Abstract
Purpose
Data are lacking on the pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin in patients with severe hepatic dysfunction. The aim of this study was to determine the pharmacokinetic parameters of platinum after administration of oxaliplatin in cancer patients with severe hepatic impairment due to extended metastases into the liver.
Patients and methods
Two female breast cancer patients and one male colon cancer patient were treated with oxaliplatin monotherapy at 130 mg/m² given as a 3-h intravenous infusion. The patients exhibited bilirubin concentrations of 9.6, 22.5 and 41.1 mg/dl indicating severe hepatic dysfunction. Serial blood samples were collected immediately before treatment, and at fixed intervals up to 27 h after start of therapy. Platinum concentrations in plasma, ultrafilterable plasma, and whole blood were determined using a validated flameless atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS) method. Pharmacokinetic data analysis was performed assuming a two-compartment model. Individual pharmacokinetic parameters were compared with a reference population with normal hepatic function.
Results
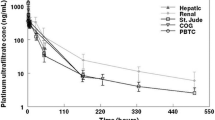
The area under the curve (AUC from 0 to infinity) as well as the elimination half-life of platinum in ultrafilterable plasma were substantially increased and clearance accordingly decreased in the three patients with severe hepatic dysfunction. In plasma and whole blood, the deviations from the reference population were less pronounced. However, partial AUC from 0 up to 2 h after end of infusion reflecting better the exposure with cytotoxic platinum species was not different or only slightly altered. Moreover, no acute oxaliplatin-associated neurotoxicity was observed.
Conclusions
The comparable platinum exposure early after administration in conjunction with the lack of acute toxicity do not support a dose reduction of oxaliplatin in patients with markedly elevated bilirubin concentrations. However, a larger number of patients must be examined before valid dose recommendations can be derived.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sasson AR, Sigurdson ER (2002) Surgical treatment of liver metastases. Semin Oncol 29:107–118
Bismuth H, Adam R, Levi F, farabos C, Waechter F, Castaing D, Majno P, Engerran L (1996) Resection of nonresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg 224:509–522
Tournigand C, Andre T, Achille E, Lledo G, Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, Quinaux E, Couteau C, Buyse M, Ganem G, Landi B, Colin P, Louvet C, de Gramont A (2004) FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol 22:229–237
Sumpter KA, Harper-Wynne C, Cunningham D, Rao S, Tebbutt N, Norman AR, Ward C, Iveson T, Nicolson M, Hickish T, Hill M, Oates J (2005) Report of two protocol planned interim analyses in a randomised multicentre phase III study comparing capecitabine with fluorouracil and oxaliplatin with cisplatin in patients with advanced oesophagogastric cancer receiving ECF. Br J Cancer 92:1976–1983
Garufi C, Nistico C, Brienza S, Vaccaro A, Dòttavio A, Zappala AR, Aschelter AM, Terzoli E (2001) Single-agent oxaliplatin in pretreated advanced breast cancer patients: a phase II study. Ann Oncol 12:179–182
Levi F, Metzger G, Massari C, Milano G (2000) Oxaliplatin: pharmacokinetics and chronopharmacological aspects. Clin Pharmacokinet 38:1–21
Massari C, Brienza S, Rotarski M, Gastiaburu J, Misset JL, Cupissol D, Alafaci E, Dutetre-Catella H, Bastian G (2000) Pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin in patients with normal versus impaired renal function. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 45:157–164
Graham MA, Lockwood GF, Greenslade D, Brienza S, Bayssas M, Gamelin E (2000) Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin: a critical review. Clin Cancer Res 6:1205–1218
Junker AM, Pieck AC, Wehmeier A, Jaehde U (2002) Interindividual differences in oxaliplatin pharmacokinetics. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 40:569–570
Eklund JW, Trifilio S, Mulcahy MF (2005) Chemotherapy dosing in the setting of liver dysfunction. Oncology (Williston Park) 19:1057–1063
Doroshow JH, Synold TW, Gandara D, Mani S, Remick SC, Mulkerin D, Hamilton A, Sharma S, Ramanathan RK, Lenz HJ, Graham M, Longmate J, Takimoto CH, Ivy P (2003) Pharmacology of oxaliplatin in solid tumor patients with hepatic dysfunction: a preliminary report of the National Cancer Institute Organ Dysfunction Working Group. Semin Oncol 30(suppl15):14–19
Raymond E, Chaney SG, Taama A, Cvitkovic E (1998) Oxaliplatin: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. Ann Oncol 9:1053–1071
Sorich J, Taubes B, Wagner A, Hochster H (2004) Oxaliplatin: practical guidelines for administration. Clin J Oncol Nursing 8:251–256
Kloft C, Appelius H, Siegert W, Schunack W, Jaehde U (1999) Determination of platinum complexes with antitumor activity in clinical samples by a rapid flameless atomic absorption spectrometry assay. Ther Drug Monit 21:631–637
US Department of Health and Human Services, FDA, CDER and CVM (2001) Guidance for industry: bioanalytical method validation
Shord SS, Bernard SA, Lindley C, Blodgett A, Mehta V, Churchel MA, Poole M, Pescatore SL, Luo FR, Chaney SG (2002) Oxaliplatin biotransformation and pharmacokinetics: a pilot study to determine the possible relationship to neurotoxicity. Anticancer Res 22: 2301–2309
Strickmann DB, Küng A, Keppler B (2002) Application of capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry for the investigation of the binding behavior of oxaliplatin to 5′-GMP in the presence of the sulfur-containing amino acid l-methionine. Electrophoresis 23:74–80
Kupsch P, Henning BF, Passarge K, Richly H, Wiesemann K, Hilger RA, Scheulen ME, Christensen O, Brendel E, Schwartz B, Hofstra E, Voigtmann R, Seeber S, Strumberg D (2005) Results of a phase I trial of sorafenib (BAY 43–9006) in combination with oxaliplatin in patients with refractory solid tumors, including colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 5:188–196
Pieck AC, Drescher A, Wiesmann KG, Messerschmidt J, Weber G, Strumberg D, Hilger RA, Scheulen ME, Jaehde U (2007) Oxaliplatin-DNA adduct formation in white blood cells after administration of oxaliplatin: a potential parameter for individual dose adaptation? (submitted)
Bastian G, Barrail A, Urien S (2003) Population pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin in patients with metastatic cancer. Anticancer Drugs 14:817–824
Ehrsson H, Wallin I, Yachnin J. (2002) Pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin in humans. Med Oncol 19:261–265
Allain P, Heudi O, Cailleux A, Le Bouil A, Larra F, Boisdron-Celle M, Gamelin E (2000) Early biotransformations of oxaliplatin after its intravenous administration to cancer patients. Drug Metab Dispos 28:1379–1384
Luo FR, Wyrick SD, Chaney SG (1999) Biotransformations of oxaliplatin in rat blood in vitro. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 13(3–4):159–169
Luo FR, Wyrick SD, Chaney SG (1999) Pharmacokinetics and biotransformations of oxaliplatin in comparison with ormaplatin following a single bolus intravenous injection in rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44:19–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baur, M., Drescher, A., Gneist, M. et al. Pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin in patients with severe hepatic dysfunction. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61, 97–104 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-007-0452-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-007-0452-5