Abstract
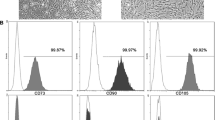
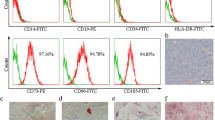
Modulation of adhesion molecules expression on the surface of cord blood (CB) CD34+ cells may assist in overcoming the delay in cord blood engraftment. Likewise, utilization of diverse growth factors such as neuropeptides could also be helpful. Therefore, we aimed to assess the role of Substance P (SP) along with a cytokine cocktail on CB CD34+ adhesion molecule expression. CB CD34+ cells were cultured in a serum-free media containing different concentrations of SP in combination with a cytokine cocktail (SCF, FL, TPO, IL-3, and IL-6). Expression of adhesion molecules CXCR4, CD44, CD49e, and CD62L was analyzed after 7 and/or 11 days of cell cultivation. Additionally, the colonogenic capacity of cells was analyzed by colony formation unit assay. Our results show an enhanced percentage of CD34+cells with CXCR4, CD44, and CD62L on day 7, as compared with control. Furthermore, an increase in frequency was observed for CD49e+ CD34+cells by day 7 in both test and control groups compared with day 0. Colonogenic assays show occurrence of more total colony formation and immature progenitor cells in SP-treated cells. Our study indicates that SP could act as an effective modulator for expression of cell adhesion molecules.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berenson RJ et al (1991) Engraftment after infusion of CD34+ marrow cells in patients with breast cancer or neuroblastoma. Blood 77(8):1717–1722
Cohen PA et al (2007) A neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist that reduces intraabdominal adhesion formation increases peritoneal matrix metalloproteinase activity. Wound Repair Regen 15(6):800–808
Corcoran KE, Patel N, Rameshwar P (2007) Stromal derived growth factor-1alpha: another mediator in neural-emerging immune system through Tac1 expression in bone marrow stromal cells. J Immunol 178(4):2075–2082
Deguchi T et al (1999) Expression of homing-associated cell adhesion molecule (H-CAM/CD44) on human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Exp Hematol 27(3):542–552
Denning-Kendall P et al (2003) Cytokine expansion culture of cord blood CD34+ cells induces marked and sustained changes in adhesion receptor and CXCR4 expressions. Stem Cells 21(1):61–70
Dravid G, Rao SG (2002) Ex vivo expansion of stem cells from umbilical cord blood: expression of cell adhesion molecules. Stem Cells 20(2):183–189
Ghaffari S et al (1995) Differentiation-associated changes in CD44 isoform expression during normal hematopoiesis and their alteration in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 86(8):2976–2985
Greco SJ et al (2004) Tachykinins in the emerging immune system: relevance to bone marrow homeostasis and maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells. Front Biosci 9:1782–1793
Hiramoto M et al (1998) Stimulatory effects of substance P on CD34 positive cell proliferation and differentiation in vitro are mediated by the modulation of stromal cell function. Int J Mol Med 1(2):347–354
Koenig JM et al (1999) L-selectin expression enhances clonogenesis of CD34+ cord blood progenitors. Pediatr Res 45(6):867–870
Lee YH et al (2004) Homing-associated cell adhesion molecules and cell cycle status on the nucleated cells in the bone marrow, mobilized peripheral blood and cord blood. J Korean Med Sci 19(4):523–528
Li Y, Douglas SD, Ho W (2000) Human stem cells express substance P gene and its receptor. J Hematother Stem Cell Res 9(4):445–452
Liu B et al (2003) Significance of increasing adhesion of cord blood hematopoietic cells and a new method: platelet microparticles. Am J Hematol 74(3):216–217
Nervi B, Link DC, DiPersio JF (2006) Cytokines and hematopoietic stem cell mobilization. J Cell Biochem 99(3):690–705
Nowicki M et al (2007) The significance of substance P in physiological and malignant haematopoiesis. J Clin Pathol 60(7):749–755
Peled A et al (1999) Dependence of human stem cell engraftment and repopulation of NOD/SCID mice on CXCR4. Science 283(5403):845–848
Prosper F, Verfaillie CM (2001) Regulation of hematopoiesis through adhesion receptors. J Leukoc Biol 69(3):307–316
Rameshwar P, Gascon P (1995) Substance P (SP) mediates production of stem cell factor and interleukin-1 in bone marrow stroma: potential autoregulatory role for these cytokines in SP receptor expression and induction. Blood 86(2):482–490
Ramirez M et al (2001) Ex vivo expansion of umbilical cord blood (UCB) CD34(+) cells alters the expression and function of alpha 4 beta 1 and alpha 5 beta 1 integrins. Br J Haematol 115(1):213–221
Sassetti C et al (1998) Identification of podocalyxin-like protein as a high endothelial venule ligand for L-selectin: parallels to CD34. J Exp Med 187(12):1965–1975
Shahrokhi S et al (2010) Substance P and calcitonin gene-related neuropeptides as novel growth factors for ex vivo expansion of cord blood CD34(+) hematopoietic stem cells. Growth Factors 28(1):66–73
Sugano Y et al (2008) Junctional adhesion molecule-A, JAM-A, is a novel cell-surface marker for long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 111(3):1167–1172
Surbek DV et al (2000) Developmental changes in adhesion molecule expressions in umbilical cord blood CD34 hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells. Am J Obstet Gynecol 183(5):1152–1157
Teixido J et al (1992) Role of beta 1 and beta 2 integrins in the adhesion of human CD34hi stem cells to bone marrow stroma. J Clin Invest 90(2):358–367
Verfaillie CM (1998) Adhesion receptors as regulators of the hematopoietic process. Blood 92(8):2609–2612
Voermans C et al (1999) Increased migration of cord blood-derived CD34+ cells, as compared to bone marrow and mobilized peripheral blood CD34+ cells across uncoated or fibronectin-coated filters. Exp Hematol 27(12):1806–1814
Wang FM et al (2008) Substance P influenced gelatinolytic activity via reactive oxygen species in human pulp cells. Int Endod J 41(10):856–862
Watt SM, Forde SP (2008) The central role of the chemokine receptor, CXCR4, in haemopoietic stem cell transplantation: will CXCR4 antagonists contribute to the treatment of blood disorders? Vox Sang 94(1):18–32
Yaraee R et al (2007) The effect of substance P on nitric oxide production by HSV-1 infected macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 7(2):135–139
Zhai QL et al (2004) Short-term ex vivo expansion sustains the homing-related properties of umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Haematologica 89(3):265–273
Zheng Y et al (2003) Ex vivo manipulation of umbilical cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells with recombinant human stem cell factor can up-regulate levels of homing-essential molecules to increase their transmigratory potential. Exp Hematol 31(12):1237–1246
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the staff of Cord Blood Bank of Bone Marrow Transplantation Research Center, especially Miss Raofi, for providing the cord blood samples. We are also grateful to Dr. Mehrdad Pedram (Dept. of Medical Genetics, Tehran University of Medical Sciences) for his helpful comments and suggestions, as well as careful editing of the manuscript. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Iran National Science Foundation and Hematology, Oncology and Stem Cell Transplantation Research Center of Tehran University of medical sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahrokhi, S., Alimoghaddam, K., Ebtekar, M. et al. Effects of neuropeptide substance P on the expression of adhesion molecules in cord blood hematopoietic stem cells. Ann Hematol 89, 1197–1205 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-1006-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-1006-1