Abstract
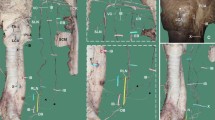
The one- or two-headed arrangement of the lateral pterygoid m. (LPM) was analysed by studying the motor nerve distribution within the muscular tissue. In all subjects, the main innervation of the lateral pterygoid m. came from the anterior trunk of the mandibular n. by one to three nerves. These nerves divided into five or six vertical branches which ramified into parallel horizontal tiny fibers. Consequently, the lateral pterygoid m. appeared to be divided into oblique sagittal planes and horizontal layers by the nerve branches, reflecting the multipennate organisation of the muscle. These layers can be selectively recruited during mandibular movements, ensuing a fine medial-lateral control. According to its nerve supply, the LPM has to be considered as a single unit made of independent functional musulo-aponeurotic layers even though its morphologic conformation is in one, two or three heads.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foucart, J.M., Girin, J.P. & Carpentier, P. Innervation of the human lateral pterygoid muscle. Surg Radiol Anat 20, 185–189 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-998-0185-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-998-0185-0