Abstract.
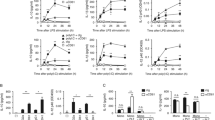
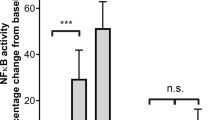
We investigated whether human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) express prothrombinase following stimulation with bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). LPS-stimulated PBMC devoid of contaminating platelets failed to activate prothrombin directly. Addition of platelets did not result in expression of prothrombinase in the absence of factor X whereas the combination of platelets and factor X resulted in strong prothrombinase activity on LPS-activated cells. The induced prothrombinase was dependent on tissue factor, as the activity was completely inhibited by an anti-tissue factor antibody. Our data suggest that platelet/monocyte cooperation is important in the generation of prothrombinase activity in response to endotoxin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pejler, .G., Geczy, .C. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells require factor X and platelets for expression of prothrombinase activity in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Ann Hematol 80, 278–283 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770100288
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770100288