Abstract
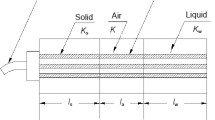
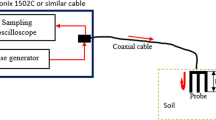
In a conducting medium, the energy of a time-domain reflectometry (TDR) pulse is dissipated and the signal is attenuated. Above a certain high conductivity, however, the signal is completely attenuated and the soil short-circuits the sensor. This behaviour of the signal with conductivity severely limits the TDR technique in measuring water content in highly saline soils. By reducing the direct contact between the conductive soil and the metallic sensor the energy of the pulse is better maintained. Different combinations were tried: we insulated the central wire, outer two wires, and all wires of a three-wire sensor with two different insulators. The first insulator was an adhesive polyethylene sheet usually used as a transparent cover and the second insulator was an adhesive tape. The insulated sensors were used to measure dielectric constants in non-saline soils and water and in saline soils. The sensors with the insulated centre wire preserve maximum energy and maintain a clear signal in saline soils. The insulating materials have very small dielectric constants. The TDR exerts a larger influence in the vicinity of the wires of the sensor during measurements. Therefore, the insulated sensor measures a dielectric constant which is smaller than the apparent dielectric constant of the surrounding medium. The type of insulating material also has an effect on the dielectric constant. Therefore, it is necessary to calibrate the sensors for the specific insulator.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 December 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mojid, M., Wyseure, G. & Rose, D. The use of insulated time-domain reflectometry sensors to measure water content in highly saline soils. Irrig Sci 18, 55–61 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002710050044
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002710050044