Abstract
Purpose
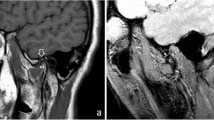
According to the functional matrix theory, the development of maxillomandibular complex may be affected by the surrounding tissues. The aim of this study was to evaluate the length and angulation of the styloid process in different types of malocclusions using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
Angulations and length of the styloid process were evaluated in CBCT images of 97 individuals retrospectively. The patients were classified as class I, II, and III groups according to sagittal skeletal classes. The mean length, anterior angulation, and medial angulation of the styloid process were analyzed. Statistical significance was evaluated at p < 0.05.
Results
The mean styloid process length in group class III was found to be significantly longer than class I (p: 0.035). Anterior angle was significantly higher in class III group than in other groups (p < 0.05). No statistically significant difference was found in medial angle between the groups (p: 0.506).
Conclusion
According to present findings, class III malocclusion is associated with the stylohyoid complex morphology due to longer styloid process lengths and higher anterior angle values.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ab Rahman S, Takeuchi K, Ohno Y, bt Ismar FNF, Sugita Y, Maeda H, Alam MK (2018) Comparison between 2D and 3D measurement of styloid process length. J Hard Tissue Biol 27:51–54
Baccetti T, Reyes BC, McNamara JA Jr (2005) Gender differences in class III malocclusion. Angle Orthod 75:510–520
Basekim CC, Mutlu H, Gungor A, Silit E, Pekkafali Z, Kutlay M, Colak A, Ozturk E, Kizilkaya E (2005) Evaluation of styloid process by three-dimensional computed tomography. Eur Radiol 15:134–139
Bastir M, Rosas A (2006) Correlated variation between the lateral basicranium and the face: a geometric morphometric study in different human groups. Arch Oral Biol 51:814–824
Buyuk C, Gunduz K, Avsever H (2018) Morphological assessment of the stylohyoid complex variations with cone beam computed tomography in a Turkish population. Folia Morphol 77:79–89
Carlson DS (2005) Theories of craniofacial growth in the postgenomic era. Semin Orthod 11:172–183
Colby CC, Del Gaudio JM (2011) Stylohyoid complex syndrome: a new diagnostic classification. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:248–252
de Andrade KM, Rodrigues CA, Watanabe PC, Mazzetto MO (2012) Styloid process elongation and calcification in subjects with tmd: clinical and radiographic aspects. Braz Dent J 23:443–450
Deljo E, Filipovic M, Babacic R, Grabus J (2012) Correlation analysis of the hyoid bone position in relation to the cranial base, mandible and cervical part of vertebra with particular reference to bimaxillary relations/teleroentgenogram analysis. Acta Inform Med 20:25–31
Dibbets J (1996) Morphological associations between the angle classes. Eur J Orthod 18:111–118
Eagle WW (1962) The symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of the elongated styloid process. Am Surg 28:1–5
Esenlik E, Plana NM, Grayson BH, Flores RL (2017) Cephalometric predictors of clinical severity in Treacher Collins syndrome. Plast Reconstr Surg 140:1240–1249
Icen M, Orhan K, Oz U, Horasan S, Avsever H (2020) Relationship between pterygomaxillary fissure morphology and maxillary/mandibular position: a cone beam computed tomography assessment. J Orofac Orthop. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00056-019-00215-4
İlgüy D, İlgüy M, Fişekçioğlu E, Dölekoğlu S (2013) Assessment of the stylohyoid complex with cone beam computed tomography. Iran J Radiol 10:21–26
Jena AK, Duggal R (2011) Hyoid bone position in subjects with different vertical jaw dysplasias. Angle Orthod 81:81–85
Jung T, Tschernitschek H, Hippen H, Schneider B, Borchers L (2004) Elongated styloid process: when is it really elongated? Dentomaxillofac Radiol 33:119–124
Kim JH, Arita ES, Pinheiro LR, Yoshimoto M, Watanabe PCA, Cortes ARG (2018) Computed tomographic artifacts in maxillofacial surgery. J Craniofac Surg 29:e78–e80
Kosar MI, Atalar MH, Sabanciogullari V, Tetiker H, Erdil FH, Cimen M, Otag I (2011) Evaluation of the length and angulation of the styloid process in the patient with pre-diagnosis of Eagle syndrome. Folia Morphol 70:295–299
Kursoglu P, Unalan F, Erdem T (2005) Radiological evaluation of the styloid process in young adults resident in Turkey’s Yeditepe University faculty of dentistry. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 100:491–494
Marsan G, Oztas E, Cura N, Kuvat SV, Emekli U (2010) Changes in head posture and hyoid bone position in Turkish class III patients after mandibular setback surgery. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 38:113–121
Moss ML (1997) The functional matrix hypothesis revisited. 1. The role of mechanotransduction. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 112:8–11
Moss ML (1997) The functional matrix hypothesis revisited. 2. The role of an osseous connected cellular network. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 112:221–226
Okur A, Özkırış M, Serin HI, Gencer ZK, Karaçavuş S, Karaca L, Kantarcı M, Saydam L (2014) Is there a relationship between symptoms of patients and tomographic characteristics of styloid process? Surg Radiol Anat 36:627–632
Onbas O, Kantarci M, Murat Karasen R, Durur I, Cinar Basekim C, Alper F, Okur A (2005) Angulation, length, and morphology of the styloid process of the temporal bone analyzed by multidetector computed tomography. Acta Radiol 46:881–886
Oz U, Orhan K, Aksoy S, Ciftci F, Özdoğanoğlu T, Rasmussen F (2016) Association between pterygoid hamulus length and apnea hypopnea index in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a combined three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography and polysomnographic study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 121:330–339
Oztunc H, Evlice B, Tatli U, Evlice A (2014) Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation of styloid process: a retrospective study of 208 patients with orofacial pain. Head Face Med 10:5
Ramirez-Yañez GO (2019) Craniofacial growth and development. In: Liem E (ed) Sleep disorders in pediatric dentistry, 1st edn. Springer, Burnaby, pp 39–56
Sahin O, Kalabalik F, Tatar B, Odabasi O (2019) Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation of styloid process in patients with temporomandibular disorders and asymptomatic individuals. J Craniofac Surg 30:2236–2238
Sancio-Goncalves FC, de Abreu MH, Netto Soares JM, Amaral SA, Barbosa Porfirio FM, Naves MD, Abdo EN (2013) Stylohyoid complex ossification in temporomandibular disorder: a case–control study. J Prosthet Dent 109:79–82
Scavone G, Caltabiano DC, Raciti MV, Calcagno MC, Pennisi M, Musumeci AG, Ettorre GC (2019) Eagle's syndrome: a case report and CT pictorial review. Radiol Case Rep 14:141–145
Shaik MA, Kaleem SM, Wahab A, Hameed S (2013) Prevalence of elongated styloid process in Saudi population of Aseer region. Eur J Dent 7:449–454
Steiner CC (1959) Cephalometrics in clinical practice. Angle Orthod 29:8–29
Sutherland K, Lee RWW, Chan TO, Ng S, Hui DS, Cistulli PA (2018) Craniofacial phenotyping in chinese and caucasian patients with sleep apnea: influence of ethnicity and sex. J Clin Sleep Med 14:1143–1151
Yavuz H, Caylakli F, Yildirim T, Ozluoglu LN (2008) Angulation of the styloid process in Eagle’s syndrome. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265:1393–1396
Yılmaz D, Orhan K, Cesur E (2020) Evaluation of the relationship between stylohyoid complex morphology and maxillary/mandibular position using cone beam computed tomography. Folia Morphol 79:148–155
Funding
The study did not receive any commercial financial or material support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FK: data collection, data management, data analysis, and manuscript editing. OŞ: project development, manuscript writing, and manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Izmir Katip Celei University (2019/No. 391).
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalabalık, F., Şahin, O. Evaluation of stylohyoid complex in subjects with different types of malocclusions using cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective study in a Turkish subpopulation. Surg Radiol Anat 42, 1095–1100 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02486-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02486-8