Abstract
Objective
The present study was undertaken to know the anatomical basis of medial sural artery (MSA) and its perforators in Nepalese.
Methods
The popliteal arteries of 16 preserved cadaveric lower limbs were injected with a mixture of red ink and glycerine. The number, location, diameter of perforators; length and intramuscular course of pedicle; the branching pattern of MSA were observed and measured.
Results
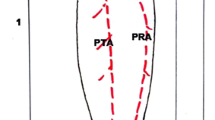
The mean of 2.2 ± 1.2 perforators (range 0–4) was observed. The perforators were clustered between 8.6 and 25.7 cm from the popliteal crease and 0.3–7.5 cm from posterior midline of leg. The dominant perforators were observed in middle 1/3rd of the leg. The average pedicle length was 12.04 ± 3.27 cm. The intramuscular courses of pedicles were observed in deep and superficial strata in 65.7 and 34.3%, respectively. The MSA originated from popliteal artery in 62.5% and common sural artery in 37.5%. An accessory MSA was found in 12.5%. Type I and Type III branching patterns of MSA were observed in 31.2% each whereas Type II was found in 37.5%. The mean external diameter of perforators and MSA were 0.85 ± 0.27 mm and 2.2 ± 0.43 mm, respectively.
Conclusions
The metrical presentation of this study provides an easy access to know about the distribution of perforators and branching pattern of MSA which will help the surgeons to make a convenient plan to harvest the MSA perforator flap in Nepalese population.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altaf FM (2011) The anatomical basis of the medial sural artery perforator flaps. West Indian Med J 60:622–627
Cavadas PC, Sanz-Gimenez-Rico JR, Camara AG, Navarro-Monzonis A, Soler-Nomdedeu S, Martinez-Soriano F (2001) The medial sural artery perforator free flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 108:1609–1615
Dusseldrop JR, Pham QJ, Ngo Q, Gianoutsos M, Moradi P (2014) Vascular anatomy of the medial sural artery perforator flap: a new classification system of intra-muscular branching patterns. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 67:1267–1275
Fujino T (1967) Contribution of axial and perforator vasculature to circulation in flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 39:125–137
Geddes CR, Morris SF, Neligan PC (2003) Perforator flaps: evolution, classification, and applications. Ann Plast Surg 50:90–99
Hallock GG (2001) Anatomic basis of the gastrocnemius perforator-based flap. Ann of Plast Surg 47:517–522
Kao HK, Chang KP, Chen YA, Wei FC, Cheng MH (2010) Anatomical basis and versatile application of the free medial sural artery perforator flap for head and neck reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 125:1135–1145
Kim HH, Joeng JH, Seul JH, Cho BC (2006) New design and identification of the medial sural perforator flap: an anatomical study and its clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1609–1618
Kosutic D, Pejkovic B, Anderhuber F, Vadnjal-Donlagic S, Zic R, Gulic R (2012) Complete mapping of lateral and medial sural artery perforators: anatomical study with Duplex-Doppler ultrasound correlation. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 65:1530–1536
Kroll SS, Rosenfield L (1988) Perforator-based flaps for low posterior midline defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 81:561
McMinn RMH (1994) Lower limb. Lastʼs anatomy: regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 173–175
Okamoto H, Sekiya I, Mizutani J, Otsuka T (2007) Anatomical basis of the medial sural artery perforator flap in Asians. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 41:125–129
Otani M, Okamoto H, Kagami H, Narita Y, Ebisawa K, Oda T (2012) Anatomical study on perforators of the medial and lateral sural artery in Asains. Nagoya Med J 52:89–98
Potparic Z, Colen LB, Sucur D, Carwell GR, Carraway JH (1995) The gastrocnemius muscle as a free-flap donor site. Plast Reconstr Surg 95:1245–1252
Shimizu F, Kato A, Sato H, Taneda H (2009) Sural perforator flap: assessment of the posterior calf region as donor site for a free fasciocutaneous flap. Microsurgery 29:253–258
Spinner R, Howe B (2016) Leg. In: Tubbs RS (ed) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1400–1417
Thione A, Valdatta L, Buoro M, Tuinder S, Mortarino C, Putz R (2004) The medial sural artery perforators: anatomic basis for a surgical plan. Ann Plast Surg 53:250–255
Torres LR, Teixeria WGJ, Setani EO, Wei TH, Zumiotti AV (2007) Skin flap of medial gastrocnemius muscle’s perforating arteries:an anatomical study. Acta Ortop Bras 15:40–42
Wong MZ, Wong CH, Tan BK, Chew KY, Tay SC (2012) Surgical anatomy of the medial sural artery perforator flap. J Reconstr Microsurg 28:555–560
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Prem Panta, Lecturer (Statistician), Department of Community Medicine, for his assistance in data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors received no specific funding for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This study underwent approval through Research and Institutional Review Committee (IRC) of Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basnet, L.M., Ghosh, S.K., Shrestha, S. et al. Anatomical study of medial sural artery and its perforators in Nepalese: an aid to reconstructive surgery. Surg Radiol Anat 40, 935–941 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-017-1956-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-017-1956-2