Abstract
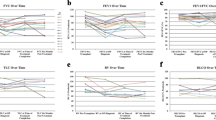
Organizing pneumonia (OP) is a complication of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) and a manifestation of peripheral airway/alveolar inflammation. Recently, alveolar nitric oxide concentration (Calv) has been revealed as a noninvasive marker of peripheral airway inflammation; however, whether Calv levels are associated with OP and peripheral airway in patients after allo-HSCT remains unclear. Herein, we evaluated whether Calv levels could reflect the presence of OP and structural airway changes in patients after allo-HSCT. We measured the eNO levels of 38 patients (6 with OP and 32 without OP) who underwent allo-HSCT. Three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) analysis of the airway was performed in 19 patients. We found that in patients with OP, Calv levels were significantly higher than in those without OP (10.6 vs. 5.5 ppb, p < 0.01). Receiver-operating characteristic analyses revealed a Calv cut-off value for OP detection of 10.2 ppb. No significant differences in the patient characteristics, except for the presence of OP (p < 0.01), were noted between the two groups stratified by the Calv cut-off value. Three-dimensional CT images of the airway revealed gradually increasing positive correlations between Calv levels and airway wall area of the third-, fourth-, and fifth-generation bronchi (r = 0.20, 0.31, 0.38; p = 0.42, 0.19, 0.038, respectively), indicating that Calv levels are strongly correlated with the wall thickness of the distal bronchi. Our results suggest that the Calv level may be a useful noninvasive detectable marker for OP after an allo-HSCT.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Yoshihara S, Yanik G, Cooke KR, Mineishi S (2007) Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS), bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), and other late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 13:749–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2007.05.001
Jinta M, Ohashi K, Ohta T, Ieki R, Abe K, Kamata N, Akiyama H, Sakamaki H (2007) Clinical features of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated organizing pneumonia. Bone Marrow Transplant 40:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705768
Nakasone H, Onizuka M, Suzuki N, Fujii N, Taniguchi S, Kakihana K, Ogawa H, Miyamura K, Eto T, Sakamaki H, Yabe H, Morishima Y, Kato K, Suzuki R, Fukuda T (2013) Pre-transplant risk factors for cryptogenic organizing pneumonia/bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 48:1317–1323. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.116
Adachi Y, Ozeki K, Ukai S, Sagou K, Fukushima N, Kohno A (2019) Patterns of onset and outcome of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol 109:700–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-019-02643-9
Cordier JF (2006) Cryptogenic organising pneumonia. Eur Respir J 28:422–446. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.06.00013505
Matsunaga K, Kuwahira I, Hanaoka M, Saito J, Tsuburai T, Fukunaga K, Matsumoto H, Sugiura H, Ichinose M, Japanese Respiratory Society Assembly on Pulmonary Physiology (2021) An official JRS statement: the principles of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) measurement and interpretation of the results in clinical practice. Respir Investig 59:34–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resinv.2020.05.006
Munakata M (2012) Exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) as a non-invasive marker of airway inflammation. Allergol Int 61:365–372. https://doi.org/10.2332/allergolint.12-RAI-0461
Puckett JL, Taylor RWE, Leu SY, Guijon OL, Aledia AS, Galant SP, George SC (2010) Clinical patterns in asthma based on proximal and distal airway nitric oxide categories. Respir Res 11:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-11-47
Tsoukias NM (1985) George SC (1998) A two-compartment model of pulmonary nitric oxide exchange dynamics. J Appl Physiol 85:653–666. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1998.85.2.653
Hirano T, Matsunaga K, Sugiura H, Minakata Y, Koarai A, Akamatsu K, Ichikawa T, Furukawa K, Ichinose M (2013) Relationship between alveolar nitric oxide concentration in exhaled air and small airway function in COPD. J Breath Res 7:046002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1752-7155/7/4/046002
Hayton C, Terrington D, Wilson AM, Chaudhuri N, Leonard C, Fowler SJ (2019) Breath biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review. Respir Res 20:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-019-0971-8
Oishi K, Hirano T, Suetake R, Ohata S, Yamaji Y, Ito K, Edakuni N, Matsunaga K (2017) Exhaled nitric oxide measurements in patients with acute-onset interstitial lung disease. J Breath Res 11:036001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1752-7163/aa6c4b
Mehrjardi MZ, Kahkouee S, Pourabdollah M (2017) Radio-pathological correlation of organizing pneumonia (OP): a pictorial review. Br J Radiol 90:20160723
de Blic J, Tillie-Leblond I, Emond S, Mahut B, Dang Duy TL, Scheinmann P (2005) High-resolution computed tomography scan and airway remodeling in children with severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:750–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2005.07.009
Nishimoto K, Karayama M, Inui N, Mori K, Kono M, Hozumi H, Suzuki Y, Furuhashi K, Enomoto N, Fujisawa T, Nakamura Y, Watanabe H, Suda T (2017) Relationship between fraction of exhaled nitric oxide and airway morphology assessed by three-dimensional CT analysis in asthma. Sci Rep 7:10187. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10504-w
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, Thomas ED (1994) Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15 Consens Conference on Acute GVHD Grading, pp 825–828
Jagasia MH, Greinix HT, Arora M, Williams KM, Wolff D, Cowen EW, Palmer J, Weisdorf D, Treister NS, Cheng GS, Kerr H, Stratton P, Duarte RF, McDonald GB, Inamoto Y, Vigorito A, Arai S, Datiles MB, Jacobsohn D, Heller T, Kitko CL, Mitchell SA, Martin PJ, Shulman H, Wu RS, Cutler CS, Vogelsang GB, Lee SJ, Pavletic SZ, Flowers ME (2015) National Institutes of Health consensus development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 21:389-401.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.12.001
Brownback KR, Frey JW, Abhyankar S (2019) Bronchoscopic features, associations, and outcomes of organizing pneumonia following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 98:2187–2195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-019-03746-3
Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Crapo R, Enright P, van der Grinten CP, Gustafsson P, Jensen R, Johnson DC, MacIntyre N, McKay R, Navajas D, Pedersen OF, Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Wanger J, ATS/ERS Task Force (2005) Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J 26:319–338. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.05.00034805
Cotes JE, Dabbs JM, Elwood PC, Hall AM, McDonald A, Saunders MJ (1972) Iron-deficiency anaemia: its effect on transfer factor for the lung (diffusiong capacity) and ventilation and cardiac frequency during sub-maximal exercise. Clin Sci 42:325–335. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs0420325
Karayama M, Inui N, Mori K, Kono M, Hozumi H, Suzuki Y, Furuhashi K, Hashimoto D, Enomoto N, Fujisawa T, Nakamura Y, Watanabe H, Suda T (2017) Respiratory impedance is correlated with morphological changes in the lungs on three-dimensional CT in patients with COPD. Sci Rep 7:41709. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41709
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.244
Högman M, Thornadtsson A, Liv P, Hua-Huy T, Dinh-Xuan AT, Tufvesson E, Dressel H, Janson C, Koskela K, Oksa P, Sauni R, Uitti J, Moilanen E, Lehtimäki L (2017) Effects of growth and aging on the reference values of pulmonary nitric oxide dynamics in healthy subjects. J Breath Res 11:047103. https://doi.org/10.1088/1752-7163/aa7957
Ye Q, Dai H, Sarria R, Guzman J, Costabel U (2011) Increased expression of tumor necrosis factor receptors in cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Respir Med 105:292–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2010.10.022
Cai M, Bonella F, Dai H, Sarria R, Guzman J, Costabel U (2013) Macrolides inhibit cytokine production by alveolar macrophages in bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Immunobiology 218:930–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2012.10.014
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi A, Afshari JT, Sahebkar A (2018) Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol 233:6425–6440. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26429
Kharitonov SA, Barnes PJ (2001) Exhaled markers of pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:1693–1722. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.163.7.2009041
Kanamori H, Fujisawa S, Tsuburai T, Yamaji S, Tomita N, Fujimaki K, Miyashita A, Suzuki S, Ishigatsubo Y (2002) Increased exhaled nitric oxide in bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 74:1356–1358. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007890-200211150-00029
Enocson A, Hubbard R, McKeever T, Russell N, Byrne J, Das-Gupta E, Watson L, Fogarty AW (2013) The acute impact of a hematopoietic allograft on lung function and inflammation: a prospective observational study. BMC Pulm Med 13:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2466-13-2
Moermans C, Poulet C, Henket M, Bonnet C, Willems E, Baron F, Beguin Y, Louis R (2013) Lung function and airway inflammation monitoring after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Respir Med 107:2071–2080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2013.10.013
Lahzami S, Schoeffel RE, Pechey V, Reid C, Greenwood M, Salome CM, Berend N, King GG (2011) Small airways function declines after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur Respir J 38:1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00018311
Fazekas T, Eickhoff P, Lawitschka A, Knotek B, Pötschger U, Peters C (2012) Exhaled nitric oxide and pulmonary complications after paediatric stem cell transplantation. Eur J Pediatr 171:1095–1101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-012-1692-x
Köktürk N, Yıldırım F, Aydoğdu M, Akı ŞZ, Yeğin ZA, Özkurt ZN, Suyanı E, Kıvılcım Oğuzülgen İ, Türköz Sucak G (2016) Is it possible to predict pulmonary complications and mortality in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients from pre-transplantation exhaled nitric oxide levels? Turk J Haematol 33:34–40. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjh.2014.0159
Suresh V, Shelley DA, Shin HW, George SC (2008) Effect of heterogeneous ventilation and nitric oxide production on exhaled nitric oxide profiles. J Appl Physiol (1985) 104:1743–1752. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01355.2007
Lehtimäki L, Karvonen T, Högman M (2020) Clinical values of nitric oxide parameters from the respiratory system. Curr Med Chem 27:7189–7199. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867327666200603141847
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the participants, physicians, and staff of the Yamaguchi University Hospital and the Yamaguchi-Ube Medical Center who participated in this study. The authors would also like to thank the radiological technologists of the Yamaguchi-Ube Medical Center for their kind assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.K., Y.N., and T.H. designed the study. Y.K. and Y.N. wrote the manuscript. Y.K. analyzed the data. All authors discussed the results and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of the Yamaguchi University Hospital (approval numbers: H28-175 and H2019-120). The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all individuals who participated in the study.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kajimura, Y., Nakamura, Y., Hirano, T. et al. Significance of alveolar nitric oxide concentration in the airway of patients with organizing pneumonia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 101, 1803–1813 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-022-04868-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-022-04868-x