Abstract
Purpose
According to the anthropological importance of soft facial tissue thickness parameters, we aimed to find the association of these parameters with Lur and Arab ethnicities, gender and body mass index (BMI). Structural equation modeling (SEM) was used.
Methods
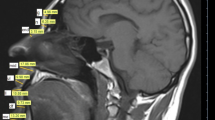
As a secondary analysis, SEM was performed on a dataset of 100 participants. The participants were from Lur and Arab populations of Ahvaz province, Iran, from those who referred for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) due to headache.
Results
Multivariate regression illustrated that mental eminence (ME), chain-lip fold (CLF) and end of nasals (END) could not be predicted by the independent variables (p > 0.05). Right masseteric region (RMST) had the maximum predictability with R2 = 0.365, followed by middle philtrum (MID) with R2 = 0.358 (p < 0.001). With respect to our criterion to enter SEM, i.e. existing at least two significant covariates at significance level of 0.05, among staying parameters, only parameters of nasion (NA), MID, superior lip (SL), RMST and left masseteric region (LMST) remained. Among these cases, MID was the only parameter that its three covariates illustrated significant association.
Conclusion
MID parameter can be predicted by gender, BMI and Arab ethnicity. By carrying out such studies and creating database, such information can be used in plastic surgery, corpse identification, and facial reconstruction software in archeology.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data are available by the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ayoub F, Saadeh M, Rouhana G, Haddad R (2019) Midsagittal facial soft tissue thickness norms in an adult Mediterranean population. Forensic Sci Int 294:217 (e211–217. e217)
Baillie LJ, Mirijali SA, Niven BE, Blyth P, Dias GJ (2015) Ancestry and BMI influences on facial soft tissue depths for a cohort of Chinese and Caucasoid women in Dunedin, New Zealand. J Forensic Sci 60:1146–1154
Briers N, Steyn M (2018) Re-assessment of South African juvenile facial soft tissue thickness data for craniofacial approximation: A comparative analysis using central tendency statistics. Forensic Sci Int 291:280 (e281–280. e213)
Codinha S (2009) Facial soft tissue thicknesses for the Portuguese adult population. Forensic Sci Int 184:80 (e81–80. e87)
De Greef S, Claes P, Vandermeulen D, Mollemans W, Suetens P, Willems G (2006) Large-scale in-vivo Caucasian facial soft tissue thickness database for craniofacial reconstruction. Forensic Sci Int 159(Suppl 1):S126-146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2006.02.034
De Greef S, Vandermeulen D, Claes P, Suetens P, Willems G (2009) The influence of sex, age and body mass index on facial soft tissue depths. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 5:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-009-9085-9
De Greef S, Willems G (2005) Three-dimensional cranio-facial reconstruction in forensic identification: latest progress and new tendencies in the 21st century. J Forensic Sci 50:12–17
Domaracki M, Stephan CN (2006) Facial soft tissue thicknesses in Australian adult cadavers. J Forensic Sci 51:5–10
Dong Y, Huang L, Feng Z, Bai S, Wu G, Zhao Y (2012) Influence of sex and body mass index on facial soft tissue thickness measurements of the northern Chinese adult population. Forensic Sci Int 222:396.e391-397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2012.06.004
Eftekhari-Moghadam AR, Latifi SM, Nazifi HR, Rezaian J (2020) Influence of sex and body mass index on facial soft tissue thickness measurements in an adult population of southwest of Iran. Surg Radiol Anat 42:1–7
El-Mehallawi IH, Soliman EM (2001) Ultrasonic assessment of facial soft tissue thicknesses in adult Egyptians. Forensic Sci Int 117:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0379-0738(00)00453-9
Fan Y, Chen J, Shirkey G, John R, Wu SR, Park H, Shao C (2016) Applications of structural equation modeling (SEM) in ecological studies: an updated review. Ecol Process 5:1–12
Ferrario VF, Sforza C (1997) Size and shape of soft-tissue facial profile: effects of age, gender, and skeletal class. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 34:498–504. https://doi.org/10.1597/1545-1569_1997_034_0498_sasost_2.3.co_2
Grabherr S, Baumann P, Minoiu C, Fahrni S, Mangin P (2016) Post-mortem imaging in forensic investigations: current utility, limitations, and ongoing developments. Res Rep Forensic Med Sci 6:25–37
Johari M, Esmaeili F, Hamidi H (2017) Facial Soft Tissue Thickness of Midline in an Iranian Sample: MRI Study. Open Dent J 11:375–383. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874210601711010375
Kim K-D, Ruprecht A, Wang G, Lee JB, Dawson DV, Vannier MW (2005) Accuracy of facial soft tissue thickness measurements in personal computer-based multiplanar reconstructed computed tomographic images. Forensic Sci Int 155:28–34
Kotrashetti VS, Mallapur MD (2016) Radiographic assessment of facial soft tissue thickness in South Indian population–An anthropologic study. J Forensic Leg Med 39:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jflm.2016.01.032
Ramesh G, Nagarajappa R, Sreedhar G, Sumalatha MN (2015) Facial soft tissue thickness in forensic facial reconstruction: Is it enough if norms set? J Forensic Res 6:1
Rashidvash V (2013) A comparative study of the race of people in Azerbaijan (atropatene) and Turks and Turkman in Iran. Int J Hum Soc Sci 2:220–230
Rhine JS, Campbell HR (1980) Thickness of facial tissues in American blacks. J Forensic Sci 25:847–858
Saadeh M, Fayyad-Kazan H, Haddad R, Ayoub F (2020) Facial soft tissue thickness differences among different vertical facial patterns. Forensic Sci Int 317:110468
Sahni D, Jit I, Gupta M, Singh P, Suri S, Sanjeev K (2002) Preliminary study on facial soft tissue thickness by magnetic resonance imaging in Northwest Indians. Forensic Sci Commun 4
Sahni D, Sanjeev SG, Jit I, Singh P (2008) Facial soft tissue thickness in northwest Indian adults. Forensic Sci Int 176:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2007.07.012
Sandamini H, Jayawardena A, Batuwitage L, Rajapakse R, Karunaratna D, Vidanapathirana M, Pallewatte A (2018) Facial soft tissue thickness trends for selected age groups of Sri Lankan adult population. Forensic Sci Int 293:102 (e101-102. e111)
Shahsavar F, Varzi AM, Ahmadi SA (2017) A genomic study on distribution of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A and HLA-B alleles in Lak population of Iran. Genom Data 11:3–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gdata.2016.11.012
Somos CP, Rea PM, Shankland S, Kranioti EF (2019) Medical imaging and facial soft tissue thickness studies for forensic craniofacial approximation: a pilot study on modern Cretans. Adv Exp Med Biol 1138:71–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-14227-8_6
Toneva D, Nikolova S, Georgiev I, Harizanov S, Zlatareva D, Hadjidekov V, Lazarov N (2018) Facial soft tissue thicknesses in Bulgarian adults: relation to sex, body mass index and bilateral asymmetry. Folia Morphol 77:570–582. https://doi.org/10.5603/FM.a2017.0114
Utsuno H, Kageyama T, Deguchi T, Umemura Y, Yoshino M, Nakamura H, Miyazawa H, Inoue K (2007) Facial soft tissue thickness in skeletal type I Japanese children. Forensic Sci Int 172:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2007.01.004
Wilkinson C (2004) Forensic facial reconstruction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Acknowledgements
The present study has been approved by the Student Research Committee of Lorestan University of Medical Sciences with the number 2124. We thank Vice-Chancellor for Research and Technology.
Funding
Lorestan University of Medical Sciences with grant number 2124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MJ Nourmohammadi: data management, data analysis, and manuscript writing. SAY Ahmadi: protocol/project development, interpretation, and manuscript writing. J Rezaian: protocol/project development and manuscript editing. All the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Lorestan University of Medical Sciences with the code IR.LUMS.REC.1400.219. As a secondary analysis, there was no direct human or animal subject.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication had been obtained in the primary study done before.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nourmohammadi, M.J., Ahmadi, S.A.Y. & Rezaian, J. Structural equation modelling to estimate facial soft tissue thickness parameters based on ethnicity, gender and body mass index: a secondary study on an Iranian dataset. Surg Radiol Anat 45, 739–746 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03147-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03147-2