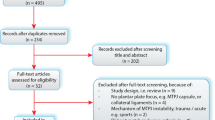
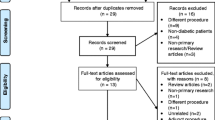
Abstract
Purpose
The aims of this review were to form a more precise description for Master Knot of Henry (MKH), and to modify classifications related to interconnections between flexor hallucis longus (FHL) and flexor digitorum longus (FDL) for showing all configurations in the literature.
Methods
A literature search was performed in main databases to obtain information related to anatomical definitions and variations of MKH. The search was carried out using the following keywords: “Master Knot of Henry”, “Chiasma plantare”, “Flexor hallucis longus” and “Flexor digitorum longus”. Information extracted from the studies was: sample size, numerical values, classifications, variation types, incidence of types, anatomical definitions of MKH, year of publication, and type of study.
Results
This study proposes that MKH should be defined as the intersection territory where FDL crosses over FHL in the plantar foot. The postchiasmatic plantar area located at distal to MKH (the narrow space between MKH and the division of FDL) should be termed as the triangle of Henry. Moreover, the classification systems showing different configurations related to interconnections situated at Henry’s triangle were updated as eight types to present all forms in the literature.
Conclusion
Our definitions may assist in determining the precise anatomical boundaries of MKH, and thus facilitate the use of MKH as a surgical landmark. In addition, our modified classification systems covering all variations in the current literature may be helpful for surgeons and anatomists to understand formations of the triangle of Henry, and the long flexor tendons of the lesser toes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MKH:
-
Master Knot of Henry
- FHL:
-
Flexor hallucis longus
- FDL:
-
Flexor digitorum longus
- QP:
-
Quadratus plantae
- CP:
-
Chiasma plantare
- MPN:
-
Medial plantar nerve
- LPN:
-
Lateral plantar nerve
- US:
-
Ultrasonography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Ali S, Griffin NL, Ellis W, Meyr AJ (2017) Communication of contrast in the flexor hallucis longus tendon with other pedal tendons at the master knot of Henry. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 107:166–170
Amlang M, Rosenow MC, Friedrich A, Zwipp H, Rammelt S (2012) Direct plantar approach to Henry’s knot for flexor hallucis longus transfer. Foot Ankle Int 33:7–13
Andrade LS, Joseph JJ, Bhat NP, Shetty A, Kalthur SG, Prasanna LC (2021) A histological study on the tendons at chiasma plantare in pes cavus. Morphologie 105:54–63
Athavale SA, Geetha GN, Swathi, (2012) Morphology of flexor digitorum accessorius muscle. Surg Radiol Anat 34:367–372
Bai D, Kurokawa H, Morita S, Miyamoto T, Mahakkanukrauh P, Tanaka Y (2021) Ultrasonographic test for detecting the chiasma plantare formation between the flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus. Surg Radiol Anat 43:1061–1065
Beger O, Elvan Ö, Keskinbora M, Ün B, Uzmansel D, Kurtoğlu Z (2018) Anatomy of master knot of Henry: a morphometric study on cadavers. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 52:134–142
Beger O, Tumentemür G, Uzun C et al (2019) Biomechanical and morphometric properties of the long flexor tendons of the toes: a cadaver study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 109:282–290
Borton DC, Lucas P, Jomha NM, Cross MJ, Slater K (1998) Operative reconstruction after transverse rupture of the tendons of both peroneus longus and brevis. Surgical reconstruction by transfer of the flexor digitorum longus tendon. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80:781–784
Collins MS, Tiegs-Heiden CA, Frick MA (2020) MRI appearance of jogger’s foot. Skeletal Radiol 49:1957–1963
Coull R, Flavin R, Stephens MM (2003) Flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer: evaluation of postoperative morbidity. Foot Ankle Int 24:931–934
Den Hartog BD (2003) Flexor hallucis longus transfer for chronic Achilles tendonosis. Foot Ankle Int 24:233–237
Donovan A, Rosenberg ZS, Bencardino JT et al (2013) Plantar tendons of the foot: MR imaging and US. Radiographics 33:2065–2085
Edama M, Kubo M, Onishi H et al (2016) Anatomical study of toe flexion by flexor hallucis longus. Ann Anat 204:80–85
Edama M, Takabayashi T, Inai T et al (2019) The relationships between the quadratus plantae and the flexor digitorum longus and the flexor hallucis longus. Surg Radiol Anat 41:689–692
Elvan Ö, Beger O, Karagül Mİ, Uzmansel D, Yılmaz NŞ, Olgunus ZK (2019) Anatomic and histological analyses of chiasma plantare and long flexor tendons of the foot on human fetuses. Surg Radiol Anat 41:775–784
Goss DA Jr, Halverson A, Philbin TM, Bull PE (2019) Minimally invasive retrograde method of harvesting the flexor hallucis longus tendon: a cadaveric study. Foot Ankle Int 40:1214–1218
Hahn F, Maiwald C, Horstmann T, Vienne P (2008) Changes in plantar pressure distribution after Achilles tendon augmentation with flexor hallucis longus transfer. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 23:109–116
Hahn F, Meyer P, Maiwald C, Zanetti M, Vienne P (2008) Treatment of chronic Achilles tendinopathy and ruptures with flexor hallucis tendon transfer: clinical outcome and MRI findings. Foot Ankle Int 29:794–802
Hayes C (2009) Henry, Arnold Kirkpatrick. In: Dictionary of Irish Biography. Cambridge UP and the Royal Irish Academy. Available via DIALOG. http://dib.cambridge.org
Henry AK (1970) Extensile exposure, 2nd edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Herbst SA, Miller SD (2006) Transection of the medial plantar nerve and hallux cock-up deformity after flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer for Achilles tendinitis: case report. Foot Ankle Int 27:639–641
Hirota K, Watanabe K, Saito Y, Katayose M (2020) Flexor hallucis longus tendon branch test: Development and validation of a new method to assess anatomical variation of the tendinous slip. Foot Ankle Surg 26:607–613
Hirota K, Watanabe K, Teramoto A, Saito Y, Katayose M (2020) Flexor hallucis longus tendinous slips and the relationship to toe flexor strength. Foot Ankle Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fas.2020.11.002
Hur MS, Kim JH, Woo JS, Choi BY, Kim HJ, Lee KS (2011) An anatomic study of the quadratus plantae in relation to tendinous slips of the flexor hallucis longus for gait analysis. Clin Anat 24:768–773
Kaushal P, Banerjee A, Dhar P (2017) Knot of Henry: role in tendon transfer. J Clin Diagn Res 11:AD01–AD02
LaRue BG, Anctil EP (2006) Distal anatomical relationship of the flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus tendons. Foot Ankle Int 27:528–532
Le Double AF (1897) Traité des variations de système musculaire de l’homme etde leur signification au point de vue de l’anthropologie zoologique. SchleicherFrères, Paris
Lewis OJ (1962) The comparative morphology of m. flexor accessorius and the associated long flexor tendons. J Anat 96:321–333
Lui TH, Chow FY (2011) “Intersection syndrome” of the foot: treated by endoscopic release of master knot of Henry. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:850–852
Mao H, Shi Z, Wapner KL, Dong W, Yin W, Xu D (2015) Anatomical study for flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer in treatment of Achilles tendinopathy. Surg Radiol Anat 37:639–647
Martin BF (1964) Observations on the muscles and tendons of the medial aspect of the sole of the foot. J Anat 98:437–453
Morimoto I, Hirata K (1988) How many toes does the human flexor hallucis longus muscle flex? St Marianna Med J 26:7–10
Mulier T, Rummens E, Dereymaeker G (2007) Risk of neurovascular injuries in flexor hallucis longus tendon transfers: an anatomic cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int 28:910–915
Murphy RL, Womack JW, Anderson T (2010) Technique tip: a new technique for harvest of the flexor hallucis longus tendon. Foot Ankle Int 31:457–459
Myerson MS, Badekas A, Schon LC (2004) Treatment of stage II posterior tibial tendon deficiency with flexor digitorum longus tendon transfer and calcaneal osteotomy. Foot Ankle Int 25:445–450
O’Sullivan E, Carare-Nnadi R, Greenslade J, Bowyer G (2005) Clinical significance of variations in the interconnections between flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus in the region of the knot of Henry. Clin Anat 18:121–125
Obituary, (1962) Arnold Kirkpatrick Henry. Lancet 279:811
Obituary (1962) Arnold Kirkpatrick Henry. Br Med J 1:1281
Oddy MJ, Flowers MJ, Davies MB (2010) Flexor digitorum longus tendon exposure for flatfoot reconstruction: a comparison of two methods in a cadaveric model. J Foot Ankle Surg 16:87–90
Panchbhavi VK, Yang J, Vallurupalli S (2008) Minimally invasive method of harvesting the flexor digitorum longus tendon: a cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int 29:42–48
Panchbhavi VK, Yang J, Vallurupalli S (2008) Surgical anatomy for a new minimally invasive approach to the flexor digitorum longus tendon: a cadaver study. J Foot Ankle Surg 14:16–20
Park DH, Gill IR, Solan MC (2013) Flexor digitorum longus tendon harvest length utilising a limited operative exposure: a cadaveric study. J Foot Ankle Surg 19:53–55
Plaass C, Abuharbid G, Waizy H, Ochs M, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Schmiedl A (2013) Anatomical variations of the flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus in the chiasma plantare. Foot Ankle Int 34:1580–1587
Pretterklieber B (2018) Morphological characteristics and variations of the human quadratus plantae muscle. Ann Anat 216:9–22
Pretterklieber B (2017) The high variability of the chiasma plantare and the long flexor tendons: anatomical aspects of tendon transfer in foot surgery. Ann Anat 211:21–32
Rajakulasingam R, Murphy J, Panchal H, James SL, Botchu R (2019) Master knot of Henry revisited: a radiologist’s perspective on MRI. Clin Radiol 74:972.e1-972.e8
Richardson DR, Willers J, Cohen BE, Davis WH, Jones CP, Anderson RB (2009) Evaluation of the hallux morbidity of single-incision flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer. Foot Ankle Int 30:627–630
Schulze FE (1867) Die Sehnenverbindung in der Planta des Menschen und der Säugethiere. Z wisschensch Zoologie 17:1–22
Spratley EM, Arnold JM, Owen JR, Glezos CD, Adelaar RS, Wayne JS (2013) Plantar forces in flexor hallucis longus versus flexor digitorum longus transfer in adult acquired flatfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 34:1286–1293
Tashjian RZ, Hur J, Sullivan RJ, Campbell JT, DiGiovanni CW (2003) Flexor hallucis longus transfer for repair of chronic achilles tendinopathy. Foot Ankle Int 24:673–676
Thomas D, Thordarson D, Nelson TJ, Charlton TP, Eberlein S, Metzger MF (2020) Knot of Henry variation and the effect on plantar flexion strength. Foot Ankle Int 41:94–100
Trnka HJ (2004) Dysfunction of the tendon of tibialis posterior. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:939–946
Turner W (1865) On variability in human structure, with illustrations, from the flexor muscles of the fingers and toes. Trans R Soc Edinb Earth Sci 24:175–189
Vasudha TK, Vani PC, Sankaranarayanan G, Rajasekhar SSSN, Dinesh Kumar V (2019) Communications between the tendons of flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus: a cadaveric study. Surg Radiol Anat 41:1411–1419
Wan-Ae-Loh P, Danginthawat P, Huanmanop T, Agthong S, Chentanez V (2021) Surface localisation of master knot of Henry, in situ and ex vivo length of flexor hallucis longus tendon: pertinent data for tendon harvesting and transfer. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 80:415–424
Wapner KL, Hecht PJ, Shea JR, Allardyce TJ (1994) Anatomy of second muscular layer of the foot: considerations for tendon selection in transfer for Achilles and posterior tibial tendon reconstruction. Foot Ankle Int 15:420–423
Wapner KL, Taras JS, Lin SS, Chao W (2006) Staged reconstruction for chronic rupture of both peroneal tendons using Hunter rod and flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer: a long-term follow up study. Foot Ankle Int 27:591–597
Winckler G, Gianoli G (1955) La véritable terminaison de la chair carrée de Sylvius (musc. quadratus plantae). Arch Anat Histol Embryol 38:47–66
Wood J (1868) Variations in human myology observed during the winter session of 1867–68 at King’s College London. Proc R Soc London 16:483–525
Zhao XY, Zhao HW, Yu M et al (2019) Anatomical study of the compositions and internal connections of the chiasma plantare (master knot of Henry): exploring its possible clinical impact. J Foot Ankle Surg 58:1235–1244
Funding
This review did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OB, FS, Rİ, ESÇ, AÖ, and MK: project development, data collection, manuscript writing, and manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beger, O., Çalışır, E.S., Sevmez, F. et al. Arnold Kirkpatrick Henry (1886–1962) and his eponym (Master Knot of Henry): a narrative review. Surg Radiol Anat 44, 157–168 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02847-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02847-x