Abstract
Background
A large patent median artery can be involved in several clinical disorders like carpal tunnel syndrome, anterior interosseous nerve syndrome and pronator syndrome.
Methods
The frequency and variability in the expression of the median artery and the expression of the other forearm arteries were recorded during two dissection courses. The topography of the arteries with their ramifications was documented on diagrams and photographs. The outer diameters of forearm arteries were measured.
Results
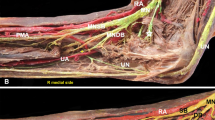
A large median artery was found in 4 of 54 arms (7.4%). The median arteries took their origin from the ulnar artery or the common interosseous artery. In one case, the median artery pierced the median nerve in its course under the pronator teres. The outer diameters of the median arteries varied between 1.5 and 2.0 mm proximally and 1.5 and 2.0 mm distally. The diameters of the radial arteries varied between 3.0 and 5.5 mm proximally and 3.0 and 4.0 mm distally and were not reduced in any of the four cases with a large median artery.
Conclusions
Surgeons should be aware of other variations in the forearm when a persistent median artery is identified, for example high median nerve bifurcations. Furthermore, it should be kept in mind that additional structures leading to nerve compression may be present in the carpal tunnel.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi B (1928) Das Arteriensystem der Japaner. Band I: A. pulmonalis, Aorta - Arcus volaris profundus. Maruzen, Kyoto, pp 308– 315
Balakrishnan C, Smith MF, Puri P (1999) Acute carpal tunnel syndrome from thrombosed persistent median artery. J Emerg Med 17:437–439
Barfred T, Hojlund AP, Berheussen K (1985) Median artery in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg (Am) 10:864–867
Boles DM, Tobias PV, Spiro F (1982) Carpal tunnel syndrome due to compression by an anomalous median artery. Surg Neurol 17:99–100
Burnham PJ (1963) Acute carpal tunnel syndrome. Median artery thrombosis as cause. Arch Surg 87:645–646
Coleman SS, Anson BJ (1961) Arterial patterns in the hand based upon a study of 650 specimens. Surg Gynecol Obstet 113:409–424
Dickinson JC, Kleinert JM (1991) Acute carpal-tunnel syndrome caused by a calcified median artery. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:610–611
Feldkamp MM, Gentili F, Hudson AR, Guha A (1995) A persistent median artery causing carpal tunnel syndrome in a patient with chronic renal failure: case report. Neurosurgery 37:140–143
Fumiere E, Dugardeyn C, Roquet ME, et al (2002) US demonstration of a thrombosed persistent median artery in carpal tunnel syndrome. JBR-BTR 85:1–3
Galassi E, Benfenati A, Tognetti F, Pozzati E (1980) Persistence of the median artery: possible cause of the carpal tunnel syndrome. Riv Neurol 50:159–166
Gassner EM, Schocke M, Peer S, et al (2002) Persistent median artery in the carpal tunnel. Color Doppler ultrasonographic findings. J Ultrasound Med 21:455–461
Gegenbaur C (1892) Lehrbuch der Anatomie des Menschen. 2. Bd. Engelmann, Leipzig, pp 259–265
George BJ, Henneberg M (1996) High frequency of the median artery of the forearm in South African newborns and infants. S Afr Med J 86:175–176
Gozdziewski S (1978) Variation of the axial arteries of the upper extremity in man. Folia morphol (Warszawa) 37:91–97
Gray DJ (1945) Some variations appearing in the dissection room. Stanford Med Bull 3:120
Gutowski KA, Olivier WA, Mehrara BJ, et al (2000) Arteriovenous malformation of a persistent median artery with a bifurcated nerve. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:1336–1339
Henle J (1868) Handbuch der systematischen Anatomie des Menschen. 3. Bd., 1. Abtlg.: Gefässlehre. Vieweg und Sohn, Braunschweig, pp 270–278
Henneberg M, George BJ (1992a) High incidence of the median artery of the forearm in a sample of recent Southern African cadavers. J Anat 180:185–188
Henneberg M, George BJ (1992b) A further study of the high incidence of the median artery of the forearm in Southern Africa. J Anat 181:151–154
Hofmann CEE (1878) Lehrbuch der Anatomie des Menschen. 2. Bd: Gefässsystem, Nervensystem und Sinnesorgane. Besold, Erlangen, p 139
Jones M, Abrahams PH, Sanudo JR, Campillo M (1997) Incidence and morphology of accessory heads of flexor pollicis longus and flexor digitorum profundus (Gantzer`s muscles). J Anat 191:451–455
Jones NF, Ming NL (1988) Persistent median artery as a cause of pronator syndrome. J Hand Surg (Am) 13:728–732
Kele H, Verheggen R, Reimers CD (2002) Carpal tunnel syndrome caused by thrombosis of the median artery: the importance of high-resolution ultrasonography for diagnosis. Case report. J Neurosurg 97:471–473
Khashaba A (2002) Carpal tunnel syndrome from thrombosed persistent median artery. J Emerg 22:55–57
Kopsch F (1914) Rauber-Kopsch: Rauber’s Lehrbuch der Anatomie des Menschen. Abteilung 3: Muskeln, Gefäße. Thieme, Leipzig, p 327
Kopuz C, Baris S, Gulman B (1997) A further morphological study of the persistent median artery in neonatal cadavers. Surg Radiol Anat 19:403–406
Krol A, Palczak A, Jedrzejewski KS (2005) Split median nerve. A report of two cases. Folia Morphol (Warszawa) 64:341–344
Lanz T von, Wachsmuth W (1959) Praktische Anatomie. Erster Band, dritter Teil: Arm. Springer, Berlin, pp 189, 200, 216
Lavey EB, Pearl RM (1981) Patent median artery as a cause of carpal tunnel syndrome. Ann Plast Surg 7:236–238
Levy M, Pauker M (1978) Carpal tunnel syndrome due to thrombosed persisting median artery. A case report. Hand 10:65–68
Libersa C, Francke JP, Mauppin JM, et al (1982) The arterial supply to the palm of the hand (arteriae palmae manus). Anat Clin 4:33–45
Lippert H, Pabst R (1985) Arterial variations in man. Bergmann, München, pp 71–77
Luschka H von (1865) Die Anatomie des Menschen. Dritter Band, erste Abtheilung: Die Glieder. Laupp’sche Buchhandlung, Tübingen, p 220
Maruyama K (1944) Seltene Varietät der Arterien der oberen Extremität bei einem Japaner (A. brachialis superficialis lateralis inferior, A. antebrachialis superficialis mediano-ulnaris, Arcus volaris superficialis vom Typus medianoulnaris). Folia Anat Jpn 22:551–567
Mauersberger W, Meese W (1975) Carpal tunnel syndrome caused by the persistence of the median artery. Neurochirurgia (Stuttgart) 18:15–19
Meckel JF (1816) Handbuch der menschlichen Anatomie. Zweiter Band: Besondere Anatomie. Gefäß- und Nervenlehre. Buchhandlung des Hallischen Waisenhauses, Halle
Michelsen H, Posner MA (2002) Medical history of carpal tunnel syndrome. Hand Clin 18:257–268
Nather A, Chacha PB, Lim P (1980) Acute carpal tunnel syndrome secondary to thrombosis of a persistent median artery (with high division of the median nerve). A case report. Ann Acad Med Singapore 9:118–121
Olave E, Prates JC, Gabrielli C, Pardi P (1997) Median artery and superficial palmar branch of the radial artery in the carpal tunnel. Scand J Plast Reconstr Hand Surg 31:13–16
Pabst R, Lippert H (1968) Beiderseitiges Vorkommen von A. brachialis superficialis, A. ulnaris superficialis und A. mediana. Anat Anz 123:223–226
Proudman TW, Menz PW (1992) An anomaly of the median artery associated with the anterior interosseous nerve syndrome. J Hand Surg (Br) 17:507–509
Quain R (1844) Anatomy of the arteries of the human body. Taylor & Walton, London, pp 235–271
Rayan GM (1986) Persistent median artery and compression neuropathy. Orthop Rev 15:241–244
Rodríguez-Niedenführ M, Burton GJ, Deu J, Sanudo JR (2001) Development of the arterial pattern in the upper limb of staged human embryos: normal development and anatomic variations. J Anat 199:407–417
Rodríguez-Niedenführ M, Sanudo JR, Vázquez T, Nearn L, Logan B, Parkin I (1999) Median artery revisited. J Anat 195:57–63
Rose RE (1995) Acute carpal tunnel syndrome secondary to thrombosis of a persistent median artery. West Indian Med J 44:32–33
Sanudo JR, Chikwe J, Evans SE (1994) Anomalous pattern of median nerve associated with persistent median artery. J Anat 185:447–451
Singer E (1933) Embryological pattern persisting in the arteries of the arm. Anat Rec 55:403–409
Srivastava SK, Pande BS (1990) Anomalous pattern of median artery in the forearm of Indians. Acta Anatomica 138:193–194
Steinke H, Esche M, Schmidt W (2004) Mehrfachvarietäten der Handarterien. Ann Anat 186:375–377
Tandler J (1897) Zur Anatomie der Arterien der Hand. Anat Hefte 7:263–282
Toranto IR (1989) Aneurysm of the median artery causing recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome and anatomic review. Plast Reconstr Surg 84:510–512
Wilhelm K, Feldmeier C (1975) Seltene Genese eines Karpaltunnelsyndroms. Münch Med Wschr 117:161–162
Wood SJ, Abrahams PH, Sanudo JR, Ferreira BJ (1997) Bilateral superficial radial artery at the wrist associated with a radial origin of a unilateral median artery. J Anat 189:691–693
Wright C, MacFarlane I (1994) Aneurysm of the median artery causing carpal tunnel syndrome. Aust N Z J Surg 64:66–67
Zeiss J, Guilliam-Haidet L (1993) MR demonstration of a persistent median artery in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr 17:482–484
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mrs. S. Widmer for the final preparation of the arterial variations in the forearms and Mr. G. Ritschel for the excellent drawings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Claassen, H., Schmitt, O. & Wree, A. Large patent median arteries and their relation to the superficial palmar arch with respect to history, size consideration and clinic consequences. Surg Radiol Anat 30, 57–63 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-007-0290-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-007-0290-5