Abstract
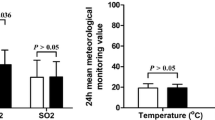
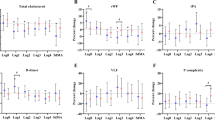
Plasma von Willebrand factor (vWF) is an important factor involving in hemostasis and various cardiovascular diseases. Air pollution is related to many respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. During the Olympic Games Beijing 2008 period (August 8 to September 17, 2008) when air quality in Beijing improved greatly, we studied the relationship between plasma vWF level and the factors of air pollution index (API), ABO blood group, and polymorphisms in vWF gene in healthy young adults. We recruited 114 healthy medical students. In a period of more than 4 months around the period of Olympic Games Beijing 2008, six blood samples at stages 1 and 2 (before Olympic Games), stages 3 and 4 (during Olympic Games), and stages 5 and 6 (after Olympic Games) were taken from every participant for the measurement of plasma vWF level and genotyping of three SNPs (rs7954855, rs7965413, and rs216311) in vWF gene. Daily air pollution index near their living places was obtained from the officially published data. The average API began to decrease from stage 2, reached to nadir in stages 3 and 4, and increased but was still lower in stages 5 and 6. Plasma vWF decreased during the experimental period in all participants. The average plasma vWF decreased from stage 2 and remained lower in stages 3–6. vWF level varied greatly among the participants (from 30 to 170 %) but decreased proportionately when we analyzed their levels individually. Participants with O blood type had lower plasma vWF level than those with A, B, and AB blood types. Those with the SNP in vWF gene causing homozygous threonine at codon 1381 had lower plasma vWF level than those with homozygous alanine or heterozygous alanine/threonine. In the 114 normal individuals, the average plasma vWF level decreased during the period of Olympic Games Beijing 2008 when air quality improved greatly. This suggests that control of air pollution may be useful to prevent some diseases such as cardiovascular diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lip GY, von Blann AD (1997) Willebrand factor: a marker of endothelial dysfunction in vascular disorder? Cardiovasc Res 34:255–265
Meigs JB, Mittleman MA, Nathan DM et al (2000) Hyperinsulinemia hyperglycemia, and impaired hemostasis: the Framingham Offspring Study. JAMA 283:221–283
De Lange M, de Geus EJ, Kluft C et al (2006) Genetic influences on fibrongen, tissue plasminogen activator-antigen and von Willebrand factor in male and females. Thromb Haemost 95:414–419
Szántó T, Schlammadinger A, Staelens S et al (2007) The A/T1381 polymorphism in the A1-domain of von Willebrand factor influences the affinity of von Willebrand factor for platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha. Thromb Haemost 98:178–185
Mancuso DJ, Tuley EA, Westfield et al (1989) Structure of gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem 264:19514–19527
Simon D, Paludo CA, Ghisleni GC et al (2003) Association studies between -1185A/G von Willebrand factor gene polymorphism and coronary artery disease. Braz J Med Biol Res 36:709–714
Keightley AM, Lam MY, Brady JN et al (1999) Variation at the von Willebrand factor (vWF) gene locus is associated with plasma vWF:Ag levels: identification of three novel single nucleotide polymorphisms in the vWF gene promoter. Blood 93:4277–4283
Simon D, Palatnikb M, Roisenberga I (2002) Analysis of the -1185A/G von Willebrand factor (VWF) gene polymorphism in two Brazilian ethnic groups and its effect on the plasma VWF levels. Thromb Res 105:519–522
Di Bitondo R, Cameron CL, Daly ME et al (2001) The −1185 A/G and −1051 G/A dimorphisms in the von Willebrand factor gene promoter and risk of myocardial infarction. Br J Haematol 115:701–706
Orstavik KH, Magnus P, Reisener H et al (1985) Factor VII and factor IX in a twin population: evidence for a major effect of ABO locus on factor VII level. Am J Hum Genet 37:89–101
Davies JA, Collins PW, Hathaway LS et al (2007) Effect of von Willebrand factor Y/C1584 on in vivo protein level and function and interaction with ABO blood group. Blood 109:2840–2846
Franchini M, Guida A, Tufano A et al (2012) Air pollution, vascular disease and thrombosis: linking clinical data and pathogenic mechanisms. J Thromb Haemost. doi:10.1111/jth.12006
Katsouyanni K (2003) Ambient air pollution and health. Br Med Bull 68:143–156
O’Neill MS, Veves A, Sarnat JA et al (2007) Air pollution and inflammation in type 2 diabetes: a mechanism for susceptibility. Occup Environ Med 64:373–379
Brook RD, Franklin B, Cascio W et al (2004) Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the expert panel on population and prevention science of the American Heart Association. Circulation 109:2655–2671
Brook RD, Rajagopalan S, Pope CA et al (2010) Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: an update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 121:2331–2378
Rückerl R, lbald-Mulli A, Koenig W et al (2006) Air pollution and markers of inflammation and coagulation in patients with coronary heart disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173:432–441
Chuang KJ, Chan CC, Su TC et al (2007) The effect of urban air pollution on inflammation, oxidative stress, coagulation, and autonomic dysfunction in young adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176:370–376
Delfino R, Staimer N, Tjoa T et al (2008) Circulating biomarkers of inflammation, antioxidant activity, and platelet activation are associated with primary combustion aerosols in subjects with coronary artery disease. Environ Health Perspect 116:898–906
Ruckerl R, Phipps RP, Schneider A et al (2007) Ultrafine particles and platelet activation in patients with coronary heart disease—results from a prospective panel study. Part Fibre Toxicol 4:1
Bowen DJ (2003) An influence of ABO blood group on the rate of proteolysis of von Willebrand factor by ADAMTS 13. J Thromb Haemost 1:33–40
O’Donnell JS, McKinnon TA, Crawley JT et al (2005) Bombay phenotype is associated with reduced plasma-VWF levels and an increased susceptibility to ADAMTS13 proteolysis. Blood 106:1988–1991
Bowen DJ, Collins PW (2004) An amino acid polymorphism in von Willebrand factor correlates with increased susceptibility to proteolysis by ADAMTS13. Blood 103:941–947
Davies JA, Collins PW, Hathaway LS et al (2008) von Willebrand factor: evidence for variable clearance in vivo according to Y/C1584 phenotype and ABO blood group. J Thromb Haemost 6:97–103
Acknowledgment
This study was jointly funded by National 863 High-Tech Research and Development Program of China (2008AA02503), National Young Scientists Fund (811D2211), and NIEHS (1R01ES015864, P30ES005022, 5P30ES007048).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Changes of plasma vWF level in response to the improvement of air quality: an observation of 114 healthy young adults. Ann Hematol 92, 543–548 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1679-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1679-3