Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this review is to present an update and summary of clinical findings of cases with a patent nasopalatine duct (NPD) reported in the literature from 1881 to 2016.
Methods
Previous articles and reviews about patent NPDs were studied and copies of all original publications were obtained for data verification. Furthermore, a literature search was conducted. In addition, the study sample was complemented with four cases recently seen in our institution.
Results
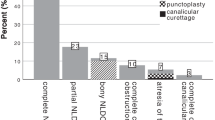
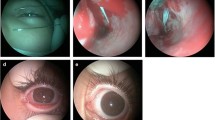
Ten out of 67 published cases were to be excluded for this analysis due to misinterpretation or misreporting in previous articles. Overall, 57 cases with NPD patency could be analyzed. Males outnumbered females in a ratio of 2:1. The mean age (when this information was available) was 34.1 ± 17.6 years (range 6–69 years). NPDs were located bilaterally (60%), unilaterally (20%) or centrally (20%). Complete or partial patency was reported in 73.9 and 26.1%, respectively. 74.1% of patients presented a variety of clinical signs and symptoms. The ability of the patient to produce a squeaky or whistling sound was the most frequent clinical finding (23.8%).
Conclusions
Caution must be exercised when reading review articles about NPD patency since wrong data have been copied in several subsequent publications. Since epidemiological data are missing with regard to patent NPDs, age and gender predilections are not warranted. Bilateral occurrence and full patency were prevailing features in the evaluated case reports of patent NPDs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams AM, Howell FV, Bullock WK (1963) Nasopalatine cysts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 16:306–332
Allard RH, van der Kwast WA, van der Waal I (1981) Nasopalatine duct cyst. Review of the literature and report of 22 cases. Int J Oral Surg 10:447–461
Allard RHB, de Vries K, van der Kwast WAM (1982) Persisting bilateral nasopalatine ducts: a developmental anomaly. Oral Surg 53:24–26
Bassetti R, Werder P, Crameri M, Ebinger A, Stähli A, Mericske-Stern R, Kuttenberger J (2015) The patent nasopalatine duct: a potential cause of unclear pain in the anterior maxilla. Quintessence Int 46:73–79
Beckett H, Gilmour AG (1995) Abnormal anterior siting of the incisive papilla with bilateral patent nasopalatine ducts. Br Dent J 178:223–224
Blackburn CW (1984) Patent nasopalatine ducts. Br Dent J 157:401–402
Broome WC, Seymour FW (1976) Partially patent nasopalatine ducts: report of cases. J Endod 2:279–282
Buchner A, Mlinek A (1972) Palatal opening of the nasopalatine duct: a developmental anomaly. Oral Surg 34:440–444
Catros S, de Gabory L, Stoll D, Deminière C, Fricain JC (2008) Use of gutta percha cores in CT scan imaging for patent nasopalatine duct. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37:1065–1066
Chandler NP, Gray A (1996) Patent nasopalatine ducts: a case report. N Z Dent J 92:80–82
Chapple IL, Ord RA (1990) Patent nasopalatine ducts: four case presentations and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 69:554–558
Cros P, Marion A, Freidel M, Dumas P (1984) Double fistule congénitale naso-palatine an arrière des incisives centrales et laterals. Rev Stomat Chir Maxillofac 85:70–71 (article in French)
Ebinger A, Katsoulis J, Mericske-Stern R, Bassetti R (2011) Der Ductus nasopalatinus: ein Fallbericht über eine seltene Anomalie im Mundbereich. Quintessenz 62:1335–1338 (article in German)
Edwards PC, Kanjirath PP, Norton NS, McVaney T, Scanlon C, Saini T (2010) Developmental oronasal fistula of the incisive papilla. Gen Dent 58:62–67
Eppley BL, Delfino JJ (1988) Bilateral nasopalatine ducts of the premaxilla. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 17:360–362
Farman AG, Gould AR, Schuler ST (1982) Patent nasopalatine ducts: a developmental anomaly. JADA 105:473–475
Fry JC (1932) Two cases of sinus in the incisive canal. Br Dent J 53:528–529
Goebel WM (1975) Bilateral patent nasopalatine ducts. J Oral Med 30:96–98
Götzfried HF (1986) Bilateral patent nasopalatine ducts. A new method of treatment. J Maxillofac Surg 14:113–115
Grohs R (1934) Epithelial rests in the region of the palatine papilla of the upper jaw. J Dent Res 14:187–188
Hattori T, Kitajima T, Kouichi N (1987) A case of patent nasopalatine duct. Jpn J Oral Maxillofac Surg 33:89–90
Jacob S, Zelano B, Gungor A, Abbott D, Naclerio R, McClintock MK (2000) Location and gross morphology of the nasopalatine duct in human adults. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:741–748
Kitamura H (1976) Development of nasopalatine ducts. In: Kitamura H (ed) Embryology of the mouth and related structures. Maruzen, Tokyo, pp 153–155
Knecht M, Kittner T, Beleites T, Hüttenbrink KB, Hummel T, Witt M (2005) Morphological and radiologic evaluation of the human nasopalatine duct. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 114:229–232
Leboucq H (1881) Le canal nasopalatin chez l’homme. Arch Biol Paris 2:386–397 (article in French)
Lee SS, Lee CH, Lee SK (2013) Patent nasopalatine duct mimicking nasopalatine duct cyst. Kor J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 37:167–174
Lehman H, Poulsen O (1983) To tilfaelde af persisterende bilateral ductus nasopalatinus. Tandlaegebladet 87:278–279 (article in Danish)
Liang X, Jacobs R, Martens W, Hu Y, Adriaensens P, Quirynen M, Lambrichts I (2009) Macro- and micro-anatomical, histological and computed tomography scan characterization of the nasopalatine canal. J Clin Periodontol 36:598–603
Lundner AS, Warunek SP (2006) Patent nasopalatine ducts after rapid maxillary expansion. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 130:96–99
MacGregor AJ (1964) Patent nasopalatine canal. A rare case of oronasal fistula. Oral Surg 18:285–292
Main DM (1970) Epithelial jaw cysts: a clinicopathological reappraisal. Br J Oral Surg 8:114–125
Meyer AW (1931) Median anterior maxillary cysts. JADA 18:1851–1877
Moreira Falci SG, Consolaro A, Rocha Dos Santos CR (2013) Bilateral patent nasopalatine duct: a case report and literature review. Gazz Med Ital 172:123–128
Moskow BS (1982) Bilateral congenital nasopalatine communication. Oral Surg 53:458–460
Moss HD, Hellstein JW, Johnson JD (2000) Endodontic considerations of the nasopalatine duct region. J Endod 26:107–110
Osman Hill WC, Darlow HM (1945) Bilateral perforate nasopalatine communication in the human adult. J Laryngol Otol 60:160–165
Pithon MM (2011) Asymptomatic patent nasopalatine ducts after rapid maxillary expansion. J Craniofac Surg 22:1333–1335
Potiquet M (1891) Du canal de Jacobson. De la possibilité de le reconnaître sur le vivant et de son rôle probable dans la pathogénie de certaines lesions de la cloison nasale. Rev Laryng Otol Rhinol 12:737–753 (article in French)
Radlanski RJ, Emmerich S, Renz H (2004) Prenatal morphogenesis of the human incisive canal. Anat Embryol (Berl) 208:265–271
Rapp R, Winter GB (1979) Color atlas of clinical conditions in pedodontics. Wolfe Medical Publications Ltd, London, p 109 (case #381)
Rawengel G (1923) Die Nasen-Gaumengänge und andere epitheliale Gebilde im vorderen Teile des Gaumens bei Neugeborenen und Erwachsenen. Arch Mikr Anat 97:507–522 (article in German)
Rodrigues MT, Munhoz EA, Cardoso CL, Junior OF, Damante JH (2009) Unilateral patent nasopalatine duct: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Otolaryngol 30:137–140
Rogers CC (1955) Patent nasopalatine fistula. Br Dent J 99:154
Roper-Hall HT (1941) Patent incisive canal. Br Dent J 71:306–309
Schulze D (2011) Interpretation von Röntgenbildern. Partiell persistierender Ductus nasopalatinus. Quintessenz 62:538 (article in German)
Shimura Y, Nakamura A, Michi K (1993) Palatal opening of the nasopalatine duct. A case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 22:142–143
Signy H, Rule DC (1982) Palatal opening of a nasopalatine duct. Br Dent J 153:371–372
Smith TD, Bhatnagar KP, Shimp KL, Kinzinger JH, Bonar CJ, Burrows AM, Mooney MP, Siegel MI (2002) Histological definition of the vomeronasal organ in humans and chimpanzees, with a comparison to other primates. Anat Rec 267:166–176
Song WC, Jo DI, Lee JY, Kim JN, Hur MS, Hu KS, Kim HJ, Shin C, Koh KS (2009) Microanatomy of the incisive canal using three-dimensional reconstruction of microCT images: an ex vivo study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 108:583–590
Suter VGA, Sendi P, Reichart PA, Bornstein MM (2011) The nasopalatine duct cyst: an analysis of the relation between clinical symptoms, cyst dimensions and involvement of neighboring anatomical structures using cone beam computed tomography. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:2595–2603
Suter VGA, Büttner M, Altermatt HJ, Reichart PA, Bornstein MM (2011) Expansive nasopalatine duct cysts with nasal involvement mimicking apical lesions of endodontic origin: a report of two cases. J Endod 37:1320–1326
Suter VGA, Warnakulasuriya S, Reichart PA, Bornstein MM (2015) Radiographic volume analysis as a novel tool to determine nasopalatine duct cyst dimensions and its association with presenting symptoms and postoperative complications. Clin Oral Invest 19:1611–1618
Valstar MH, van den Akker HP (2008) Patent nasopalatine duct: a diagnostic pitfall. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46:304–305
von Arx T, Bornstein MM (2009) Der offene Ductus nasopalatinus. Eine seltene Missbildung und diagnostische Falle. Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed 119:379–389 (article in German)
Werder P, Bassetti R, Kuttenberger J (2016) Surgical treatment option of the patent nasopalatine duct: a case report. J Surg Case Rep. doi:10.1093/jscr/rjw090
Wessels Q, Hoogland PVJ, Vorster W (2014) Anatomical evidence for an endocrine activity of the vomeronasal organ in human. Clin Anat 27:856–860
Winslow CP, Chan KH, Strain JD (1998) Imaging quiz case 2. Patent nasopalatine duct. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 124:1275/1277–1278
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Bernadette Rawyler, Medical Illustrator, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern, Switzerland, for the schematic illustrations and Ines Badertscher, Multimedia Specialist, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern, Switzerland, for preparation of case figures. We also thank the librarians Eveline Schuler, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland, and Sam Yuk Chuen Lee, University Libraries, The University of Hong Kong, Prince Philip Dental Hospital, Hong Kong SAR, China, for the meticulous search and provision of copies of all requested articles. Furthermore, we thank Dr. Ray Tanaka, Applied Oral Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China, for the translation of a Japanese case report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Arx, T., Schaffner, M. & Bornstein, M.M. Patent nasopalatine ducts: an update of the literature and a series of new cases. Surg Radiol Anat 40, 165–177 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-017-1926-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-017-1926-8