Abstract
External quality assurance (EQA) programs are vital to ensure high quality and standardized results in molecular diagnostics. It is important that EQA for quantitative analysis takes into account the variation in methodology. Results cannot be expected to be more accurate than limits of the technology used, and it is essential to recognize factors causing substantial outlier results. The present study aimed to identify parameters of specific importance for JAK2 V617F quantification by quantitative PCR, using different starting materials, assays, and technical platforms. Sixteen samples were issued to participating laboratories in two EQA rounds. In the first round, 19 laboratories from 11 European countries analyzing JAK2 V617F as part of their routine diagnostics returned results from in-house assays. In the second round, 25 laboratories from 17 countries participated. Despite variations in starting material, assay set-up and instrumentation the laboratories were generally well aligned in the EQA program. However, EQA based on a single technology appears to be a valuable tool to achieve standardization of the quantification of JAK2 V617F allelic burden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The discovery of the c.1849G>T mutation leading to the p.Val617Phe (V617F) substitution in JAK2 [1,2,3,4] has been a landmark in molecular diagnosis of the myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET), and primary myelofibrosis (PMF). Quantification of the mutation has shown that mutation burden also could reflect different subtypes of MPN. The majority of patients with PV or fibrotic PMF have been reported to have more than 50% JAK2 V617F while the opposite has been seen in ET patients [5, 6]. In addition, quantification of the allelic burden in JAK2 V617F-positive patients is increasingly used to monitor treatment response of new targeted therapies as well as in transplanted patients [7,8,9].
For molecular diagnosis, it has been recommended that the assay should be sensitive enough to detect a mutant burden around 1% [10]. The combination of a sensitive detection and reproducible quantification of JAK2 V617F challenges the methodology used in a routine setting. Conventional Sanger sequencing does not show the required sensitivity in cases with low mutation burden, and methodologies involving next generation sequencing are unnecessarily labor intensive and expensive for mutation detection of a single nucleotide substitution. Instead, the use of quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) has been shown to be a both sensitive and cost-effective method [11] and superior in sensitivity compared to qualitative methods [12]. As a step towards standardization of reliable molecular diagnostics, the European Leukemia Net (ELN) and MPN&MPNr-EuroNet have evaluated performance of different allele-specific (AS)-qPCR assays [8]. This work, involving 12 laboratories from seven countries recommended a JAK2 V617F qPCR assay which showed consistent performance across different qPCR platforms [13]. Even so, variation between laboratories and different instrumental setups can be substantial despite the use of the same experimental protocol. To ensure high quality and standardized quantitative results, external quality assurance (EQA) programs are vital. A program dedicated to JAK2 V617F detection by qPCR is advantageous since no additional bias on quantification would be introduced by comparison to a different methodology. MPN&MPNr-EuroNet has performed two rounds of EQA based on qPCR assays. In addition to providing an EQA to participating laboratories in the network, the aim was to identify parameters critical for the quantification of JAK2 V617F. Such factors would have a substantial impact also on an EQA result, and thus need to be identified in order to design a beneficial EQA program which would be useful in clinical routine.
Materials and methods
Participants
For the first quality assurance round (QA1), 19 laboratories from 11 countries across Europe analyzing JAK2 V617F by qPCR as part of their routine diagnostics returned results obtained with in-house assays. In the second QA (QA2), 25 laboratories from 17 countries participated.
Samples and references
Blood samples from JAK2 V617F-positive patients were collected after informed consent according to the guidelines of the Danish Regional Science Ethics Committee. In QA1, ten blood samples were collected, aliquoted, and distributed to participating laboratories by an overnight courier. DNA was extracted locally from whole blood according to each participant’s standard procedure. Six participants received extra blood and extracted DNA also from hemolyzed blood (n = 3) or granulocytes (n = 3) in addition to whole blood. In QA2, six unknown samples prepared by spiking JAK2 V617F-positive HEL cell line DNA into normal wild-type donor DNA was sent out. In both QA1 and QA2, a common reference for calibration corresponding to 75%, 23%, 3%, and 0.3% JAK2 V617F was created by spiking a 648 bp PCR fragment containing the c.1849G>T mutation into normal wild-type donor DNA and distributed with the samples. Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) was used to obtain a reference value for each sample in the trials by taking the mean of four replicates repeated three times. In QA2, values obtained by ddPCR in a separate laboratory were added to the mean as well.
Quantification of JAK2 V617F by qPCR
Copy numbers for JAK2 V617F and JAK2 WT and the allelic ratios of JAK2 V617F expressed as % [JAK2 V617F copy number/(JAK2 WT copy number + JAK2 V617F copy number)] were determined by the participating laboratories according to the assay used in the clinical routine. All results were sent to one laboratory for further analysis. To determine general variation of qPCR within an assay, data was collected from control samples and repeatedly analyzed according to the Larsen protocol [13] during 12 months in one laboratory. The analysis was performed by different persons on two PCR instruments, and batches for reagents were changed during the 12-month period. Percentage JAK2 V617F was calculated for each sample and the coefficient of variation (CV) for the assay was determined.
Results
Similar EQA results with different starting materials, qPCR assays, and qPCR instruments
To identify the parameters of specific importance for causing outliers in a JAK2 V617F EQA where a quantitative value of mutation burden is determined by qPCR, different starting materials, different qPCR assays, and different technical platforms were included. In total, 16 samples with unknown mutation burden were issued to participating laboratories. In QA1, samples were divided into four groups based on the reference levels of JAK2 V617F as determined by ddPCR: < 2% (n = 4), 2–10% (n = 3), 10–20% (n = 2), and > 30% (n = 2). Results were analyzed in detail for one sample in each group.
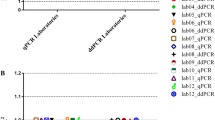
To test starting material for the analysis, six different laboratories extracted DNA from purified granulocytes or hemolyzed blood in addition to whole blood. JAK2 V617F was analyzed from both types of starting materials in parallel using routine protocol(s). Although differences could be noted between starting materials when comparisons were made within the same laboratory, the difference was in the same range as between the laboratories and different assays (Fig. 1).
Comparison of different starting materials for quantitative analysis of JAK2 V617F on selected samples. JAK2 V617F detection was performed in parallel using different starting materials in samples with four different levels of JAK2 V617F mutation. One of the six participating laboratories analyzed the samples with two different assays yielding a total of seven sets of data. Assigned values of JAK2 V617F are reference values as determined by ddPCR. These are indicated in the graphs by headings and dotted lines
To study the influence of assay protocols on EQA results, 19 laboratories from 11 countries analyzing JAK2 V617F by qPCR as part of their routine diagnostics returned results from their assay protocol used in clinical diagnostics in QA1. One of the laboratories returned results from two different assays yielding 20 sets of data in total. Various qPCR assay protocols were used: Larsen [13], n = 6; Lippert [5], n = 5; Ipsogen Mutaquant kit (Qiagen, Marseille, France), n = 4; and other protocols (in-house assays), n = 5. Although reported copy numbers in samples varied between laboratories (data not shown), the % JAK2 V617F was rather consistent across different assays (Table 1). In QA2, 25 laboratories from 17 countries returned results. Two of the laboratories returned results from two different assays yielding 27 sets of data. In QA2, the majority of participating laboratories used the Larsen assay (n = 18) or a modification of this assay (n = 4). Five laboratories reported results obtained by another assay. The six samples issued in QA2 were divided into the same groups as for QA1 (< 2% (n = 2), 2–10% (n = 1), 10–20% (n = 2), and > 30% (n = 1)) and one sample from each group was analyzed in detail. Overall, variations were similar in QA1 and in QA2 (Table 1). Although there was a relative consistency in quantification of JAK2 V617F allelic burdens above 2%, a higher variation was noted in samples with low mutation burden (< 2%).
Next, we studied whether different qPCR platforms could introduce substantial variation. The majority of QA1 participants used instruments from Applied Biosystems (Foster City, CA, USA). Eleven sets of data were analyzed on these instruments (ABI7300/7500/7500FAST/7900HT). The remaining laboratories used Lightcycler LC480 (Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Germany, n = 4), Rotorgene (3000A/Q; Corbett Life Science, Sydney, Australia; Qiagen, n = 3), or Stratagene (MX3000/MX3500; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA, n = 2) for analysis. For all but Applied Biosystems instruments, groups were very small, which resulted in single outliers having a substantial impact on the results. In addition, different versions of instruments from the same manufacturer were used in all groups. Nonetheless, no major difference depending on qPCR instrument could be seen (Fig. 2).
JAK2 V617F results obtained with different qPCR instruments on selected samples. Different versions of instruments were included in each group according to text. ABI n = 11, LC n = 4, Rotorgene n = 3, and Stratagene n = 2. Median values in each group are indicated by a black line in boxes. Assigned values of JAK2 V617F are reference values as determined by ddPCR. These are indicated in the graphs by headings
For comparison, CV for the Larsen assay over a stretch of one year was determined in one participating laboratory. During that period of time, a control sample of 4.5% JAK2 V617F was analyzed 97 times and a sample of 13% was analyzed 64 times on two instruments (Rotorgene Q, Fig. 3). CV for calculated % JAK2 V617F was 26% in both cases.
To evaluate whether the differences between assays and qPCR instruments were substantial enough to affect the result of an EQA, z-scores were determined for selected samples in QA1. A z-score between 2 and − 2 was considered as satisfactory performance, a z-score between 2 and 3 or between − 2 and − 3 was considered as a warning, and a z-score above 3 or below − 3 was considered as critical. Results showed that three participants obtained a warning, while the remaining participants got a satisfactory performance. None was scored as “critical” (Table 2).
Discussion
Bias altering qPCR results may occur at several steps of JAK2 V617F assays, even when laboratories use the same methodology. Starting material for the analysis as well as technical platform, assay design and batch variations can influence the results. Even among laboratories using the same qPCR protocol for quantitative assays, considerable variation has been reported [14]. Standardized results are vital not only to aid in diagnosis of patients but also in clinical, multicenter studies. One way to test how well individual laboratories align to predicted results is through participating in EQA. Moreover, EQA are central tools for the accreditation and assessment of laboratory performance. To design a useful EQA for quantitative analysis, it is important to take into account the variation of the methodology in focus. If expectations of consistency in results are set too high, beyond the limits of the technology used, there is a risk that a well-performing laboratory will get poor or inadequate results just because of natural variation in the method, or because of the influence of a particular parameter which has not been identified as important for outcome. Therefore, it is essential to recognize factors which would cause substantial outliers in the tests, as well as which variation could be expected from different qPCR technical platforms.
A previous study has shown that the results obtained for the detection of the JAK2 mutation were comparable in whole blood and in purified granulocytes, and that no false negative was reported in whole blood if the qPCR assay used was able to detect < 1% JAK2 V617F [15]. However, in this study, the allelic ratio was reported to be on average 15% lower in whole blood than in purified granulocytes; the low-average JAK2 V617F values was due to a minority of the whole blood samples. The choice of the starting material could thus be of importance in individual cases depending on the question asked. In the present study, the starting material used for the analysis did not affect the performance in EQA for the majority of laboratories.
In both QA1 and QA2, samples with low mutation burden (< 2% JAK2 V617F) were included, and a greater variation was seen for these samples. This reflects the sensitivity of the assay and the qPCR setup in each laboratory. In addition, when dealing with low JAK2 V617F copy numbers stochastic variation will add to the overall variation. However, for low mutation burden, specificity of the assay is an equally important issue. The background level where cross-reaction with the wild-type allele could occur must be clearly defined by each laboratory to avoid false positive results [10].
To be able to compare results, over time as well as between laboratories, there is a need to standardize the results with respect to the quantitative level of mutation burden. In chronic myeloid leukemia, where the level of expression of the fusion gene BCR-ABL1 is correlated to prognosis, a conversion factor has been established to correct for differences across laboratories. This factor is used to align results to an international scale which is anchored to clinical results [16, 17]. However, the original conversion factor was based on the sample exchange with a reference laboratory and this procedure is both time-consuming and expensive and a risk for inborn errors due to bias cannot be ruled out. To overcome this, primary references intended for the calibration of a secondary reference material have been established [18]. In addition, a certified reference plasmid for the calibration of BCR-ABL1 quantification has been manufactured [19]. As reported in a previous international study [11], a common reference material remains a useful tool for laboratories also for JAK2 V617F, as it allows decreasing or suppressing differences in copy numbers in certain laboratories. In addition, it also allows adjustment for batch variations, e.g., due to differences in quality of primer oligonucleotides. A first WHO reference panel for JAK2 V617F has recently been established and is now available [20]. This holds promise to further improve assay standardization. With increasing clinical demands for molecular monitoring, both EQA programs and standardized JAK2 V617F reference material are needed to identify and maintain validated laboratories.
In conclusion, variation in method due to the starting material, assay set-up, or qPCR equipment did not result in significant outliers in the EQA programs included in this study. However, EQA based on a single technology remains a valuable tool to achieve standardization of JAK2 V617F quantification.
References
James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C, Garcon L, Raslova H, Berger R, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Villeval JL, Constantinescu SN, Casadevall N, Vainchenker W (2005) A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature 434(7037):1144–1148. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03546
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S, Vassiliou GS, Bench AJ, Boyd EM, Curtin N, Scott MA, Erber WN, Green AR, Cancer Genome P (2005) Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 365(9464):1054–1061. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)71142-9
Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR, Tichelli A, Cazzola M, Skoda RC (2005) A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med 352(17):1779–1790. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa051113
Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJ, Boggon TJ, Wlodarska I, Clark JJ, Moore S, Adelsperger J, Koo S, Lee JC, Gabriel S, Mercher T, D'Andrea A, Frohling S, Dohner K, Marynen P, Vandenberghe P, Mesa RA, Tefferi A, Griffin JD, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Golub TR, Lee SJ, Gilliland DG (2005) Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell 7(4):387–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2005.03.023
Lippert E, Boissinot M, Kralovics R, Girodon F, Dobo I, Praloran V, Boiret-Dupre N, Skoda RC, Hermouet S (2006) The JAK2-V617F mutation is frequently present at diagnosis in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Blood 108(6):1865–1867. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-01-013540
Passamonti F, Rumi E, Pietra D, Della Porta MG, Boveri E, Pascutto C, Vanelli L, Arcaini L, Burcheri S, Malcovati L, Lazzarino M, Cazzola M (2006) Relation between JAK2 (V617F) mutation status, granulocyte activation, and constitutive mobilization of CD34+ cells into peripheral blood in myeloproliferative disorders. Blood 107(9):3676–3682. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-09-3826
Kiladjian JJ, Cassinat B, Chevret S, Turlure P, Cambier N, Roussel M, Bellucci S, Grandchamp B, Chomienne C, Fenaux P (2008) Pegylated interferon-alfa-2a induces complete hematologic and molecular responses with low toxicity in polycythemia vera. Blood 112(8):3065–3072. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-03-143537
Jovanovic JV, Ivey A, Vannucchi AM, Lippert E, Oppliger Leibundgut E, Cassinat B, Pallisgaard N, Maroc N, Hermouet S, Nickless G, Guglielmelli P, van der Reijden BA, Jansen JH, Alpermann T, Schnittger S, Bench A, Tobal K, Wilkins B, Cuthill K, McLornan D, Yeoman K, Akiki S, Bryon J, Jeffries S, Jones A, Percy MJ, Schwemmers S, Gruender A, Kelley TW, Reading S, Pancrazzi A, McMullin MF, Pahl HL, Cross NC, Harrison CN, Prchal JT, Chomienne C, Kiladjian JJ, Barbui T, Grimwade D (2013) Establishing optimal quantitative-polymerase chain reaction assays for routine diagnosis and tracking of minimal residual disease in JAK2-V617F-associated myeloproliferative neoplasms: a joint European LeukemiaNet/MPN&MPNr-EuroNet (COST action BM0902) study. Leukemia 27(10):2032–2039. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.219
Utke Rank C, Weis Bjerrum O, Larsen TS, Kjaer L, de Stricker K, Riley CH, Hasselbalch HC (2015) Minimal residual disease after long-term interferon-alpha2 treatment: a report on hematological, molecular and histomorphological response patterns in 10 patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Leuk Lymphoma 57:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3109/10428194.2015.1049171
Bench AJ, White HE, Foroni L, Godfrey AL, Gerrard G, Akiki S, Awan A, Carter I, Goday-Fernandez A, Langabeer SE, Clench T, Clark J, Evans PA, Grimwade D, Schuh A, McMullin MF, Green AR, Harrison CN, Cross NC, British Committee for Standards in H (2013) Molecular diagnosis of the myeloproliferative neoplasms: UK guidelines for the detection of JAK2 V617F and other relevant mutations. Br J Haematol 160(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12075
Lippert E, Girodon F, Hammond E, Jelinek J, Reading NS, Fehse B, Hanlon K, Hermans M, Richard C, Swierczek S, Ugo V, Carillo S, Harrivel V, Marzac C, Pietra D, Sobas M, Mounier M, Migeon M, Ellard S, Kroger N, Herrmann R, Prchal JT, Skoda RC, Hermouet S (2009) Concordance of assays designed for the quantification of JAK2V617F: a multicenter study. Haematologica 94(1):38–45. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.13486
Perricone M, Palandri F, Ottaviani E, Angelini M, Bagli L, Bellesia E, Donati M, Gemmati D, Zucchini P, Mancini S, Marchica V, Trubini S, De Matteis G, Di Zacomo S, Favarato M, Fioroni A, Bolzonella C, Maccari G, Navaglia F, Gatti D, Toffolatti L, Orlandi L, Laloux V, Manfrini M, Galieni P, Giannini B, Tieghi A, Barulli S, Serino ML, Maccaferri M, Scortechini AR, Giuliani N, Vallisa D, Bonifacio M, Accorsi P, Salbe C, Fazio V, Gusella M, Toffoletti E, Salvucci M, Svaldi M, Gherlinzoni F, Cassavia F, Orsini F, Martinelli G (2017) Assessment of the interlaboratory variability and robustness of JAK2V617F mutation assays: a study involving a consortium of 19 Italian laboratories. Oncotarget 8(20):32608–32617. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15940
Larsen TS, Christensen JH, Hasselbalch HC, Pallisgaard N (2007) The JAK2 V617F mutation involves B- and T-lymphocyte lineages in a subgroup of patients with Philadelphia-chromosome negative chronic myeloproliferative disorders. Br J Haematol 136(5):745–751. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06497.x
Raggi CC, Verderio P, Pazzagli M, Marubini E, Simi L, Pinzani P, Paradiso A, Orlando C (2005) An Italian program of external quality control for quantitative assays based on real-time PCR with Taq-Man probes. Clin Chem Lab Med: CCLM / FESCC 43(5):542–548. https://doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2005.094
Hermouet S, Dobo I, Lippert E, Boursier MC, Ergand L, Perrault-Hu F, Pineau D (2007) Comparison of whole blood vs purified blood granulocytes for the detection and quantitation of JAK2(V617F). Leukemia 21(5):1128–1130. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404588
Hughes TP, Kaeda J, Branford S, Rudzki Z, Hochhaus A, Hensley ML, Gathmann I, Bolton AE, van Hoomissen IC, Goldman JM, Radich JP, International Randomised Study of Interferon versus STISG (2003) Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 349(15):1423–1432. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa030513
Hughes T, Deininger M, Hochhaus A, Branford S, Radich J, Kaeda J, Baccarani M, Cortes J, Cross NC, Druker BJ, Gabert J, Grimwade D, Hehlmann R, Kamel-Reid S, Lipton JH, Longtine J, Martinelli G, Saglio G, Soverini S, Stock W, Goldman JM (2006) Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: review and recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood 108(1):28–37. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-01-0092
White HE, Matejtschuk P, Rigsby P, Gabert J, Lin F, Lynn Wang Y, Branford S, Muller MC, Beaufils N, Beillard E, Colomer D, Dvorakova D, Ehrencrona H, Goh HG, El Housni H, Jones D, Kairisto V, Kamel-Reid S, Kim DW, Langabeer S, Ma ES, Press RD, Romeo G, Wang L, Zoi K, Hughes T, Saglio G, Hochhaus A, Goldman JM, Metcalfe P, Cross NC (2010) Establishment of the first World Health Organization International Genetic Reference Panel for quantitation of BCR-ABL mRNA. Blood 116(22):e111–e117. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-06-291641
White H, Deprez L, Corbisier P, Hall V, Lin F, Mazoua S, Trapmann S, Aggerholm A, Andrikovics H, Akiki S, Barbany G, Boeckx N, Bench A, Catherwood M, Cayuela JM, Chudleigh S, Clench T, Colomer D, Daraio F, Dulucq S, Farrugia J, Fletcher L, Foroni L, Ganderton R, Gerrard G, Gineikiene E, Hayette S, El Housni H, Izzo B, Jansson M, Johnels P, Jurcek T, Kairisto V, Kizilors A, Kim DW, Lange T, Lion T, Polakova KM, Martinelli G, McCarron S, Merle PA, Milner B, Mitterbauer-Hohendanner G, Nagar M, Nickless G, Nomdedeu J, Nymoen DA, Leibundgut EO, Ozbek U, Pajic T, Pfeifer H, Preudhomme C, Raudsepp K, Romeo G, Sacha T, Talmaci R, Touloumenidou T, Van der Velden VH, Waits P, Wang L, Wilkinson E, Wilson G, Wren D, Zadro R, Ziermann J, Zoi K, Muller MC, Hochhaus A, Schimmel H, Cross NC, Emons H (2015) A certified plasmid reference material for the standardisation of BCR-ABL1 mRNA quantification by real-time quantitative PCR. Leukemia 29(2):369–376. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.217
Sanzone P, Hawkins R, Rigsby P, Boyle J (2016) Collaborative study to evaluate the proposed WHO 1st International Reference Panel for Genomic JAK2 V617F. vol WHO/BS/2016.2293, WHO/BS/2016.2293 edn
Acknowledgements
We thank Pia Nielsen, Lone Hartmann Hansen and Tina Brandt Christensen for technical assistance.
Funding
RK acknowledges the support received by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF): F4702-B20 and P29018-B30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
FD is employed by the MLL Munich Leukemia Laboratory. SA is a member of Qiagen Scientific Advisory Board—Haemato Oncology.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Asp, J., Skov, V., Bellosillo, B. et al. International external quality assurance of JAK2 V617F quantification. Ann Hematol 98, 1111–1118 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3570-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3570-8