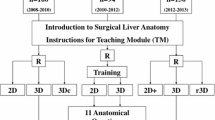
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of the Hisense computer-assisted surgery system (CAS) in teaching pediatric liver surgical anatomy.
Methods
The research subjects were residents who underwent standardized training at the Department of Pediatric Surgery at Yijishan Hospital of Wannan Medical College from May 2022 to May 2023.
Results
The study recruited a total of 62 students, with 31 students assigned to the Hisense CAS group (12 males and 19 females) and the remaining 31 students serving as controls (Control group, 15 males and 16 females). There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics observed between the two groups. This study found that the average scores of the Hisense CAS teaching group in the liver surgery evaluations were higher than those of the control group. Specifically, the Hisense CAS group had an average score of 84.25 ± 5.70 points in the liver surgery knowledge test, 77.10 ± 8.12 points in the image reading test, and 70.58 ± 8.79 points in the surgical simulation test, while the traditional teaching group had average scores of 73.45 ± 6.12 points, 69.81 ± 6.05 points, and 66.42 ± 6.61 points, respectively; the differences between the two groups were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Furthermore, this study also found that the Hisense CAS teaching model resulted in significantly better teaching satisfaction on the part of the residents in terms of standardized teaching for physicians in pediatric liver surgical anatomy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study demonstrated greater satisfaction of the residents with the use of 3D reconstruction added to traditional teaching sessions and better performance during the posttraining evaluation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The descriptive quantitative and qualitative data results to support the fndings of this study are included within the article. Full datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CAS:
-
Computer-assisted surgery system
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
References
Fang C, Zhang P, Qi X (2019) Digital and intelligent liver surgery in the new era: prospects and dilemmas. EBioMedicine 41:693–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.017
Fang CH, Zhang P, Zhou WP, Zhou J, Dai CL, Liu JF, Jia WD, Liang X, Zeng SL, Wen S (2020) Efficacy of three-dimensional visualization technology in the precision diagnosis and treatment for primary liver cancer: a retrospective multicenter study of 1 665 cases in China. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 58:375–382. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20200220-00105
Fischer L, Thorn M, Neumann JO, Schobinger M, Heimann T, Grenacher L, Meinzer HP, Friess H, Buchler MW (2005) The segments of the hepatic veins-is there a spatial correlation to the Couinaud liver segments? Eur J Radiol 53:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.02.003
Gao Y, Hu J, Zhang X, Zhang M, Wang D, Zheng X, Liu S, Lu Y (2019) Use of Hisense computer-assisted surgery system enhances infrapyloric lymph node dissection for gastric cancer. J Surg Res 242:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2019.04.019
Gavriilidis P, Edwin B, Pelanis E, Hidalgo E, De’Angelis N, Memeo R, Aldrighetti L, Sutcliffe RP (2022) Navigated liver surgery: state of the art and future perspectives. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 21:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbpd.2021.09.002
Geller DA, Tohme S (2021) Liver anatomy quiz: test your knowledge. J Gastrointest Surg 25:1093–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-020-04582-x
Ichida H, Imamura H, Yoshioka R, Mizuno T, Mise Y, Kuwatsuru R, Kawasaki S, Saiura A (2021) Re-evaluation of the Couinaud classification for segmental anatomy of the right liver, with particular attention to the relevance of cranio-caudal boundaries. Surgery 169:333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2020.08.029
Kong X, Nie L, Zhang H, Wang Z, Ye Q, Tang L, Huang W, Li J (2016) Do 3D printing models improve anatomical teaching about hepatic segments to medical students? A randomized controlled study. World J Surg 40:1969–1976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-016-3541-y
Kong X, Nie L, Zhang H, Wang Z, Ye Q, Tang L, Li J, Huang W (2016) Do three-dimensional visualization and three-dimensional printing improve hepatic segment anatomy teaching? A randomized controlled study. J Surg Educ 73:264–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsurg.2015.10.002
Li X, Duan R, He Y, Qin J, Liu R, Dai S, Zhou J, Zeng X, Duan J, Gao P, Yang X, Li C (2022) Application of three-dimensional visualization technology in the anatomical variations of hilar bile ducts in Chinese population. Front Surg 9:934183. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2022.934183
Liu H, Wang F, Liu B, Zheng Z, Zhao J, Zhang J (2021) Application of three-dimensional reconstruction with a Hisense computer-assisted system in upper pancreatic lymph node dissection during laparoscopic-assisted radical gastrectomy. Asian J Surg 44:730–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asjsur.2020.12.034
Liu J, Xiu W, Duan G, Dong Q (2022) Application of 3D simulation software in chemotherapy and hepatoblastoma surgery in children. Front Surg 9:908381. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2022.908381
Liu Y, Xia N, Duan Y, Wu X, Zhao C, Jin C, Chen X, Gao Q, Wang Y, Wang F, Wang F, Chen Y, Dong Q, Hao X (2023) Application of computer-assisted surgery in pediatric mediastinal tumor surgery. Int J Med Robot 19:e2489. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.2489
Mojtahed A, Nunez L, Connell J, Fichera A, Nicholls R, Barone A, Marieiro M, Puddu A, Arya Z, Ferreira C, Ridgway G, Kelly M, Lamb HJ, Caseiro-Alves F, Brady JM, Banerjee R (2022) Repeatability and reproducibility of deep-learning-based liver volume and Couinaud segment volume measurement tool. Abdom Radiol (NY) 47:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03262-x
Nickel F, Hendrie JD, Bruckner T, Kowalewski KF, Kenngott HG, Muller-Stich BP, Fischer L (2016) Successful learning of surgical liver anatomy in a computer-based teaching module. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11:2295–2301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1354-y
Patra A, Asghar A, Chaudhary P, Ravi KS (2022) Integration of innovative educational technologies in anatomy teaching: new normal in anatomy education. Surg Radiol Anat 44:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02868-6
Salazar D, Thompson M, Rosen A, Zuniga J (2022) Using 3D printing to improve student education of complex anatomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Med Sci Educ 32:1209–1218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40670-022-01595-w
Shahbaz M, Miao H, Farhaj Z, Gong X, Weikai S, Dong W, Jun N, Shuwei L, Yu D (2023) Mixed reality navigation training system for liver surgery based on a high-definition human cross-sectional anatomy data set. Cancer Med 12:7992–8004. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.5583
Su L, Zhou XJ, Dong Q, Zhang H, Shen F, Chen YJ, Hao XW, Li XF (2015) Application value of computer assisted surgery system in precision surgeries for pediatric complex liver tumors. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:18406–18412
Xiu W, Liu J, Li T, Hao X, Liu H, Xia N, Duan Y, Jiang Z, Shang C, Dong Q (2021) Application value of computer-assisted surgery system in pediatric hepatic hemangioma. Pediatr Surg Int 37:1575–1583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-021-04972-5
Yang X, Wang H, Dong B, Hu B, Hao X, Chen X, Zhao J, Dong Q, Zhu C (2021) Standard liver volume-predicting formulae derived from normal liver volume in children under 18 years of age. Front Pediatr 9:629645. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.629645
Zhao J, Zhou XJ, Zhu CZ, Wu Y, Wei B, Zhang G, Hao XW, Zhang H, Jiang Z, Dong Q (2017) 3D simulation assisted resection of giant hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma in children. Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon) 22:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/24699322.2017.1358401
Zygomalas A, Kehagias I (2019) Up-to-date intraoperative computer assisted solutions for liver surgery. World J Gastrointest Surg 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v11.i1.1
Acknowledgements
We thank all the researchers who participated in this study.
Funding
This study was funded by the Anhui provincial Department of Education university research project (Grant No. 2023AH051763), Talent Introduction Fund of Yijishan Hospital of Wannan Medical College (Grant No. YR202203), the Scientific Research Project of Wannan Medical College (Grant No. WK2022ZF08), the Teaching quality and teaching reform project of Wannan Medical College (Grant No. 2022xnfz09), the Applied basic research project of Science and Technology Bureau of Wuhu City (Grant No. 2023jc25). The funders had no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript. JL, WX, and AL contributed equally to this paper. JL, NX, and QD designed the research, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript; GD, NJ, FW, and BW analyzed and interpreted the data, JL, NX, FW, and QD designed the research, analyzed the data, and corrected the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no confict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional Scientifc Committee (IRB) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Yijishan Hospital, Wannan Medical College (No. LLSC-2022-065), and written consent was obtained from the parents of the children.
Consent for publication
All the authors gave consent for the publication of the report.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Xiu, W., Lin, A. et al. Can Hisense computer-assisted surgery system (Hisense CAS) improve anatomy teaching in pediatric liver surgery?. Surg Radiol Anat 46, 117–124 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03277-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03277-7