Abstract
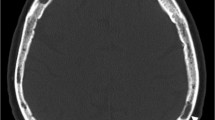
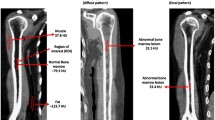
The objective of this study is to evaluate the prognostic features of multiple myeloma (MM) using whole-body low-dose computed tomography (WBLDCT). One hundred three patients with biopsy-proven MM who underwent WBLDCT were retrospectively enrolled. The evolution of osteolytic lesions overtime was performed by measuring the maximum axial diameter at the baseline (T0) and the end of follow-up (Te), by using a cut-off value of 10 mm. The location and dimension of up to three lesions were registered. The time-to-fracture (TTF) was recorded. Sixty-three percent of patients presented a focal pattern, 22% a diffuse pattern, and 15% a combined one. Seventy-two percent of patients with lesions ≤ 10 mm presented stability, 27% a dimensional increase, and 1% a decrease. Patients with lesions >10 mm showed a statistically significant difference regarding the mean difference of axial diameter between T0 and Te (p = 0.015). Patients with lesions >10 mm showed an odds ratio (OR) of 29.8 (95%CIs 3.8–230.5) to develop at least one fracture. Mean TTF was significantly lower in patients with lesions >10 mm in comparison with lesions ≤ 10 mm (9 ± 3 vs 23 ± 7 months, respectively, p = 0.011). WBLDCT represents a reliable imaging-based tool for proper management of MM patients, showing that diffuse form or small lytic lesions may deserve a less frequent follow-up.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- ALARA:
-
As low as reasonably achievable
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTDIvol:
-
CT dose index volume
- DLP:
-
Dose length product
- ED:
-
Effective dose
- EMD:
-
Extramedullary disease
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- IMWG:
-
International Myeloma Working Group
- MM:
-
Multiple myeloma
- MGUS:
-
Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance
- MPR:
-
MultiPlanar Reconstruction
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- O-MAR:
-
Metal Artifact Reduction for Orthopedic Implants
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- WBLDCT:
-
Whole-body low-dose CT
- WBXR:
-
Whole-body X-ray survey
- WL:
-
Window level
- WW:
-
Window width
References
Terpos E, Dimopoulos M-A (2005) Myeloma bone disease: pathophysiology and management. Ann Oncol 16:1223–1231. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdi235
Terpos E, Morgan G, Dimopoulos MA, et al. (2013) International Myeloma Working Group recommendations for the treatment of multiple myeloma–related bone disease. JCO 31:2347–2357. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.47.7901
Zamagni E, Tacchetti P, Cavo M (2019) Imaging in multiple myeloma: how? When? Blood 133:644–651. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-08-825356
Chantry A, Kazmi M, Barrington S, Goh V, Mulholland N, Streetly M, Lai M, Pratt G, the British Society for Haematology Guidelines (2017) Guidelines for the use of imaging in the management of patients with myeloma. Br J Haematol 178:380–393. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14827
Rajkumar SV (2011) Multiple myeloma: 2011 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 86:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.21913
Moulopoulos LA, Koutoulidis V, Hillengass J, Zamagni E, Aquerreta JD, Roche CL, Lentzsch S, Moreau P, Cavo M, Miguel JS, Dimopoulos MA, Rajkumar SV, Durie BGM, Terpos E, Delorme S (2018) Recommendations for acquisition, interpretation, and reporting of whole-body low dose CT in patients with multiple myeloma and other plasma cell disorders: a report of the IMWG Bone Working Group. Blood Cancer J 8:95. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-018-0124-1
Horger M, Claussen CD, Bross-Bach U, Vonthein R, Trabold T, Heuschmid M, Pfannenberg C (2005) Whole-body low-dose multidetector row-CT in the diagnosis of multiple myeloma: an alternative to conventional radiography. Eur J Radiol 54:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.04.015
Kröpil P, Fenk R, Fritz LB, Blondin D, Kobbe G, Mödder U, Cohnen M (2008) Comparison of whole-body 64-slice multidetector computed tomography and conventional radiography in the staging of multiple myeloma. Eur Radiol 18:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0738-3
Ormond Filho AG, Carneiro BC, Pastore D, Silva IP, Yamashita SR, Consolo FD, Hungria VTM, Sandes AF, Rizzatti EG, Nico MAC (2019) Whole-body imaging of multiple myeloma: diagnostic criteria. RadioGraphics 39:1077–1097. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2019180096
Hillengass J, Moulopoulos LA, Delorme S, Koutoulidis V, Hielscher T, Engelhart J, Drake MT, Rajkumar SV, Oestergaard B, Abildgaard N, Hinge M, Plesner T, Suehara Y, Matsue K, Caers J, Withofs N, Dimopoulos MA, Goldschmidt H, Lentzsch S, Durie BG, Terpos E (2016) Findings of whole-body computed tomography compared to conventional skeletal survey in patients with monoclonal plasma cell disorders-a study of the International Myeloma Working Group. Blood 128:4468
Hinge M, Andersen KT, Lund T, Jorgensen HB, Holdgaard PC, Ormstrup TE, Ostergaard LL, Plesner T (2016) Baseline bone involvement in multiple myeloma-a prospective comparison of conventional X-ray, low-dose computed tomography, and 18fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in previously untreated patients. Haematologica 101:e415–e418
Wolf MB, Murray F, Kilk K, Hillengass J, Delorme S, Heiss C, Neben K, Goldschmidt H, Kauczor HU, Weber MA (2014) Sensitivity of whole-body CT and MRI versus projection radiography in the detection of osteolysis in patients with monoclonal plasma cell disease. Eur J Radiol 83:1222–1230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.02.008
Hillengass J, Usmani S, Rajkumar SV, Durie BGM, Mateos MV, Lonial S, Joao C, Anderson KC, García-Sanz R, Riva E, du J, van de Donk N, Berdeja JG, Terpos E, Zamagni E, Kyle RA, San Miguel J, Goldschmidt H, Giralt S, Kumar S, Raje N, Ludwig H, Ocio E, Schots R, Einsele H, Schjesvold F, Chen WM, Abildgaard N, Lipe BC, Dytfeld D, Wirk BM, Drake M, Cavo M, Lahuerta JJ, Lentzsch S (2019) International Myeloma Working Group consensus recommendations on imaging in monoclonal plasma cell disorders. Lancet Oncol 6:E302–E312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30309-2
Huda W, Ogden KM, Khorasani MR (2008) Converting dose-length product to effective dose at CT. Radiology 248:995–1003. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2483071964
Pianko MJ, Terpos E, Roodman GD, Divgi CR, Zweegman S, Hillengass J, Lentzsch S (2014) Whole-body low-dose computed tomography and advanced imaging techniques for multiple myeloma bone disease. Clin Cancer Res 20:5888–5897. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1692
Amos B, Agarwal A, Kanekar S (2016) Imaging of multiple myeloma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 30:843–865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2016.03.007
Chrzan R, Jurczyszyn A, Urbanik A (2017) Whole-body low-dose computed tomography (WBLDCT) in assessment of patients with multiple myeloma – pilot study and standard imaging protocol suggestion. Pol J Radiol 82:356–363. https://doi.org/10.12659/PJR.901742
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Local Ethical Committee’s review of the protocol deemed that formal approval was not required owing to the retrospective, observational, and anonymous nature of this study.
Consent to participate
All patients signed the informed consent form to be eligible for this study.
Consent for publication
All patients gave consent for information about themselves to be published in scientific journals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ippolito, D., Giandola, T., Maino, C. et al. Whole-body low-dose computed tomography (WBLDCT) in staging and re-staging of multiple myeloma. Ann Hematol 100, 1241–1249 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04468-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04468-1