Abstract
Introduction
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) induces cancer cell-specific apoptosis by binding to a TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Binding of the Fas ligand on cytotoxic T lymphocytes to the Fas receptor on hepatocytes is also known to induce apoptosis. The aim of this study was to clarify changes of cytokines in patients with liver cirrhosis (LC) and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC) receiving intra-arterial combination chemotherapy.
Methods
Twenty-one adult Japanese LC patients with aHCC received intra-arterial combination chemotherapy. The serum levels of TNF-alpha, soluble TNF receptor-I (sTNFr-I), soluble Fas ligand (sFas L), and soluble Fas (sFas) were evaluated.
Results
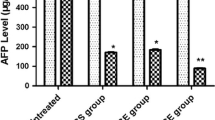
Thirteen of the 21 patients (group R) showed an objective response, while the other eight patients (group N) showed no response. The serum level of TNF-alpha was lower after chemotherapy than before chemotherapy in group N, but there was no difference of serum sTNFr-I levels between before and after chemotherapy and there were also no differences between the two groups. The serum sFas levels were higher after chemotherapy than before chemotherapy in group N, while there was no difference among groups.
Conclusions
These results indicate that a high serum TNF-alpha level and a low serum sFas level might be important for successful combined arterial chemotherapy in LC patients with aHCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H, Tomimatsu M, Okazaki N, Hasegawa H, Nakajima Y, Onishi K (1985) Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Study of 850 patients. Cancer 56:918–928
Nagasue N, Yukaya H, Hamada T, Hirosue S, Kanashima R, Inokuchi K (1984) The natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. A study of 100 untreated cases. Cancer 54:1461–1465
Toyoda H, Nakano S, Kumada T, Takeda I, Sugiyama K, Osada T, Kirishima S, Suga T, Takahashi M (1995) The efficacy of continuous local arterial infusion of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin through an implanted reservoir for severe advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 52:295–299
Murata K, Shiraki K, Kawakita T, Yamamoto N, Okano H, Nakamura M, Sakai Takahisa, Deguchi M, Ohmori S, Nakano T (2003) Low-dose chemotherapy of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil or doxorubicin via implanted fusion port for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res 23:1719–1722
Okuda K, Tanaka M, Shibata J, Ando E, Ogata T, Kinoshita H, Eriguchi N, Aoyagi S, Takikawa K (1999) Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with continuous low dose administration of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil for multiple recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical treatment. Oncol Rep 6:587–591
Nagai H, Matsui T, Kanayama M, Momiyama K, Ikoma A, Okano N, Ikehara T, Matsumaru K, Watanabe M, Iida K, Ishii K, Sumino Y, Miki K (2007) Assessment of combined intra-arterial low-dose 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, and leucovolin chemotherapy for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma using the Japan integrated staging score. J Med Soc Toho 54:21–28
Nagai H, Kanayama M, Higami K, Momiyama K, Ikoma A, Okano N, Matsumaru K, Watanabe M, Ishii K, Sumino Y, Miki K (2007) Twenty-four hour intra-arterial infusion of 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, and leucovorin is more effective than 6-hour infusion for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 13(2):280–284
Scanlon KJ, Newman EW, Lu Y, Priest DG (1986) Biochemical basis for cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil synergism in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8923–8925
Shirasaka T, Shimamoto Y, Ohsimo H, Saito M, Fukusima M (1993) Metabolic basis of the synergistic antitumor activities of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin in rodent tumor models in vivo. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 32:167–172
Ensminger WD, Gyves JW (1983) Clinical pharmacology of hepatic arterial chemotherapy. Semin Oncol 10:176–182
Shiraki K, Yamanaka T, Inoue H, Kawakita T, Enokimura N, Okano Hiroshi, Sugimoto K, Murata K, Nakano T (2005) Expression of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol 26:1273–1281
Nagane M, Pan G, Weddle JJ, Dixit VM, Cavenee WK, Huang HJ (2000) Increased death receptor 5 expression by chemotherapeutic agents in human gliomas causes synergistic cytotoxicity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 60:847–853
Wenn J, Ramadevi N, Nguyen D, Perkins C, Worthington E, Bhalla K (2000) Antileukemic drugs increase death receptor 5 levels and enhance Apo-2L-induced apoptosis of human acute leukemia cells. Blood 96:3900–3906
Ganten TM, Haas TL, Sykora J, Stahl H, Sprick MR, Fas SC, Krueger A, Weigand MA, Grosse-Wilde A, Stremmel W, Krammer PH, Walczak H (2004) Enhanced caspase-8 recruitment to and activation at the DISC is critical for sensitisation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by chemotherapeutic drugs. Cell Death Differ 11:S86–S96
Yamamoto T, Nagano H, Sakon M, Wada H, Eguchi H, Kondo M, Damdinsuren B, Ota H, Nakamura M, Wada H, Marubashi S, Miyamoto A, Dono K, Umeshita K, Nakamori S, Yagita H, Monden M (2004) Partial contribution of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)/TRAIL receptor pathway to antitumor effects of onterferon-alpha/5-fluorouracil against hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:7884–7895
Nagata S, Golstein P (1995) The Fas death factor. Science 267:1449–1455
Armitage RJ (1994) Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily members and their ligands. Curr Opin Immunol 6:407–413
Nakamura M, Nagano H, Sakon M, Yamamoto T, Ota H, Wada H, Damdisuren B, Noda T, Marubashi S, Miyamoto A, Takeda Y, Umeshita K, Nakamori S, Dono K, Monden M (2007) Role of the Fas/FasL pathway in combination therapy with interferon-a and fluorouracil against hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro. J Hepatol 46:77–88
Iwamiya T, Sawada S, Ohta Y (1994) Repeated arterial infusion chemotherapy for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma using an implantable drug delivery system. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 33(Suppl):S134–S138
Kudo M, Chung H, Osaki Y (2003) Prognostic staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma (CLIP score): its value and limitations, and a proposal for new staging system, the Japan integrated staging score (JIS score). J Gastroenterol 38:207–215
Beutler B, Cerami A (1998) Cachectin (tumor necrosis factor): a macrophage hormone governing cellular metabolism and inflammatory response. Endocr Rev 9:57–66
Tracey KJ, Vlassara H, Cerami A (1989) Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor. Lancet 1(8647):1122–1126
Brockhause M, Schoenfeld HJ, Schlaeger EJ, Hunziker W, Lesslauer W, Loetscher H (1990) Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:3127–3131
Hohmann HP, Remy R, Brockhause M, Van Loon AP (1989) Two different cell types have different major receptors for human tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). J Biol Chem 264:1429–1434
Ruberti G, Cascino I, Papoff G, Eramo A (1996) Fas splicing variants and their effect on apoptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 406:125–134
Iio S, Hayashi N, Mita E, Ueda K, Mochizuki K, Hiramatsu N, Kanto T, Sasaki Y, Kasahara A, Hori M (1998) Serum levels of soluble Fas antigen in chronic hepatitis C patients. J Hepatol 29:517–523
Zylberberg H, Rimaniol AC, Pol S, Masson A, De Groote D, Berthelot P, Bach JF, Brechot C, Zavala F (1999) Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in chronic hepatitis C: a correlation with histological fibrosis and activity. J Hepatol 30:185–191
Waage A, Liabakk N, Lien E, Lamvik J, Espevik T (1992) p55 and p75 tumor necrosis factor receptors in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 80:2577–2583
Marinos G, Naoumov NV, Rossol S, Torre F, Wong PY, Gallati H, Portmann B, Williams R (1995) Tumor necrosis factor receptors in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 108:1453–1463
Seishima M, Takemura M, Saito K, Ando K, Noma A (1997) Increased serum soluble Fas (sFas) concentrations in HCV-positive patients with liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol 27:424–425
Jodo S, Kobayashi S, Nakajima Y, Matsunaga T, Nakayama N, Ogura N, Kayagaki N, Okumura K, Koike T (1998) Elevated serum levels of soluble Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Exp Immunol 112:166–1671
Hayashi N, Mita E (1997) Fas system and apoptosis in viral hepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:S223–S226
Peng Z, Tang H, Ling Y, Han G (2001) Apoptosis and Fas system are significantly involved in the process of liver cirrhosis converting into HCC. J Tongji Med Univ 21(2):126–129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, H., Miyaki, D., Matsui, T. et al. Changes of cytokines in cirrhosis patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated by intra-arterial chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62, 271–276 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-007-0602-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-007-0602-9