Abstract
Background
Primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by decreased platelet count. While corticosteroids are a useful first-line therapy for ITP patients, their long-term effectiveness is limited, and the determinants of corticosteroid sensitivity in ITP patients remain largely unknown. Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), a member of the mammalian sirtuin family, is related to the anti-inflammatory effects of corticosteroids. Here, we investigate the contribution of the SIRT1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs12778366 and rs4746720 to ITP susceptibility.
Methods
We recruited 330 ITP patients and 309 healthy controls from Han population, and performed genotyping of SIRT1 rs12778366 and rs4746720 using a MassARRAY system. The results were validated in another 55 ITP patients from ethnic minorities.
Results
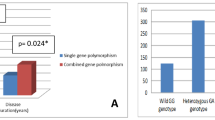
Using clinical data of patients and controls from Han polulation, including corticosteroid sensitivity, susceptibility, refractoriness, and severity, our results revealed that the CC/TC genotypes of SIRT1 rs12778366 were associated with a 2.034-fold increased risk of corticosteroid resistance compared to the homozygous major TT genotype (dominant, CC/TC vs. TT, OR = 2.034, 95% CI = 1.039–3.984, p = 0.038). In contrast, the CC/CT genotype of SIRT1 rs4746720 showed a 0.560-fold decreased risk of corticosteroid resistance (dominant, 95% CI = 0.321–0.976, OR = 0.560, p = 0.041). The C allele substitute in SIRT1 rs12778366 was significantly associated with the corticosteroid sensitivity of ITP patients (p = 0.021). The similar results were obtained in minority ITP patients.
Conclusion
This study indicates that SIRT1 rs12778366 and rs4746720 may be genetic factors related to corticosteroid sensitivity in ITP patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Lambert MP, Gernsheimer TB (2017) Clinical updates in adult immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 129(21):2829–2835. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-03-754119
Provan D, Arnold DM, Bussel JB, Chong BH, Cooper N, Gernsheimer T, Ghanima W, Godeau B, Gonzalez-Lopez TJ, Grainger J, Hou M, Kruse C, McDonald V, Michel M, Newland AC, Pavord S, Rodeghiero F, Scully M, Tomiyama Y, Wong RS, Zaja F, Kuter DJ (2019) Updated international consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv 3(22):3780–3817. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000812
Wei Y, Ji XB, Wang YW, Wang JX, Yang EQ, Wang ZC, Sang YQ, Bi ZM, Ren CA, Zhou F, Liu GQ, Peng J, Hou M (2016) High-dose dexamethasone vs prednisone for treatment of adult immune thrombocytopenia: a prospective multicenter randomized trial. Blood 127(3):296–302. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-07-659656
Mithoowani S, Gregory-Miller K, Goy J, Miller MC, Wang G, Noroozi N, Kelton JG, Arnold DM (2016) High-dose dexamethasone compared with prednisone for previously untreated primary immune thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Haematol 3(10):e489–e496. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2352-3026(16)30109-0
Cheng Y, Wong RS, Soo YO, Chui CH, Lau FY, Chan NP, Wong WS, Cheng G (2003) Initial treatment of immune thrombocytopenic purpura with high-dose dexamethasone. New Engl J Med 349(9):831–836. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa030254
Mazzucconi MG, Fazi P, Bernasconi S, De Rossi G, Leone G, Gugliotta L, Vianelli N, Avvisati G, Rodeghiero F, Amendola A, Baronci C, Carbone C, Quattrin S, Fioritoni G, D’Alfonso G, Mandelli F (2007) Therapy with high-dose dexamethasone (HD-DXM) in previously untreated patients affected by idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a GIMEMA experience. Blood 109(4):1401–1407. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-12-015222
Ghanima W, Godeau B, Cines DB, Bussel JB (2012) How I treat immune thrombocytopenia: the choice between splenectomy or a medical therapy as a second-line treatment. Blood 120(5):960–969. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-12-309153
Durcan L, O’Dwyer T, Petri M (2019) Management strategies and future directions for systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. Lancet 393(10188):2332–2343. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)30237-5
Langer AL, Leader A, Kim-Schulze S, Ginzburg Y, Merad M, Glassberg J (2019) Inhaled steroids associated with decreased macrophage markers in nonasthmatic individuals with sickle cell disease in a randomized trial. Ann Hematol 98(4):841–849. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-019-03635-9
Feng Q, Xu M, Yu YY, Hou Y, Mi X, Sun YX, Ma S, Zuo XY, Shao LL, Hou M, Zhang XH, Peng J (2017) High-dose dexamethasone or all-trans-retinoic acid restores the balance of macrophages towards M2 in immune thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost 15(9):1845–1858. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.13767
Hou Y, Feng Q, Xu M, Li GS, Liu XN, Sheng Z, Zhou H, Ma J, Wei Y, Sun YX, Yu YY, Qiu JH, Shao LL, Liu XG, Hou M, Peng J (2016) High-dose dexamethasone corrects impaired myeloid-derived suppressor cell function via Ets1 in immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 127(12):1587–1597. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-10-674531
Li J, Wang Z, Hu S, Zhao X, Cao L (2013) Correction of abnormal T cell subsets by high-dose dexamethasone in patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Immunol Lett 154(1–2):42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2013.08.006
Chen Y, Xie Y, Ruan M, Shi J (2018) The levels of T lymphocyte subsets in immune thrombocytopenia associated with anti-GPIIb/IIIa- and/or anti-GPIbα-mediated responses are differentially sensitive to dexamethasone. Acta Haematol 140(1):60–66. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491977
Rhen T, Cidlowski JA (2005) Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids–new mechanisms for old drugs. N Engl J Med 353(16):1711–1723. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra050541
Diaz-Jimenez D, Petrillo MG, Busada JT, Hermoso MA, Cidlowski JA (2020) Glucocorticoids mobilize macrophages by transcriptionally up-regulating the exopeptidase DPP4. J Biol Chem 295(10):3213–3227. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.010894
Ito K, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM (2000) Glucocorticoid receptor recruitment of histone deacetylase 2 inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced histone H4 acetylation on lysines 8 and 12. Mol Cell Biol 20(18):6891–6903. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.20.18.6891-6903.2000
Gomes AP, Price NL, Ling AJ, Moslehi JJ, Montgomery MK, Rajman L, White JP, Teodoro JS, Wrann CD, Hubbard BP, Mercken EM, Palmeira CM, de Cabo R, Rolo AP, Turner N, Bell EL, Sinclair DA (2013) Declining NAD(+) induces a pseudohypoxic state disrupting nuclear-mitochondrial communication during aging. Cell 155(7):1624–1638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.037
Sun J, He X, Zhu Y, Ding Z, Dong H, Feng Y, Du J, Wang H, Wu X, Zhang L, Yu X, Lin A, McDonald T, Zhao D, Wu H, Hua WK, Zhang B, Feng L, Tohyama K, Bhatia R, Oberdoerffer P, Chung YJ, Aplan PD, Boultwood J, Pellagatti A, Khaled S, Kortylewski M, Pichiorri F, Kuo YH, Carlesso N, Marcucci G, Jin H, Li L (2018) SIRT1 activation disrupts maintenance of myelodysplastic syndrome stem and progenitor cells by restoring TET2 function. Cell Stem Cell 23(3):355-369.e359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2018.07.018
Dong L, Bi Y, Jia A, Yu Q, Wang Y, Wang Y, Yang Q, Cao Y, He Y, Liu R, Li Y, Liu G (2020) Crucial role of histone deacetylase SIRT1 in myeloid-derived suppressor cell-mediated reprogramming of CD4(+) T-cell differentiation. Cell Mol Immunol 17(7):785–787. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-0419-6
Berliner JA (1975) Formation of enlarged mitochondria in a liver cell line in response to a synthetic glucocorticoid. J Cell Biol 64(3):711–716. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.64.3.711
Pan S, Cui Y, Fu Z, Zhang L, Xing H (2019) MicroRNA-128 is involved in dexamethasone-induced lipid accumulation via repressing SIRT1 expression in cultured pig preadipocytes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 186:185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.10.013
Lee H, Kim M, Park YH, Park JB (2018) Dexamethasone downregulates SIRT1 and IL6 and upregulates EDN1 genes in stem cells derived from gingivae via the AGE/RAGE pathway. Biotechnol Lett 40(3):509–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2493-0
Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, Chua KF, Greer PL, Lin Y, Tran H, Ross SE, Mostoslavsky R, Cohen HY, Hu LS, Cheng HL, Jedrychowski MP, Gygi SP, Sinclair DA, Alt FW, Greenberg ME (2004) Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 303(5666):2011–2015. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094637
Luo J, Nikolaev AY, Imai S, Chen D, Su F, Shiloh A, Guarente L, Gu W (2001) Negative control of p53 by Sir2alpha promotes cell survival under stress. Cell 107(2):137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00524-4
Yeung F, Hoberg JE, Ramsey CS, Keller MD, Jones DR, Frye RA, Mayo MW (2004) Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J 23(12):2369–2380. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600244
Rodgers JT, Lerin C, Haas W, Gygi SP, Spiegelman BM, Puigserver P (2005) Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1alpha and SIRT1. Nature 434(7029):113–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03354
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P, Elliott P, Geny B, Laakso M, Puigserver P, Auwerx J (2006) Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 127(6):1109–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.013
Nasiri M, Rauf M, Kamfiroozie H, Zibaeenezhad MJ, Jamali Z (2018) SIRT1 gene polymorphisms associated with decreased risk of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease. Gene 672:16–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.117
Sarumaru M, Watanabe M, Inoue N, Hisamoto Y, Morita E, Arakawa Y, Hidaka Y, Iwatani Y (2016) Association between functional SIRT1 polymorphisms and the clinical characteristics of patients with autoimmune thyroid disease. Autoimmunity 49(5):329–337. https://doi.org/10.3109/08916934.2015.1134506
Consiglio CR, Juliana da Silveira S, Monticielo OA, Xavier RM, Brenol JC, Chies JA (2014) SIRT1 promoter polymorphisms as clinical modifiers on systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Biol Rep 41(7):4233–4239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3294-3
Rai E, Sharma S, Kaul S, Jain K, Matharoo K, Bhanwer AS, Bamezai RN (2012) The interactive effect of SIRT1 promoter region polymorphism on type 2 diabetes susceptibility in the North Indian population. PloS One 7(11):e48621. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048621
Provan D, Stasi R, Newland AC, Blanchette VS, Bolton-Maggs P, Bussel JB, Chong BH, Cines DB, Gernsheimer TB, Godeau B, Grainger J, Greer I, Hunt BJ, Imbach PA, Lyons G, McMillan R, Rodeghiero F, Sanz MA, Tarantino M, Watson S, Young J, Kuter DJ (2010) International consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 115(2):168–186. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-06-225565
Biason-Lauber A, Böni-Schnetzler M, Hubbard BP, Bouzakri K, Brunner A, Cavelti-Weder C, Keller C, Meyer-Böni M, Meier DT, Brorsson C, Timper K, Leibowitz G, Patrignani A, Bruggmann R, Boily G, Zulewski H, Geier A, Cermak JM, Elliott P, Ellis JL, Westphal C, Knobel U, Eloranta JJ, Kerr-Conte J, Pattou F, Konrad D, Matter CM, Fontana A, Rogler G, Schlapbach R, Regairaz C, Carballido JM, Glaser B, McBurney MW, Pociot F, Sinclair DA, Donath MY (2013) Identification of a SIRT1 mutation in a family with type 1 diabetes. Cell Metab 17(3):448–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.02.001
Niederer F, Ospelt C, Brentano F, Hottiger MO, Gay RE, Gay S, Detmar M, Kyburz D (2011) SIRT1 overexpression in the rheumatoid arthritis synovium contributes to proinflammatory cytokine production and apoptosis resistance. Ann Rheum Dis 70(10):1866–1873. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2010.148957
Grabiec AM, Krausz S, de Jager W, Burakowski T, Groot D, Sanders ME, Prakken BJ, Maslinski W, Eldering E, Tak PP, Reedquist KA (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress inflammatory activation of rheumatoid arthritis patient synovial macrophages and tissue. J Immunol 184(5):2718–2728. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0901467
Lim HW, Kang SG, Ryu JK, Schilling B, Fei M, Lee IS, Kehasse A, Shirakawa K, Yokoyama M, Schnölzer M, Kasler HG, Kwon HS, Gibson BW, Sato H, Akassoglou K, Xiao C, Littman DR, Ott M, Verdin E (2015) SIRT1 deacetylates RORγt and enhances Th17 cell generation. J Exp Med 212(5):607–617. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20132378
Lim HW, Kang SG, Ryu JK, Schilling B, Fei M, Lee IS, Kehasse A, Shirakawa K, Yokoyama M, Schnölzer M, Kasler HG, Kwon HS, Gibson BW, Sato H, Akassoglou K, Xiao C, Littman DR, Ott M, Verdin E (2015) SIRT1 deacetylates RORγt and enhances Th17 cell generation. J Exp Med 212(6):973. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.2013237805062015c
Nimmagadda VK, Makar TK, Chandrasekaran K, Sagi AR, Ray J, Russell JW, Bever CT Jr (2017) SIRT1 and NAD+ precursors: Therapeutic targets in multiple sclerosis a review. J Neuroimmunol 304:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.07.007
McAleer MA, Jakasa I, Stefanovic N, McLean WHI, Kezic S, Irvine AD (2020) Topical corticosteroids normalize both skin and systemic inflammatory markers in infant atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. Online ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.19703
Hetland ML, Haavardsholm EA, Rudin A, Nordström D, Nurmohamed M, Gudbjornsson B, Lampa J, Hørslev-Petersen K, Uhlig T, Grondal G, Østergaard M, Heiberg MS, Twisk J, Lend K, Krabbe S, Hyldstrup LH, Lindqvist J, Hultgård Ekwall AK, Grøn KL, Kapetanovic M, Faustini F, Tuompo R, Lorenzen T, Cagnotto G, Baecklund E, Hendricks O, Vedder D, Sokka-Isler T, Husmark T, Ljoså MA, Brodin E, Ellingsen T, Söderbergh A, Rizk M, Olsson ÅR, Larsson P, Uhrenholt L, Just SA, Stevens DJ, Laurberg TB, Bakland G, Olsen IC, van Vollenhoven R (2020) Active conventional treatment and three different biological treatments in early rheumatoid arthritis: phase IV investigator initiated, randomised, observer blinded clinical trial. BMJ 371:m4328. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m4328
Tang CH (2020) Research of Pathogenesis and Novel Therapeutics in Arthritis 2.0. Int J Mol Sci 21(21):8125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218125
Hernandez-Pacheco N, Vijverberg SJ, Herrera-Luis E, Li J, Sio YY, Granell R, Corrales A, Maroteau C, Lethem R, Perez-Garcia J, Farzan N, Repnik K, Gorenjak M, Soares P, Karimi L, Schieck M, Pérez-Méndez L, Berce V, Tavendale R, Eng C, Sardon O, Kull I, Mukhopadhyay S, Pirmohamed M, Verhamme KM, Burchard EG, Kabesch M, Hawcutt DB, Melén E, Potočnik U, Chew FT, Tantisira KG, Turner S, Palmer CN, Flores C, Pino-Yanes M, Maitland-van der Zee AH (2020) Genome-wide association study of asthma exacerbations despite inhaled corticosteroids use. Eur Respir j 10:2003388. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.03388-2020
Ito K, Chung KF, Adcock IM (2006) Update on glucocorticoid action and resistance. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117(3):522–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2006.01.032
Wandler AM, Huang BJ, Craig JW, Hayes K, Yan H, Meyer LK, Scacchetti A, Monsalve G, Dail M, Li Q, Wong JC, Weinberg O, Hasserjian RP, Kogan SC, Jonsson P, Yamamoto K, Sampath D, Nakitandwe J, Downing JR, Zhang J, Aster JC, Taylor BS, Shannon K (2020) Loss of glucocorticoid receptor expression mediates in vivo dexamethasone resistance in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 34(8):2025–2037. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-0748-6
Matthews JG, Ito K, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM (2004) Defective glucocorticoid receptor nuclear translocation and altered histone acetylation patterns in glucocorticoid-resistance patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol 113(6):1100–1108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2004.03.018
Ma L, Fang M, Liang Y, Xiang Y, Jia Z, Sun X, Wang Y, Qin J (2013) Low expression of glucocorticoid receptor alpha isoform in adult immune thrombocytopenia correlates with glucocorticoid resistance. Ann Hematol 92(7):953–960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1705-5
Kojika S, Sugita K, Inukai T, Saito M, Iijima K, Tezuka T, Goi K, Shiraishi K, Mori T, Okazaki T, Kagami K, Ohyama K, Nakazawa S (1996) Mechanisms of glucocorticoid resistance in human leukemic cells: implication of abnormal 90 and 70 kDa heat shock proteins. Leukemia 10(6):994–999
Johnson DM, Newby RF, Bourgeois S (1984) Membrane permeability as a determinant of dexamethasone resistance in murine thymoma cells. Cancer Res 44(6):2435–2440
Liu S, Verma M, Michalec L, Liu W, Sripada A, Rollins D, Good J, Ito Y, Chu H, Gorska MM, Martin RJ, Alam R (2018) Steroid resistance of airway type 2 innate lymphoid cells from patients with severe asthma: the role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J Allergy Clin Immunol 141(1):257-268.e256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.03.032
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [91942306, 81770133, 81900122, 81800112], Shandong Provincial Key Research and Development Program [2019JZZY011016] and Rongxiang Regenerative Medicine Foundation of Shandong University [2019SDRX-02], and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province [ZR2019PH005].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiang Hu and Qi Feng designed the research, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; Shuwen Wang performed the research, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; Xiaoyu Zhang, Shaoqiu Leng, Yanqi Zhang, and Ju Li performed the research and evaluated the data; Jun Peng designed the research and reviewed the work; Zeping Zhou analyzed the data and reviewed the work, and all authors read and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The Medical Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University reviewed and approved this study. All subjects in this study were in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants or their legal guardians.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Zhang, X., Leng, S. et al. SIRT1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with corticosteroid sensitivity in primary immune thrombocytopenia patients. Ann Hematol 100, 2453–2462 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04583-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04583-z