Abstract
Background
Two pairs of sagittal longitudinal striae, medial and lateral, are slender bundles of fibers located on the dorsal surface of corpus callosum, situated deeply in the longitudinal fissure of telencephalon. Imbedded in the structure of tiny gyrus, indusium griseum, they are, in fact, supracallosal fibers of the fornix, previously called fornix longus.
Methods
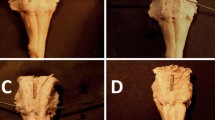
Longitudinal striae were investigated in 25 fixed human brains obtained from autopsies. Macrodissection and morphometric methods were used in order to find out and analyze the appearance and gross morphological variability of longitudinal striae, as well as their inter-individual relations.
Results
Lateral longitudinal striae were located along the sulci of corpus callosum. Medial striae were positioned along the sagittal midline and they were mostly individual. However, they were at times connected, spanned or duplicated. Longitudinal striae make a characteristic pattern on the dorsal surface of corpus callosum. A classification of striae is made on the basis of their appearance.
Conclusions
Although similar at first sight the striae, especially medial ones, have some individual features which make the pattern variable. Medial striae are more variable than the lateral ones. Perhaps functional neuroimaging and DT MRI will disclose the enigma of these striae.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arroyo-Guijarro J, Prats-Galino A, Ruano-Gil D, Costa-Lloet C (1988) Comparative study of the MLSe of the hippocampus (formerly called “nerves of Lancisi”) in the fighting bull and domestic bull. (French). Bull Assoc Anat 72:15–19
Bogen JE (1997) The neurosurgeon’s interest in the corpus callosum. In: Greenblatt SH, Dagi TF, Epstein MH (eds) A history of neurosurgery. American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Park Ridge, pp 489–498
Calabrese P, Markowitch HJ, Harders AG, Scholz M, Gehlen W (1995) Fornix damage in memory. A case report. Cortex 31:555–564
Carpenter MB (1996) Olfactory pathways, hippocampal formation, and amygdala. In: Satterfield TS (ed) Core text of neuroanatomy, 4th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 369–371
Chao LP, Kan KS, Hung FM (1982) Immunohistochemical localisation of choline acetyltransferase in rabit forebrain. Brain Res 235:65–82
Chronister RB, Hardy SGP (1997) The limbic system. In: Haines DE (ed) Fundamental neuroscience. Churchill Livingstone, London, pp 443–454
Clark CR, Geffen GM (1989) Corpus callosum surgery and recent memory. A review. Brain 112:165–175
Crossman AR (2005) Limbic lobe. In: Standring S et al (eds) Gray’s anatomy. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 404–409
Daitz H (1953) Note on the fibre content of the brain fornix system in man. Brain 76:509–512
Di Ieva A, Tschabitscher M, Rodriguez y Baen R (2007) Lancisi’s nerves and the seat of the soul. Neurosurgery 60:563–568
Dimond SJ, Scammell RE, Brouwers EY, Weeks R (1977) Functions of the centre section (trunk) of the corpus callosum in man. Brain 100:543–562
Economo C (1929) The cytoarchitectonics of the human cerebral cortex. Humphrey Milford Oxford University press, London, pp 129–167
Fitzgerald MJT (1997). The limbic system. In: Neuroanatomy, basic and clinical, 3rd edn. W.B. Saunders, London, pp 259–269
Hernandez-Peon R et al (1963) Limbic cholinergic pathways involved in sleep and emotional behavior. Exp Neurol 8:93–111
Jinkins RJ (1999) High field, high resolution MR imaging of the human indusium griseum—letter. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 5:524–525
Kotter R, Meyer N (1992) The limbic system: a review of its empirical foundation. Behav Brain Res 52:105–127
Künzle H (2004) The hippocampal continuation (indusium griseum) its connectivity in the hedgehog terenc and its status within the hippocampal formation of higher vertebrates. Anat embryol 208:183–213
Leighton PM (1999) Dr. Leighton Mark was invited to comment on this issue. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:982–984
Malobabic S, Puskas L, Vela A (1988) Enlarged medial longitudinal (supracallosal) stria in one human brain. Acta Biol Med Exp 13:87–90
McMackin D, Cockburn J, Anslow P, Gaffan D (1995) Correlation of fornix damage with memory impairment in six cases of colloid cyst removal. Acta Neurol (Wien) 135:12–18
Merchenthaler I, Gorcs T, Setalo G (1982) Neurons containing luteinising hormone-releasing hormone in the indusium griseum of the rat. Acta Morphol Acad Sci Hung 30:151–156
Nakada T (1999) High field, high resolution MR imaging of the human indusium griseum. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:524–525
Sadler TW (1995) Central nervous system. In: Coryell P (ed) Langmans medical embryology. Williams and Wilkins, London, pp 396–412
Sidman RL, Rakic P (1982) Development of the human nervous system. In: Haymaker W, Adams RD (eds) Histology and histopathology of the nervous system. CC Thomas, Springfield
Standring S et al (eds) (2005). Gray’s anatomy, 39th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 262–270
Testut L, Latarjet A (1948) Système nerveux central. In: Traité d’ anatomie humaine. Paris, G. Doin and C’e, pp 1017–1018; 1176–1181
Von Cramon DY, Schuri U (1992) The septo-hippocampal pathways and their relevance to human memory: a case report. Cortex 28:411–422
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlovic, S., Stefanovic, N., Malobabic, S. et al. Longitudinal striae of the human fornix: shape, relations and variations. Surg Radiol Anat 31, 501–506 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-009-0471-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-009-0471-5