Abstract
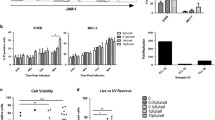
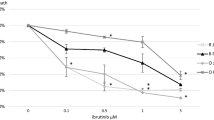
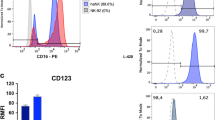
The monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) alemtuzumab (anti-CD52) and rituximab (anti-CD20) produce objective clinical responses in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). However, their mechanisms of action are not fully understood. Therefore, we investigated the mechanisms of lymphoma and CLL cell killing by two anti-CD20 antibodies (rituximab, B1) and by alemtuzumab. All antibodies induced complement-independent cell death in B-lymphoid cell lines Raji, Ramos, and Mec-1. The efficiency of cell killing was increased by the addition of human complement in Raji but not Ramos cells. Both alemtuzumab and rituximab also killed freshly isolated CLL cells, with a much stronger response for alemtuzumab (from eight of eight patients) compared to rituximab (from two of six patients). Cell morphology and Western blot analyses revealed that the antibody-induced cell death lacked some typical features of apoptosis such as chromatin condensation or poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) cleavage. Taken together, the results suggest that the tumor killing activity of these MoAbs is not only mediated by complement-mediated cytotoxicity (CDC) or antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC), but also by a nonclassic, caspase-independent apoptotic pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrd JC, Murphy T, Howard RS, Lucas MS, Goodrich A, Park K, Pearson M, Waselenko JK, Ling G, Grever MR, Grillo-Lopez AJ, Rosenberg J, Kunkel L, Flinn IW (2001) Rituximab using a thrice weekly dosing schedule in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma demonstrates clinical activity and acceptable toxicity. J Clin Oncol 19:2153–2164
Huhn D, von Schilling C, Wilhelm M, Ho AD, Hallek M, Kuse R, Knauf W, Riedel U, Hinke A, Srock S, Serke S, Peschel C, Emmerich B (2001) Rituximab therapy of patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 98:1326–1331
O’Brien SM, Kantarjian H, Thomas DA, Giles FJ, Freireich EJ, Cortes J, Lerner S, Keating MJ (2001) Rituximab dose-escalation trial in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 19:2165–2170
Byrd JC, Kitada S, Flinn IW, Aron JL, Pearson M, Lucas D, Reed JC (2002) The mechanism of tumor cell clearance by rituximab in vivo in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: evidence of caspase activation and apoptosis induction. Blood 99:1038–1043
Schulz H, Klein SK, Rehwald U, Reiser M, Hinke A, Knauf WU, Aulitzky WE, Hensel M, Herold M, Huhn D, Hallek M, Diehl V, Engert A (2002) Phase 2 study of a combined immunochemotherapy using rituximab and fludarabine in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 100:3115–3120
Keating M, Manshouri T, O’Brien S, Wierda W, Kantarjian H, Washington L, Lerner S, Albitar M (2002) A high proportion of molecular remission can be obtained with a fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab combination (FCR) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Blood 100:205a
Keating MJ, Flinn I, Jain V, Binet JL, Hillmen P, Byrd J, Albitar M, Brettman L, Santabarbara P, Wacker B, Rai KR (2002) Therapeutic role of alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) in patients who have failed fludarabine: results of a large international study. Blood 99:3554–3561
Rai KR, Freter CE, Mercier RJ, Cooper MR, Mitchell BS, Stadtmauer EA, Santabarbara P, Wacker B, Brettman L (2002) Alemtuzumab in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients who also had received fludarabine. J Clin Oncol 20:3891–3897
Schulz H, Winkler U, Staak JO, Engert A (2000) The monoclonal antibodies Campath-1h and rituximab in the therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Onkologie 23:526–532
Lundin J, Kimby E, Bjorkholm M, Broliden PA, Celsing F, Hjalmar V, Mollgard L, Rebello P, Hale G, Waldmann H, Mellstedt H, Osterborg A (2002) Phase II trial of subcutaneous anti-CD52 monoclonal antibody alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) as first-line treatment for patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Blood 100:768–773
Stashenko P, Nadler LM, Hardy R, Schlossman SF (1980) Characterization of a human B lymphocyte-specific antigen. J Immunol 125:1678–1685
Riley JK, Sliwkowski MX (2000) CD20: a gene in search of a function. Semin Oncol 27:17–24
Tedder TF, Engel P (1994) CD20: a regulator of cell-cycle progression of B lymphocytes. Immunol Today 15:450–454
O’Keefe TL, Williams GT, Davies SL, Neuberger MS (1998) Mice carrying a CD20 gene disruption. Immunogenetics 48:125–132
Xia MQ, Hale G, Lifely MR, Ferguson MA, Campbell D, Packman L, Waldmann H (1993) Structure of the CAMPATH-1 antigen, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored glycoprotein which is an exceptionally good target for complement lysis. Biochem J 293:633–640
Hale G, Xia MQ, Tighe HP, Dyer MJ, Waldmann H (1990) The CAMPATH-1 antigen (CDw52). Tissue Antigens 35:118–127
Maloney DG, Smith B, Rose A (2002) Rituximab: mechanism of action and resistance. Semin Oncol 29:2–9
Hofmeister JK, Cooney D, Coggeshall KM (2000) Clustered CD20 induced apoptosis: src-family kinase, the proximal regulator of tyrosine phosphorylation, calcium influx, and caspase 3-dependent apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol Dis 26:133–143
Shan D, Ledbetter JA, Press OW (2000) Signaling events involved in anti-CD20-induced apoptosis of malignant human B cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 48:673–683
Golay J, Zaffaroni L, Vaccari T, Lazzari M, Borleri GM, Bernasconi S, Tedesco F, Rambaldi A, Introna M (2000) Biologic response of B lymphoma cells to anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in vitro: CD55 and CD59 regulate complement-mediated cell lysis. Blood 95:3900–3908
Clynes RA, Towers TL, Presta LG, Ravetch JV (2000) Inhibitory Fc receptors modulate in vivo cytoxicity against tumor targets. Nat Med 6:443–446
Crowe JS, Hall VS, Smith MA, Cooper HJ, Tite JP (1992) Humanized monoclonal antibody CAMPATH-1H: myeloma cell expression of genomic constructs, nucleotide sequence of cDNA constructs and comparison of effector mechanisms of myeloma and Chinese hamster ovary cell-derived material. Clin Exp Immunol 87:105–110
Rowan W, Tite J, Topley P, Brett SJ (1998) Cross-linking of the CAMPATH-1 antigen (CD52) mediates growth inhibition in human B- and T-lymphoma cell lines, and subsequent emergence of CD52-deficient cells. Immunology 95:427–436
Cioca DP, Kitano K (2002) Apoptosis induction by hypercross-linking of surface antigen CD5 with anti-CD5 monoclonal antibodies in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 16:335–343
Nuessler V, Stotzer O, Gullis E, Pelka-Fleischer R, Pogrebniak A, Gieseler F, Wilmanns W (1999) Bcl-2, bax and bcl-xL expression in human sensitive and resistant leukemia cell lines. Leukemia 13:1864–1872
Shan D, Ledbetter JA, Press OW (1998) Apoptosis of malignant human B cells by ligation of CD20 with monoclonal antibodies. Blood 91:1644–1652
Kaufmann SH (1998) Cell death induced by topoisomerase-targeted drugs: more questions than answers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1400:195–211
Mathas S, Rickers A, Bommert K, Dorken B, Mapara MY (2000) Anti-CD20- and B-cell receptor-mediated apoptosis: evidence for shared intracellular signaling pathways. Cancer Res 60:7170–7176
Cross TG, Scheel-Toellner D, Henriquez NV, Deacon E, Salmon M, Lord JM (2000) Serine/threonine protein kinases and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 256:34–41
Mateo V, Lagneaux L, Bron D, Biron G, Armant M, Delespesse G, Sarfati M (1999) CD47 ligation induces caspase-independent cell death in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat Med 5:1277–1284
Drenou B, Blancheteau V, Burgess DH, Fauchet R, Charron DJ, Mooney NA (1999) A caspase-independent pathway of MHC class II antigen-mediated apoptosis of human B lymphocytes. J Immunol 163:4115–4124
Rossmann ED, Lundin J, Lenkei R, Mellstedt H, Osterborg A (2001) Variability in B-cell antigen expression: implications for the treatment of B-cell lymphomas and leukemias with monoclonal antibodies. Hematol J 2:300–306
Cardarelli PM, Quinn M, Buckman D, Fang Y, Colcher D, King DJ, Bebbington C, Yarranton G (2002) Binding to CD20 by anti-B1 antibody or F(ab′)(2) is sufficient for induction of apoptosis in B-cell lines. Cancer Immunol Immunother 51:15–24
Chan HT, Hughes D, French RR, Tutt AL, Walshe CA, Teeling JL, Glennie MJ, Cragg MS (2003) CD20-induced lymphoma cell death is independent of both caspases and its redistribution into triton X-100 insoluble membrane rafts. Cancer Res 63:5480–5489
Treon SP, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Young G, Doss D, Schlossman R, Anderson KC (2001) Tumor cell expression of CD59 is associated with resistance to CD20 serotherapy in patients with B-cell malignancies. J Immunother 24:263–271
Golay J, Lazzari M, Facchinetti V, Bernasconi S, Borleri G, Barbui T, Rambaldi A, Introna M (2001) CD20 levels determine the in vitro susceptibility to rituximab and complement of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: further regulation by CD55 and CD59. Blood 98:3383–3389
Weng WK, Levy R (2001) Expression of complement inhibitors CD46, CD55, and CD59 on tumor cells does not predict clinical outcome after rituximab treatment in follicular non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 98:1352–1357
Bannerji R, Kitada S, Flinn IW, Pearson M, Young G, Reed JC, Byrd JC (2003) Apoptotic-regulatory and complement-protecting protein expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: relationship to in vivo Rituximab resistance. J Clin Oncol 21:1466–1471
Anderson DR, Grillo-Lopez A, Vams C, Chambers KS, Hanna N (1997) Targeted anti-cancer therapy using rituximab, a chimeric anti-CD20 antibody (IDEC-C2B8) in the treatment of non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma. Biochem Soc Trans 25:705–708
van der Kolk LE, Grillo-Lopez AJ, Baars JW, Hack CE, van Oers MH (2001) Complement activation plays a key role in the side-effects of rituximab treatment. Br J Haematol 115:807–811
Cragg MS, Glennie MJ (2004) Antibody specificity controls in vivo effector mechanisms of anti-CD20. Blood 103:2738–2743
van der Kolk LE, Evers LM, Omene C, Lens SM, Lederman S, van Lier RA, van Oers MH, Eldering E (2002) CD20-induced B cell death can bypass mitochondria and caspase activation. Leukemia 16:1735–1744
Lesage S, Steff AM, Philippoussis F, Page M, Trop S, Mateo V, Hugo P (1997) CD4+CD8+ thymocytes are preferentially induced to die following CD45 cross-linking, through a novel apoptotic pathway. J Immunol 159:4762–4771
Bellosillo B, Villamor N, Lopez-Guillermo A, Marce S, Esteve J, Campo E, Colomer D, Montserrat E (2001) Complement-mediated cell death induced by rituximab in B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders is mediated in vitro by a caspase-independent mechanism involving the generation of reactive oxygen species. Blood 98:2771–2777
Stanglmaier M, Reis S, Hallek M (2000) Stimulation of programmed cell death (PCD) and tyrosine kinases by monoclonal antibodies against CD20 and CD52 in B-CLL cells and B-cell lines in vitro. Blood 96:160a
Pedersen IM, Buhl AM, Klausen P, Geisler CH, Jurlander J (2002) The chimeric anti-CD20 antibody rituximab induces apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells through a p38 mitogen activated protein-kinase-dependent mechanism. Blood 99:1314–1319
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanglmaier, M., Reis, S. & Hallek, M. Rituximab and alemtuzumab induce a nonclassic, caspase-independent apoptotic pathway in B-lymphoid cell lines and in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Ann Hematol 83, 634–645 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-004-0917-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-004-0917-0