Abstract
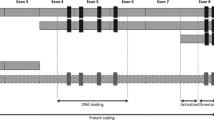
IKZF1 deletion is a recurrent genomic alteration in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and is divided into dominant-negative (DN) and loss of function (LOF) deletions. The prognostic impact of each deletion has not been fully elucidated. We retrospectively analyzed 117 patients with adult B-ALL including 60 patients with BCR::ABL1-positive B-ALL and 57 patients with BCR::ABL1-negative B-ALL by the fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) method for IKZF1 deletion and multiplex PCR for the 4 most common IKZF1 deletions (∆4–7, ∆2–7, ∆2–8, and ∆4–8). Samples, in which IKZF1 deletion was detected by FISH but a specific type of deletion was not identified by the PCR, were categorized as “other.” Patients were classified into a DN group that had at least 1 allele of ∆4–7 (n = 23), LOF and other group (n = 40), and wildtype group (n = 54). DN type IKZF1 deletions were found in 33.3% of BCR::ABL1-positive cases and 5.2% of BCR::ABL1-negative cases. LOF and other type IKZF1 deletions were found in 43.4% of BCR::ABL1-positive cases and 24.6% of BCR::ABL1-negative cases. Patients with the DN group showed significantly higher overall survival (OS) than that of the LOF and other and WT groups (P = 0.011). Multivariate analysis including age, WBC counts, complex karyotype, and DN type IKZF1 deletion showed that the DN type of IKZF1 deletion (HR = 0.22, P = 0.013) had a positive impact and age ≥ 65 (HR = 1.92, P = 0.029) had a negative impact on OS. The prognostic impact of IKZF1 deletion depends on the type of deletion and DN type of IKZF1 deletion showed better prognosis in adult B-ALL patients.
Clinical trial registration This study was part of a prospective observational study (Hokkaido Leukemia Net, UMIN000048611). It was conducted in compliance with ethical principles based on the Helsinki Declaration and was approved by the institutional review board of Hokkaido University Hospital (#015–0344).





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Georgopoulos K, Bigby M, Wang JH, Molnar A, Wu P, Winandy S, Sharpe A (1994) The Ikaros gene is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages. Cell 79(1):143–156
Georgopoulos K (2002) Haematopoietic cell-fate decisions, chromatin regulation and ikaros. Nat Rev Immunol 2(3):162–174. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri747
Kastner P, Dupuis A, Gaub MP, Herbrecht R, Lutz P, Chan S (2013) Function of Ikaros as a tumor suppressor in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Blood Res 3(1):1–13
Olsson L, Johansson B (2015) Ikaros and leukaemia. Br J Haematol 169(4):479–491. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13342
John LB, Ward AC (2011) The Ikaros gene family: transcriptional regulators of hematopoiesis and immunity. Mol Immunol 48(9–10):1272–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2011.03.006
Mullighan CG, Su X, Zhang J, Radtke I, Phillips LA, Miller CB, Ma J, Liu W, Cheng C, Schulman BA, Harvey RC, Chen IM, Clifford RJ, Carroll WL, Reaman G, Bowman WP, Devidas M, Gerhard DS, Yang W, Relling MV, Shurtleff SA, Campana D, Borowitz MJ, Pui CH, Smith M, Hunger SP, Willman CL, Downing JR, Children’s Oncology G (2009) Deletion of IKZF1 and prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 360(5):470–480. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0808253
Asai D, Imamura T, Suenobu S, Saito A, Hasegawa D, Deguchi T, Hashii Y, Matsumoto K, Kawasaki H, Hori H, Iguchi A, Kosaka Y, Kato K, Horibe K, Yumura-Yagi K, Hara J, Oda M, Japan Association of Childhood Leukemia S (2013) IKZF1 deletion is associated with a poor outcome in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Japan. Cancer Med 2(3):412–419. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.87
Boer JM, van der Veer A, Rizopoulos D, Fiocco M, Sonneveld E, de Groot-Kruseman HA, Kuiper RP, Hoogerbrugge P, Horstmann M, Zaliova M, Palmi C, Trka J, Fronkova E, Emerenciano M, do Socorro Pombo-de-Oliveira M, Mlynarski W, Szczepanski T, Nebral K, Attarbaschi A, Venn N, Sutton R, Schwab CJ, Enshaei A, Vora A, Stanulla M, Schrappe M, Cazzaniga G, Conter V, Zimmermann M, Moorman AV, Pieters R, den Boer ML (2016) Prognostic value of rare IKZF1 deletion in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: an international collaborative study. Leukemia 30(1):32–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.199
Martinelli G, Iacobucci I, Storlazzi CT, Vignetti M, Paoloni F, Cilloni D, Soverini S, Vitale A, Chiaretti S, Cimino G, Papayannidis C, Paolini S, Elia L, Fazi P, Meloni G, Amadori S, Saglio G, Pane F, Baccarani M, Foa R (2009) IKZF1 (Ikaros) deletions in BCR-ABL1-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia are associated with short disease-free survival and high rate of cumulative incidence of relapse: a GIMEMA AL WP report. J Clin Oncol 27(31):5202–5207. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.21.6408
van der Veer A, Waanders E, Pieters R, Willemse ME, Van Reijmersdal SV, Russell LJ, Harrison CJ, Evans WE, van der Velden VH, Hoogerbrugge PM, Van Leeuwen F, Escherich G, Horstmann MA, Mohammadi Khankahdani L, Rizopoulos D, De Groot-Kruseman HA, Sonneveld E, Kuiper RP, Den Boer ML (2013) Independent prognostic value of BCR-ABL1-like signature and IKZF1 deletion, but not high CRLF2 expression, in children with B-cell precursor ALL. Blood 122(15):2622–2629. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-10-462358
Iacobucci I, Storlazzi CT, Cilloni D, Lonetti A, Ottaviani E, Soverini S, Astolfi A, Chiaretti S, Vitale A, Messa F, Impera L, Baldazzi C, D’Addabbo P, Papayannidis C, Lonoce A, Colarossi S, Vignetti M, Piccaluga PP, Paolini S, Russo D, Pane F, Saglio G, Baccarani M, Foa R, Martinelli G (2009) Identification and molecular characterization of recurrent genomic deletions on 7p12 in the IKZF1 gene in a large cohort of BCR-ABL1-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients: on behalf of Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche dell’Adulto Acute Leukemia Working Party (GIMEMA AL WP). Blood 114(10):2159–2167. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-08-173963
Kuiper RP, Waanders E, van der Velden VH, van Reijmersdal SV, Venkatachalam R, Scheijen B, Sonneveld E, van Dongen JJ, Veerman AJ, van Leeuwen FN, van Kessel AG, Hoogerbrugge PM (2010) IKZF1 deletions predict relapse in uniformly treated pediatric precursor B-ALL. Leukemia 24(7):1258–1264. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.87
Yang YL, Hung CC, Chen JS, Lin KH, Jou ST, Hsiao CC, Sheen JM, Cheng CN, Wu KH, Lin SR, Yu SL, Chen HY, Lu MY, Wang SC, Chang HH, Lin SW, Su YN, Lin DT (2011) IKZF1 deletions predict a poor prognosis in children with B-cell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a multicenter analysis in Taiwan. Cancer Sci 102(10):1874–1881. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02031.x
Mi JQ, Wang X, Yao Y, Lu HJ, Jiang XX, Zhou JF, Wang JH, Jiao B, Shen SH, Tang JY, Gu LJ, Jiang H, Ma LY, Hao SG, Chen FY, Xiong SM, Shen ZX, Chen Z, Chen B, Chen SJ (2012) Newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia in China (II): prognosis related to genetic abnormalities in a series of 1091 cases. Leukemia 26(7):1507–1516. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.23
Krentz S, Hof J, Mendioroz A, Vaggopoulou R, Dorge P, Lottaz C, Engelmann JC, Groeneveld TW, Korner G, Seeger K, Hagemeier C, Henze G, Eckert C, von Stackelberg A, Kirschner-Schwabe R (2013) Prognostic value of genetic alterations in children with first bone marrow relapse of childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 27(2):295–304. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.155
Waanders E, van der Velden VH, van der Schoot CE, van Leeuwen FN, van Reijmersdal SV, de Haas V, Veerman AJ, van Kessel AG, Hoogerbrugge PM, Kuiper RP, van Dongen JJ (2011) Integrated use of minimal residual disease classification and IKZF1 alteration status accurately predicts 79% of relapses in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 25(2):254–258. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.275
Steeghs EMP, Boer JM, Hoogkamer AQ, Boeree A, de Haas V, de Groot-Kruseman HA, Horstmann MA, Escherich G, Pieters R, den Boer ML (2019) Copy number alterations in B-cell development genes, drug resistance, and clinical outcome in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Rep 9(1):4634. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41078-4
van der Veer A, Zaliova M, Mottadelli F, De Lorenzo P, Te Kronnie G, Harrison CJ, Cave H, Trka J, Saha V, Schrappe M, Pieters R, Biondi A, Valsecchi MG, Stanulla M, den Boer ML, Cazzaniga G (2014) IKZF1 status as a prognostic feature in BCR-ABL1-positive childhood ALL. Blood 123(11):1691–1698. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-06-509794
O’Reilly J, Russell LJ, Cooney J, Ensor HM, Purtill D, Wright M, Moorman AV (2013) Unravelling the prognostic effect of IKZF1 deletions and IGH@-CRLF2 in adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Pathology 45(6):609–612. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAT.0b013e3283653bd1
Yao QM, Liu KY, Gale RP, Jiang B, Liu YR, Jiang Q, Jiang H, Zhang XH, Zhang MJ, Chen SS, Huang XJ, Xu LP, Ruan GR (2016) Prognostic impact of IKZF1 deletion in adults with common B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. BMC Cancer 16:269. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2300-7
Sun L, Liu A, Georgopoulos K (1996) Zinc finger-mediated protein interactions modulate Ikaros activity, a molecular control of lymphocyte development. EMBO J 15(19):5358–5369
Kobitzsch B, Gokbuget N, Schwartz S, Reinhardt R, Bruggemann M, Viardot A, Wasch R, Starck M, Thiel E, Hoelzer D, Burmeister T (2017) Loss-of-function but not dominant-negative intragenic IKZF1 deletions are associated with an adverse prognosis in adult BCR-ABL-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2016.161273
Hashiguchi J, Onozawa M, Oguri S, Fujisawa S, Tsuji M, Okada K, Nakagawa M, Hashimoto D, Kahata K, Kondo T, Shimizu C, Teshima T (2018) Development of a fluorescence in situ hybridization probe for detecting IKZF1 deletion mutations in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Mol Diagn 20(4):446–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoldx.2018.02.005
Caye A, Beldjord K, Mass-Malo K, Drunat S, Soulier J, Gandemer V, Baruchel A, Bertrand Y, Cave H, Clappier E (2013) Breakpoint-specific multiplex polymerase chain reaction allows the detection of IKZF1 intragenic deletions and minimal residual disease monitoring in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 98(4):597–601. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2012.073965
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48(3):452–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.244
Onozawa M, Aplan PD (2012) Illegitimate V(D)J recombination involving nonantigen receptor loci in lymphoid malignancy. Genes Chromosom Cancer 51(6):525–535. https://doi.org/10.1002/Gcc.21942
Dupuis A, Gaub MP, Legrain M, Drenou B, Mauvieux L, Lutz P, Herbrecht R, Chan S, Kastner P (2013) Biclonal and biallelic deletions occur in 20% of B-ALL cases with IKZF1 mutations. Leukemia 27(2):503–507. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.204
Mullighan CG, Miller CB, Radtke I, Phillips LA, Dalton J, Ma J, White D, Hughes TP, Le Beau MM, Pui CH, Relling MV, Shurtleff SA, Downing JR (2008) BCR-ABL1 lymphoblastic leukaemia is characterized by the deletion of Ikaros. Nature 453(7191):110–114. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06866
Yamashita Y, Shimada A, Yamada T, Yamaji K, Hori T, Tsurusawa M, Watanabe A, Kikuta A, Asami K, Saito AM, Horibe K (2013) IKZF1 and CRLF2 gene alterations correlate with poor prognosis in Japanese BCR-ABL1-negative high-risk B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60(10):1587–1592. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.24571
Gupta SK, Bakhshi S, Gupta R, Sharma P, Pushpam D, Sahoo RK, Kamal VK (2021) IKZF1 deletion subtyping and outcome analysis in BCR-ABL1-negative pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a single-institution experience from North India. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 21(8):e666–e673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2021.03.007
Kim M, Park J, Kim DW, Kim YJ, Jeon YW, Yoon JH, Shin SH, Yahng SA, Lee SE, Cho BS, Eom KS, Kim HJ, Min CK, Cho SG, Kim Y, Lee JW, Han K, Min WS, Lee S (2015) Impact of IKZF1 deletions on long-term outcomes of allo-SCT following imatinib-based chemotherapy in adult Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL. Bone Marrow Transplant 50(3):354–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.281
Fedullo AL, Messina M, Elia L, Piciocchi A, Gianfelici V, Lauretti A, Soddu S, Puzzolo MC, Minotti C, Ferrara F, Martino B, Chiusolo P, Calafiore V, Paolini S, Vignetti M, Vitale A, Guarini A, Foa R, Chiaretti S (2019) Prognostic implications of additional genomic lesions in adult Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 104(2):312–318. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.196055
Zhang W, Kuang P, Li H, Wang F, Wang Y (2017) Prognostic significance of IKZF1 deletion in adult B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis. Ann Hematol 96(2):215–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-016-2869-6
Pui CH, Relling MV, Downing JR (2004) Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 350(15):1535–1548. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra023001
Brown PA, Shah B, Advani A, Aoun P, Boyer MW, Burke PW, DeAngelo DJ, Dinner S, Fathi AT, Gauthier J, Jain N, Kirby S, Liedtke M, Litzow M, Logan A, Luger S, Maness LJ, Massaro S, Mattison RJ, May W, Oluwole O, Park J, Przespolewski A, Rangaraju S, Rubnitz JE, Uy GL, Vusirikala M, Wieduwilt M, Lynn B, Berardi RA, Freedman-Cass DA, Campbell M (2021) Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 19(9):1079–1109. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2021.0042
Ribera J, Morgades M, Zamora L, Montesinos P, Gomez-Segui I, Pratcorona M, Sarra J, Guardia R, Nomdedeu J, Tormo M, Martinez-Lopez J, Hernandez-Rivas JM, Gonzalez-Campos J, Barba P, Escoda L, Genesca E, Sole F, Milla F, Feliu E, Ribera JM, Spanish PG, the Spanish Society of H (2015) Prognostic significance of copy number alterations in adolescent and adult patients with precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia enrolled in PETHEMA protocols. Cancer 121(21):3809–3817. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29579
Tang S, Shen H, Qu C, Dai H, Zhu X, Xue S, Ding Z, Lu J, Wu D, Tang X (2019) Ikaros family zinc-finger 1 mutation is an independent factor for the poor prognosis of adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation can improve clinical outcomes. Bone Marrow Transplant 54(2):236–243. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0249-7
Mitchell RJ, Kirkwood AA, Barretta E, Clifton-Hadley L, Lawrie E, Lee S, Leongamornlert D, Marks DI, McMillan AK, Menne TF, Papaemmanuil E, Patel B, Patrick P, Rowntree CJ, Zareian N, Alapi KZ, Moorman AV, Fielding AK (2021) IKZF1 alterations are not associated with outcome in 498 adults with B-precursor ALL enrolled in the UKALL14 trial. Blood Adv 5(17):3322–3332. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004430
Ito Y, Ozawa H, Eto T, Miyamoto T, Kamimura T, Ogawa R, Uchida N, Wake A, Fujisaki T, Ohno Y, Takase K, Okumura H, Takamatsu Y, Kawano N, Akashi K, Nagafuji K (2023) IKZF1(plus) alterations are not associated with outcomes in Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients enrolled in the FBMTG ALL/MRD2008 trial. Eur J Haematol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.13972
Funding
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) (17K16174; K.O.), and Scientific Research (C) (16K09836; 20K08745; M.O.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.K. and M.O. designed the study, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. J.H. developed FISH analysis and S.O. and S.F. performed FISH. S.Y., N.M., S.Y., T.M., S.H., H.G., and T.E. provided a critique of the manuscript. A.M., T.K., D.H., K.O., S.O., Y.K., Y.T., S.Y., T.M., J.H., T.N., M.I., K.W., Y.H., K.F., T.I., and H.S. recruited and treated the patients. T.T. revised and approved the manuscript. All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript and approved it for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Patient consent statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all individuals included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, H., Onozawa, M., Yoshida, S. et al. Dominant-negative type of IKZF1 deletion showed a favorable prognosis in adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann Hematol 102, 3103–3113 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-023-05405-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-023-05405-0