immunity, while activation of type 1 T cells promotes antitumor immunity. However, the immunological features of liver cirrhosis (LC) patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC) treated by intra-arterial chemotherapy are still unclear. The aim of this study was to assess the influence of intra-arterial combination chemotherapy on the Th1/Th2 balance in LC patients with aHCC.
Methods
Twenty-one adult Japanese LC patients with aHCC were treated by intra-arterial combination chemotherapy. The control group was composed of 20 adult Japanese patients with chronic hepatitis C diagnosed from examination of liver biopsy specimens. All control patients were over 55 years old and were stage 1 according to the fibrosis score of Desment.
Results
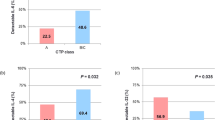
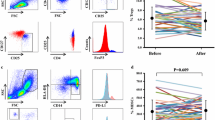
Thirteen of the 21 aHCC patients (group R) showed an objective response, but the other 8 patients (group N) showed no response. There were no significant differences of Th1 cells between group R and group N either before or after chemotherapy. Although there was no significant difference from group R, group N had a significantly higher percentage of Th2 cells than the control group both before and after chemotherapy (p < 0.05 by Tukey’s test).
Conclusions
These results indicate that the Th1/Th2 balance might be a useful indicator of the effect of intra-arterial combination chemotherapy in LC patients with aHCC. Inhibition of an increase of Th2 cells might be important for the efficacy of intra-arterial chemotherapy in such patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H, Tomimatsu M, Okazaki N, Hasegawa H, Nakajima Y, Onishi K (1985) Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Study of 850 patients. Cancer 56:918–928
Nagasue N, Yukaya H, Hamada T, Hirosue S, Kanashima R, Inokuchi K (1984) The natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. A study of 100 untreated cases. Cancer 54:1461–1465
Toyoda H, Nakano S, Kumada T, Takeda I, Sugiyama K, Osada T, Kirishima S, Suga T, Takahashi M (1995) The efficacy of continuous local arterial infusion of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin through an implanted reservoir for severe advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 52:295–299
Murata K, Shiraki K, Kawakita T, Yamamoto N, Okano H, Nakamura M, Sakai Takahisa, Deguchi M, Ohmori S, Nakano T (2003) Low-dose chemotherapy of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil or doxorubicin via implanted fusion port for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res 23:1719–1722
Okuda K, Tanaka M, Shibata J, Ando E, Ogata T, Kinoshita H, Eriguchi N, Aoyagi S, Takikawa K (1999) Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with continuous low dose administration of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil for multiple recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical treatment. Oncol Rep 6:587–591
Nagai H, Matsui T, Kanayama M, Momiyama K, Ikoma A, Okano N, Ikehara T, Matsumaru K, Watanabe M, Iida K, Ishii K, Sumino Y, Miki K (2007) Assessment of combined intra-arterial low-dose 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, and leucovolin chemotherapy for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma using the Japan integrated staging score. J Med Soc Toho 54:21–28
Nagai H, Kanayama M, Higami K, Momiyama K, Ikoma A, Okano N, Matsumaru K, Watanabe M, Ishii K, Sumino Y, Miki K (2007) Twenty-four hour intra-arterial infusion of 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, leucovorin is more effective than 6-hour infusion for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 13(2):280–284
Shevach EM (2001) Certified professionals: CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cell. J Exp Med 193:F41–F46
Stephens LA, Mottet C, Mason D, Powrie F (2001) Human CD4+ CD25+ thymoctes and peripheral T cells have immune suppressive activity in vitro. Eur J Immunol 31:1247–1254
Jonuleit H, Schmitt E, Stassen M, Tuettenberg A, Knop J, Enk AH (2001) Identification and functional characterization of human CD4+ CD25+ T cells with regulatory properties isolated from peripheral blood. J Exp Med 193:1285–1294
Mosmann TR, Coffman RL (1989) Th1 and Th2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different funtional properties. Annu Rev Immunol 7:145–173
O’Garra A (1998) Cytokines induce the development of funtionally heterogenous T helper cell subsets. Immunity 8:275–283
Roitt I (ed) (1997) Essential immunology, 9th edn. Blackwell, Malden, MA
Kuby J, Cameron J, Todd C, Mitchell J (2000) Immunology. 4th edn. Freeman Company, New York
Kobayashi M, Kobayashi H, Pollard RB, Suzuki F (1998) A pathogenic role of Th2 cells and their cytokine products on the pulmonary metastasis of murine B16 melanoma. J Immunol 160:5869–5873
Zitvogel L, Mayordomo JI, Tjandrawan T, DeLeo AB, Clarke MR, Lotze MT, Storkus WJ (1996) Therapy of murine tumors with tumor peptide-pulsed dendritic cells: dependence on T cells, B7 costimulation, and T helper cell 1-associated cytokines. J Exp Med 183:87–97
Tsung K, Meko JB, Peplinski GR, Tsung YL, Norton JA (1997) IL-12 induces T helper 1-directed antitumor response. J Immunol 158:3359–3365
Weiner GJ, Liu HM, Wooldridge JE, Dahle CE, Krieg AM (1997) Immunostimulatory oligodeoxynucleotides containing the CpG motif are effective as immune adjuvants in tumor antigen immunization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10833–10837
Hu H-M, Urba WJ, Fox BA (1998) Gene-modified tumor vaccine with therapeutic potential shifts tumor-specific T cell response from Type 2 to a type 1 cytokine profile. J Immunol 161:3033
Iwamiya T, Sawada S, Ohta Y (1994) Repeated arterial infusion chemotherapy for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma using an implantable drug delivery system. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol 33(Suppl.):S134–S138
Shinohara M, Ishii K, Takamura N (2003) Long-term changes of peripheral blood CD4-positive T cell subsets (Th1, Th2) in chronic hepatitis C patients with a sustained response no response to IFN. Hepatol Res 27: 260–265
Jung T, Schauer U, Heusser C, Neumann C, Rieger C (1993) Detection of intracellular cytokines by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 159:197–207
Kudo M, Chung H, Osaki Y (2003) Prognostic staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma (CLIP score): its value and limitations, and a proposal for new staging system, the Japan Integrated Staging score (JIS score). J Gastroenterol 38:207–215
Takamura N, Ishii K, Shinohara M, Kawafune T, Sumino Y (2002) Analysis of peripheral blood CD4 positive T cells using intracellular staging method in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Med Soc Toho Univ 49:45–52
Ishii K, Takamura N, Shinohara M, Shin H, Ikehara T, Hata S, Kawafune T, Sumino Y, Ohmoto Y (2002) Intracellular cytokine analysis of CD4-positive T cells predictive of sustained response to interferon therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci 47:778–783
Fukuzawa K, Takahashi K, Furuta K, Tagaya T, Ishikawa T, Wada K, Omoto Y, Koji T, Kakumu S (2001) Expression of Fas/Fas ligand and its involvement in infiltrating lymphocytes in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 36:681–688
Yakirevich E, Lefel O, Sova Y, Stein A, Cohen O, Izhak OB, Resnick MB (2002) Activated status of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and apoptosis in testicular seminoma. J Pathol 196:67–75
Ikeguchi M, Oi K, Hirooka Y, Kaibara N (2004) CD8+ lymphocyte infiltration and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 30:53–57
Sakaguchi S (2004) Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 22:531–562
Unitt E, Rushbrook SM, Marshall A, Davies S, Gibbs P, Morris LS, Coleman N, Alexander GJ (2005) Compromised lymphocytes infiltrate hepatocellular carcinoma: the role of T-regulatory cells. Hepatology 41:722–730
Ormandy LA, Hillemann T, Wedemeyer H, Manns MP, Greten TF, Korangy F (2005) Increased populations of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 65:2457–2464
Yang XH, Yamagiwa S, Ichida T, Matsuda Y, Sugahara S, Watanabe H, Sato Y, Abo T, Horwitz DA, Aoyagi Y (2006) Increase of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in the liver of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 45:254–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, H., Miyaki, D., Matsui, T. et al. Th1/Th2 balance: an important indicator of efficacy for intra-arterial chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62, 959–963 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0685-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0685-y