Abstract
Aim
The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between each root of maxillary premolars and molars and the maxillary sinus floor according to sex, sinus position, and age by decade in a Turkish population by using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scanning.
Methodology
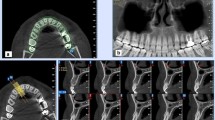
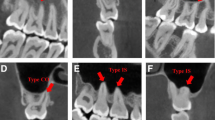
We evaluated a database of 5,166 (2,680 maxillary premolars and 2,486 maxillary molars) CBCT scans obtained from 849 patients. The vertical relationship between each root of the molar and premolar teeth to the sinus floor was classified into three types: type 1, the roots penetrated into the sinus floor; type 2, the roots contacted the sinus floor; and type 3, the roots extended below the sinus floor.
Results
The results of the classification of each root in relationship to the sinus floor were as follows: type 3 occurred most frequently in the first (92.4 %) and second (71.6 %) premolar teeth, type 1 (34.2 %) occurred most frequently in the palatinal roots of the first molar teeth, type 3 occurred most frequently in the mesiobuccal (39.9 %) and distobuccal (39.7 %) roots of the first molar teeth, and type 2 (36.7 %) occurred most frequently in the mesiobuccal roots of the second molar teeth. No significant differences were found between the left and right sides, but several differences were found between males and females. The relationship between the posterior teeth and the sinus floor differed according to the age decade interval (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The maxillary first premolars have no relationship with the maxillary sinus floor, but the maxillary second molars are closer to the sinus floor. Also the second decade and males were most susceptible to undesirable results.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariji Y, Obayashi N, Goto M, Izumi M, Naitoh M, Kurita K, Shimozato KAriji E (2006) Roots of the maxillary first and second molars in horizontal relation to alveolar cortical plates and maxillary sinus: computed tomography assessment for infection spread. Clin Oral Investig 10:35–41
Asaumi R, Sato I, Miwa Y, Imura K, Sunohara M, Kawai T, Yosue T (2010) Understanding the formation of maxillary sinus in Japanese human foetuses using cone beam CT. Surg Radiol Anat 32:745–751
Baker AS (1991) Role of anaerobic bacteria in sinusitis and its complications. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 154:17–22
Beck-Mannagetta J, Necek D (1986) Radiologic findings in aspergillosis of the maxillary sinus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 62:345–349
Ben Amor M, Khalifa Z, Romdhane N, Zribi S, Ben Gamra O, Mbarek C, El Khedim A (2013) Orbital complications of sinusitis. J Fr Ophtalmol 36:488–493
Bornstein MM, Wasmer J, Sendi P, Janner SF, Buser D, Von Arx T (2012) Characteristics and dimensions of the Schneiderian membrane and apical bone in maxillary molars referred for apical surgery: a comparative radiographic analysis using limited cone beam computed tomography. J Endod 38:51–57
Brook I, Friedman EM, Rodriguez WJ, Controni G (1980) Complications of sinusitis in children. Pediatrics 66:568–572
Brullmann DD, Schmidtmann I, Hornstein S, Schulze RK (2012) Correlation of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) findings in the maxillary sinus with dental diagnoses: a retrospective cross-sectional study. Clin Oral Investig 16:1023–1029
Clayman GL, Adams GL, Paugh DR, Koopmann CF Jr (1991) Intracranial complications of paranasal sinusitis: a combined institutional review. Laryngoscope 101:234–239
Cotton TP, Geisler TM, Holden DT, Schwartz SA, Schindler WG (2007) Endodontic applications of cone-beam volumetric tomography. J Endod 33:1121–1132
De Foer C, Fossion E, Vaillant JM (1990) Sinus aspergillosis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 18:33–40
Eberhardt JA, Torabinejad M, Christiansen EL (1992) A computed tomographic study of the distances between the maxillary sinus floor and the apices of the maxillary posterior teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 73:345–346
Ehrich DG, Brian JD Jr, Walker WA (1993) Sodium hypochlorite accident: inadvertent injection into the maxillary sinus. J Endod 19:180–182
Fava LR (1993) Calcium hydroxide paste in the maxillary sinus: a case report. Int Endod J 26:306–310
Georgescu CE, Rusu MC, Sandulescu M, Enache AM, Didilescu AC (2012) Quantitative and qualitative bone analysis in the maxillary lateral region. Surg Radiol Anat 34:551–558
Harorh A, Bocutoglu O (1995) The comparison of vertical height and width of maxillary sinus by means of Waters’ view radiograms taken from dentate and edentulous cases. Ann Dent 54:47–49
Hauman CH, Chandler NP, Tong DC (2002) Endodontic implications of the maxillary sinus: a review. Int Endod J 35:127–141
Jun BC, Song SW, Park CS, Lee DH, Cho KJ, Cho JH (2005) The analysis of maxillary sinus aeration according to aging process; volume assessment by 3-dimensional reconstruction by high-resolutional CT scanning. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:429–434
Jung YH, Cho BH (2012) Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography. Imaging Sci Dent 42:219–224
Kavanagh CP, Taylor J (1998) Inadvertent injection of sodium hypochlorite into the maxillary sinus. Br Dent J 185:336–337
Kilic C, Kamburoglu K, Yuksel SP, Ozen T (2010) An assessment of the relationship between the maxillary sinus floor and the maxillary posterior teeth root tips using dental cone-beam computerized tomography. Eur J Dent 4:462–467
Kosko JR, Hall BE, Tunkel DE (1996) Acquired maxillary sinus hypoplasia: a consequence of endoscopic sinus surgery? Laryngoscope 106:1210–1213
Kretzschmar DP, Kretzschmar JL (2003) Rhinosinusitis: review from a dental perspective. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 96:128–135
Kwak HH, Park HD, Yoon HR, Kang MK, Koh KS, Kim HJ (2004) Topographic anatomy of the inferior wall of the maxillary sinus in Koreans. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 33:382–388
Lu Y, Liu Z, Zhang L, Zhou X, Zheng Q, Duan X, Zheng G, Wang H, Huang D (2012) Associations between maxillary sinus mucosal thickening and apical periodontitis using cone-beam computed tomography scanning: a retrospective study. J Endod 38:1069–1074
Maillet M, Bowles WR, Mcclanahan SL, John MT, Ahmad M (2011) Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of maxillary sinusitis. J Endod 37:753–757
Maloney PL, Doku HC (1968) Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin. J Can Dent Assoc (Tor) 34:591–603
Marais JT, Van Der Vyver PJ (1996) Invasion of the maxillary sinus with calcium hydroxide. J Dent Assoc S Afr 51:279–281
Mehra P, Murad H (2004) Maxillary sinus disease of odontogenic origin. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 37:347–364
Nishimura T, Iizuka T (2002) Evaluation of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis after conservative therapy using CT and bone SPECT. Clin Imaging 26:153–160
Nowak R, Mehlis G (1975) Studies on the state of pneumatization of the sinus maxillaris. Anat Anz 138:143–151
Orlay HG (1966) Overfilling in root canal treatment. Two accidents with N2. Br Dent J 120:376
Pagin O, Centurion BS, Rubira-Bullen IR, Alvares Capelozza AL (2013) Maxillary sinus and posterior teeth: accessing close relationship by cone-beam computed tomographic scanning in a Brazilian population. J Endod 39:748–751
Patel NA, Ferguson BJ (2012) Odontogenic sinusitis: an ancient but under-appreciated cause of maxillary sinusitis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 20:24–28
Rosen MD, Sarnat BG (1955) Change of volume of the maxillary sinus of the dog after extraction of adjacent teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 8:420–429
Scarfe WC, Levin MD, Gane D, Farman AG (2009) Use of cone beam computed tomography in endodontics. Int J Dent 2009:634567
Shanbhag S, Karnik P, Shirke P, Shanbhag V (2013) Association between periapical lesions and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening: a retrospective cone-beam computed tomographic study. J Endod 39:853–857
Shapiro R, Schorr S (1980) A consideration of the systemic factors that influence frontal sinus pneumatization. Invest Radiol 15:191–202
Sharan A, Madjar D (2006) Correlation between maxillary sinus floor topography and related root position of posterior teeth using panoramic and cross-sectional computed tomography imaging. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 102:375–381
Sharan A, Madjar D (2008) Maxillary sinus pneumatization following extractions: a radiographic study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 23:48–56
Thomas A, Raman R (1989) A comparative study of the pneumatization of the mastoid air cells and the frontal and maxillary sinuses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 10:S88
Vallo J, Suominen-Taipale L, Huumonen S, Soikkonen K, Norblad A (2010) Prevalence of mucosal abnormalities of the maxillary sinus and their relationship to dental disease in panoramic radiography: results from the Health 2000 Health Examination Survey. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 109:e80–e87
Watzek G, Bernhart T, Ulm C (1997) Complications of sinus perforations and their management in endodontics. Dent Clin North Am 41:563–583
Wehrbein H, Diedrich P (1992) Progressive pneumatization of the basal maxillary sinus after extraction and space closure. Fortschr Kieferorthop 53:77–83
Conflict of interest
The authors deny any conflicts of interest. I affirm that I/We have no financial affiliation (e.g., employment, direct payment, stock holdings, retainers, consultantships, patent licensing arrangements or honoraria), or involvement with any commercial organization with direct financial interest in the subject or materials discussed in this manuscript, nor have any such arrangements existed in the past 3 years.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ok, E., Güngör, E., Çolak, M. et al. Evaluation of the relationship between the maxillary posterior teeth and the sinus floor using cone-beam computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat 36, 907–914 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-014-1317-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-014-1317-3