Abstract
Purpose
In our study, we aimed to determine the topographic analysis of sternal foramen cases incidentally detected in patients underwent thoracic computed tomography.
Materials and methods
Patients aged 18 and over who were admitted to the thoracic surgery outpatient clinic for various reasons and underwent thoracic computed tomography (CT) between January 1, 2018 and January 1, 2019 were evaluated retrospectively. Thoracic CT scans of all patients with sternal foramen were evaluated by applying 3D bone configuration to evaluate foramina in the sternum and ribs. The data obtained were analyzed statistically by SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences Version 21.0).
Results
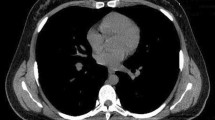
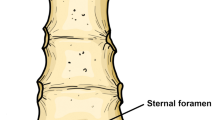
Nine hundred and twelve patients were evaluated and sternal foramen prevalence was found to be 8.44% in our study. Of the 68 patients included in the study, 48 were male and 20 were female. The sternal foramen was localized in the corpus in 66.2% of the patients, whereas it was localized in xiphoid in 33.8%. Nine patients had scoliosis deformity and three patients had foramen in the rib.
Conclusion
Sternal foramen is a more common defect than thought, and should be kept in mind in clinical practice to prevent complications.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktan ZA, Savas R (1998) Anatomic and HRCT demonstration of midline sternal foramina. Turk J Med Sci 28:511–514
Ashley GT (1956) The relationship between the pattern of ossification and the definitive shape of the mesosternum in man. J Anat 90:87–105
Azizi S, Bakhtiary MK, Goodarzi M (2012) Congenital sternal foramen in a stillborn Holstein calf. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2:83–84
Babinski MA, de Lemos L, Babinski MS, Goncalves MV, De Paula RC, Fernandes RM (2015) Frequency of sternal foramen evaluated by MDCT: a minor variation of great relevance. Surg Radiol Anat 37:287–291
Bayarogulları H, Yengil E, Davran R, Aglagul E, Karazincir S, Balcı A (2014) Evaluation of the postnatal development of the sternum and sternal variations using multidetector CT. Diagn Interv Radiol 20(1):82–89
Boruah DK, Prakash A, Yadav RR, Dhingani DD, Achar S, Augustine A, Mahanta K (2016) The safe zone for blinded sternal interventions based on CT evaluation of midline congenital sternal foramina. Skelet Radiol 45:1619–1628
Choi PJ, Iwanaga J, Tubbs RS (2017) A comprehensive review of the sternal foramina and its clinical significance. Cureus 9(12):e1929. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.1929(Published online 8 Dec 2017)
El-Busaid H, Kaisha W, Hassanali J, Hassan S, Ogeng'o J, Mandela P (2012) Sternal foramina and variant xiphoid morphology in a Kenyan population. Folia Morphol 71:19–22
Gkantsinikoudis N, Chaniotakis C, Gkasdaris G, Georgiou N, Kapetanakis S (2017) Morphological approach of the sternal foramen: an anatomic study and a short review of the literature. Folia Morphol 76(3):484–490
Gossner J (2013) Relationship of sternal foramina to vital structures of the chest: A computed tomographic study. Anat Res Int 2013:650601. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/650601(Published online 2 Oct 2013)
Kumarasamy SA, Agrawal R (2011) A large sternal foramen. IJAV 4:195–198
Paraskevas G, Tzika M, Anastasopoulos N, Kitsoulis P, Sofidis G, Natsis K (2015) Sternal foramina: incidence in Greek population, anatomy and clinical considerations. Surg Radiol Anat 37(7):845–851
Paraskevas GK, Tzika M, Natsis K (2016) Double sternal foramina in a dried sternum: a rare normal variant and its radiologic assessment. Surg Radiol Anat 38(8):991–993
Saccheri P, Sabbadini G, Toso F, Travan L (2012) A keyhole-shaped sternal defect in an ancient human skeleton. Surg Radiol Anat 34:965–968
Xie YZ, Wang BJ, Yun JS, Chung GH, Ma ZB, Li XJ et al (2014) Morphology of the human xiphoid process: dissection and radiography of cadavers and MDCT of patients. Surg Radiol Anat 36(3):209–217
Yekeler E, Tunaci M, Tunaci A, Dursun M, Acunas G (2006) Frequency of sternal variations and anomalies evaluated by MDCT. Am J Roentgenol 186(4):956–960
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research and/or authorship of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzucuoglu, M., Albayrak, I. Topographic evaluation of sternal foramen patients with thoracic computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat 42, 405–409 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-019-02416-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-019-02416-3