Abstract
The gene RAI was originally described as an inhibitor of RelA/p65 subunit of nuclear factor κB (NF–κB). Here, we analyse the association between genetic variation in the genes RAI and CD3EAP and outcome of 348 myeloma patients treated with high-dose treatment (HDT), 146 patients treated with interferon-α (INF-α) as maintenance treatment, 177 patients treated with thalidomide, and 74 patients treated with bortezomib at relapse and address if the effects of polymorphisms in CD3EAP and RAI are modified by a functional polymorphism in NFКB1. By linkage disequilibrium mapping, we found that variant alleles of several polymorphisms in a sub-region of 19q13.3 spanning the regions RAI-intron1-1 to RAI intron1-3 and the region exon1 to exon3–6 in CD3EAP were associated with prolonged time-to-treatment failure (TTF; p = 0.003) and overall survival (OS; p = 0.02). Haplotype analyses revealed that none of the haplotypes were more strongly associated to TTF or OS than the two strongly linked SNPs, RAI-intron1-1 (rs4572514) and CD3EAP G-21A (rs967591). The association of RAI-intron1-1 and CD3EAP G-21A with TTF was independent of NFKB1-94 ins/del, but homozygous ins-allele carriers which were also variant allele carriers of RAI-intron1-1 or CD3EAP G-21A had the longest OS. Among patients treated with INF-α or thalidomide, no effect was seen in relation to genotype. Our results indicate that polymorphism in RAI and CD3EAP are associated with outcome of myeloma patients treated with HDT. Combination analyses with the functional polymorphism in NFKB1 suggest that a possibly functional effect of RAI or CD3EAP could be related to NF–κB availability.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MM:
-
multiple myeloma
- OS:
-
overall survival
- TTF:
-
time-to-treatment failure
- HDT:
-
high-dose treatment
- SNP:
-
single-nucleotide polymorphism
- LD:
-
linkage disequilibrium
- CI:
-
confidence interval
- RR:
-
relative risk
- ERCC1 :
-
excision-repair cross-complementing 1
- ERCC2 :
-
excision-repair cross-complementing 2
- RAI :
-
RelA associated inhibitor (also named PPP1R13L protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13 like and iASPP)
- CD3EAP :
-
CD3e molecule epsilon-associated protein (also named ASE1 anti-sense to ERCC1)
- NER:
-
nucleotide excision repair
References
Rockenbauer E, Bendixen MH, Bukowy Z, Yin J, Jacobsen NR, Hedayati M, Vogel U, Grossman L, Bolund L, Nexo BA (2002) Association of chromosome 19q13.2–3 haplotypes with basal cell carcinoma: tentative delineation of an involved region using data for single nucleotide polymorphisms in two cohorts. Carcinogenesis 23:1149–1153
Nexo BA, Vogel U, Olsen A, Ketelsen T, Bukowy Z, Thomsen BL, Wallin H, Overvad K, Tjonneland A (2003) A specific haplotype of single nucleotide polymorphisms on chromosome 19q13.2–3 encompassing the gene RAI is indicative of post-menopausal breast cancer before age 55. Carcinogenesis 24:899–904
Vogel U, Laros I, Jacobsen NR, Thomsen BL, Bak H, Olsen A, Bukowy Z, Wallin H, Overvad K, Tjonneland A, Nexo BA, Raaschou-Nielsen O (2004) Two regions in chromosome 19q13.2–3 are associated with risk of lung cancer. Mutat Res 546:65–74
Vangsted A, Gimsing P, Klausen TW, Nexo BA, Wallin H, Andersen P, Hokland P, Lillevang ST, Vogel U (2007) Polymorphisms in the genes ERCC2, XRCC3 and CD3EAP influence treatment outcome in multiple myeloma patients undergoing autologous bone marrow transplantation. Int J Cancer 120:1036–1045
de Boer J, Hoeijmakers JH (2000) Nucleotide excision repair and human syndromes. Carcinogenesis 21:453–460
Laska MJ, Strandbygard D, Kjeldgaard A, Mains M, Corydon TJ, Memon AA, Sorensen BS, Vogel U, Jensen UB, Nexo BA (2007) Expression of the RAI gene is conducive to apoptosis: studies of induction and interference. Exp Cell Res 313:2611–2621
Laska MJ, Lowe SW, Zender L, Hearn S, Vogel U, Jensen UB, Bric A, Nexo BA (2009) Enforced expression of PPP1R13L increases tumorigenesis and invasion through p53-dependent and p53-independent mechanisms. Mol Carcinog 48:832–842
Yang JP, Hori M, Sanda T, Okamoto T (1999) Identification of a novel inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB, RelA-associated inhibitor. J Biol Chem 274:15662–15670
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, O’Neil NJ, Trigiante G, Crook T, Hsieh JK, O’Connor DJ, Zhong S, Campargue I, Tomlinson ML, Kuwabara PE, Lu X (2003) iASPP oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53 conserved from worm to human. Nat Genet 33:162–167
Ochs RL, Stein TW Jr, Chan EK, Ruutu M, Tan EM (1996) cDNA cloning and characterization of a novel nucleolar protein. Mol Biol Cell 7:1015–1024
Whitehead CM, Winkfein RJ, Fritzler MJ, Rattner JB (1997) ASE-1: a novel protein of the fibrillar centres of the nucleolus and nucleolus organizer region of mitotic chromosomes. Chromosoma 106:493–502
Yamazaki T, Hamano Y, Tashiro H, Itoh K, Nakano H, Miyatake S, Saito T (1999) CAST, a novel CD3epsilon-binding protein transducing activation signal for interleukin-2 production in T cells. J Biol Chem 274:18173–18180
Nissen KK, Vogel U, Nexo BA (2009) Association of a single nucleotide polymorphic variation in the human chromosome 19q13.3 with drug responses in the NCI60 cell lines. Anticancer Drugs 20:174–178
Vangsted AJ, Klausen TW, Gimsing P, Andersen NF, Abildgaard N, Gregersen H, Vogel U (2009) A polymorphism in NFKB1 is associated with improved effect of interferon-{alpha} maintenance treatment of patients with multiple myeloma after high-dose treatment with stem cell support. Haematologica 94:1274–1281
Vangsted AJ, KlausenTW, Andersen NF, Abildgaard N, Gang AO, Gregersen H, Vogel U, Gimsing P (2010) Improved survival of multiple myeloma patients with late relapse after high-dose treatment and stem cell support; a population-based study of 348 patients in Denmark in 1994–2004. Eur J Haematol 85:209
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Saber AT, Nielsen LR, Dictor M, Hagmar L, Mikoczy Z, Wallin H (1998) K-ras mutations in sinonasal adenocarcinomas in patients occupationally exposed to wood or leather dust. Cancer Lett 126:59–65
Vangsted AJ, Klausen TW, Ruminski W, Gimsing P, Andersen NF, Gang AO, Abildgaard N, Knudsen LM, Nielsen JL, Gregersen H, Vogel U (2009) The polymorphism IL-1beta T-31 C is associated with a longer overall survival in patients with multiple myeloma undergoing auto-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 43:539–545
Nexo BA, Vogel U, Olsen A, Nyegaard M, Bukowy Z, Rockenbauer E, Zhang X, Koca C, Mains M, Hansen B, Hedemand A, Kjeldgaard A, Laska MJ, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Cold S, Overvad K, Tjonneland A, Bolund L, Borglum AD (2008) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of a breast cancer susceptibility locus near RAI/PPP1R13L/iASPP. BMC Med Genet 9:56
Karban AS, Okazaki T, Panhuysen CI, Gallegos T, Potter JJ, Bailey-Wilson JE, Silverberg MS, Duerr RH, Cho JH, Gregersen PK, Wu Y, Achkar JP, Dassopoulos T, Mezey E, Bayless TM, Nouvet FJ, Brant SR (2004) Functional annotation of a novel NFKB1 promoter polymorphism that increases risk for ulcerative colitis. Hum Mol Genet 13:35–45
Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD (1998) How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem 67:227–264
Ghiringhelli F, Apetoh L, Tesniere A, Aymeric L, Ma Y, Ortiz C, Vermaelen K, Panaretakis T, Mignot G, Ullrich E, Perfettini JL, Schlemmer F, Tasdemir E, Uhl M, Genin P, Civas A, Ryffel B, Kanellopoulos J, Tschopp J, Andre F, Lidereau R, McLaughlin NM, Haynes NM, Smyth MJ, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L (2009) Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic cells induces IL-1beta-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors. Nat Med 15:1170–1178
Hideshima T, Ikeda H, Chauhan D, Okawa Y, Raje N, Podar K, Mitsiades C, Munshi NC, Richardson PG, Carrasco RD, Anderson KC (2009) Bortezomib induces canonical nuclear factor-kappaB activation in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 114:1046–1052
Acknowledgement
We thank Bettina Hansen and Lars Bentzen for expert technical assistance. Participants from the Nordic Myeloma Study Group (NMSG) are thanked. This work was supported by The Research Fund at Region Sjaelland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 46 kb)
ESM 2
The genotype frequency of SNPs in the genes XPD, RAI, CD3EAP and ERCC1 located in the sub-region 19q13.3 (DOC 76 kb)
ESM 3
Characteristics of the patient population subdivided by the polymorphisms. (DOC 48 kb)
ESM 4
Supplement. Combination analysis of NFKB1-94ins/del, CD3EAP G-21A and RAI-intron1-1 (DOC 41 kb)
ESM 5
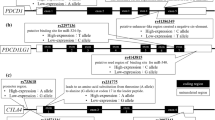
Linkage disequilibrium among 33 SNPs in the genes ERCC2, RAI and ERCC1. Plot of relative D’/LOD scores between the 33 SNPs from 348 Caucasian multiple myeloma patients produced by the programme Haplo-view (http://www.broad.mit.eud/mpg/haploview). Blue arrows: SNPs represented in haplotype analysis including RAI, ASE1 and ERCC1. Red arrows: SNPs represented in haplotype analysis in the gene CD3EAP (PPT 234 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vangsted, A.J., Klausen, T.W., Gimsing, P. et al. The importance of a sub-region on chromosome 19q13.3 for prognosis of multiple myeloma patients after high-dose treatment and stem cell support: a linkage disequilibrium mapping in RAI and CD3EAP . Ann Hematol 90, 675–684 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-1105-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-1105-z