Abstract
Purpose
Body mass index (BMI) has been shown to influence the outcome of various surgical procedures. The purpose of this study is to assess the relationship between BMI, gender, and the distribution of subcutaneous and perirenal fat.
Methods
A retrospective review was performed for 123 patients who underwent radical or partial nephrectomy. Preoperative CT scans were reviewed by two independent observers. Subcutaneous fat was measured at three locations and perirenal fat was measured at six locations. Statistical analysis was performed using the Student’s t test and the Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
Results
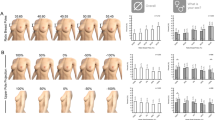
Mean anterior subcutaneous fat was significantly greater in females than in males (2.54 vs. 1.78 cm, p < 0.001) as was mean right posterolateral subcutaneous fat (2.78 vs. 2.21 cm, p = 0.03). With regard to perirenal fat, men were greater than women for all perirenal locations around the left kidney. For the right kidney, men were greater than women for four out of six perirenal positions. In both men and women, BMI was strongly correlated with subcutaneous fat. However, BMI was weakly correlated with perirenal fat.
Conclusions
Women exceed men in subcutaneous fat, while men exceed women in perirenal fat. Obese patients are very likely to have large amounts of subcutaneous fat, but will not necessarily have proportionally increased fat around their kidneys when compared to the patients with lower BMI. These differences may have important implications for surgical approaches to the kidney.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson KM, Lindler TU, Lamberton GR, Baron PW, Ojogho OK, Baldwin DD (2008) Laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: effect of perirenal fat upon donor operative time. J Endourol 22(10):2269–2274
Brown JA, Rodin DM, Lee B, Dahl DM (2005) Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and body mass index: an assessment of 151 sequential cases. J Urol 173:442–445
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Routledge Academic, New York
Ferrara CM, Goldberg AP, Nicklas BJ, Sorkin JD, Ryan AS (2008) Sex differences in insulin action and body fat distribution in overweight and obese middle-aged and older men and women. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 33:784–790
Friedl KE (2004) Can you be large, not obese? The distinction between body weight, body fat, abdominal fat in occupational standards. Diabetes Technol Ther 6:732–749
Hamdy O, Porramatikul S, Al-Ozairi E (2006) Metabolic obesity: the paradox between visceral and subcutaneous fat. Curr Diabetes Rev 2:367–3739
Lemieux S, Prud’homme D, Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Despres JP (1993) Sex differences in the relation of visceral adipose tissue accumulation to total body fatness. Am J Clin Nutr 58:463–467
Pareek G, Hedican SP, Lee FT Jr, Nakada SY (2005) Shock wave lithotripsy success determined by skin-to-stone distance on computed tomography. Urology 66:941–944
Pareek G, Armenakas NA, Panagopoulos G, Bruno JJ, Fracchia JA (2005) Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy success based on body mass index and Hounsfield units. Urology 65:33–36
Conflict of interest statement
Brian Eisner is a speaker for Boston Scientific Corporation and a consultant for the Ravine Group and PercSys. Marshall Stoller is a consultant for the Ravine Group and PercSys. Matthew Cooperberg is a consultant for Abbott. All other authors have no disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eisner, B.H., Zargooshi, J., Berger, A.D. et al. Gender differences in subcutaneous and perirenal fat distribution. Surg Radiol Anat 32, 879–882 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0692-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0692-7