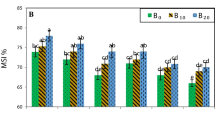
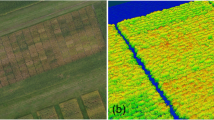
Abstract
Water scarcity, salinity stress and excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers are the main threats to agricultural production in arid/semi-arid Hetao Irrigation District (HID), China. This study investigated the effects of different water and nitrogen management strategies in various hydrological years. An agricultural hydrological model was employed to simulate changes in soil moisture, salinity, nitrogen application rates, crop growth, and yield. The results showed that an irrigation strategy aiming to water stress (MAD ≤ p) enabled the crop to bypass salinity stress and achieve higher yields. (For example, the wet year of 2020 required 78.8 and 75.3 mm of irrigation on July 29th and August 21th, respectively. The dry year of 2021 required 74.9, 75.7 and 76.8 mm of irrigation on July 20th, July 31th and August 15th, respectively.) The effect of MAD > p irrigation strategy on sunflower yield and nitrogen leaching was relatively small, and the use of MAD ≤ p irrigation strategy increased sunflower yield but also increased nitrogen leaching. The results of the combined piecewise structural equation modelling indicated that when soil water content was low and soil salinity was high, nitrogen fertilizer could be applied appropriately to reduce salt stress on the crop. Considering sunflower yield, water use efficiency, water infiltration, and nitrate N leaching together, a higher yield and less NO3−-N leaching could be obtained by irrigating 150 mm and applying 140 kg ha−1 of N in wet years and 240 mm and 180 kg ha−1 of N in dry years. The results were used to comprehensively evaluate the effectiveness of irrigation and nitrogen application in the HID, and to optimize irrigation and nitrogen management strategies, with the aim of reducing water consumption, enhancing irrigation efficiency, and mitigating the risk of nitrogen leaching.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Akhtar M, Hussain F, Ashraf MY, Qureshi TM, Akhter J, Awan AR (2012) Influence of salinity on nitrogen transformations in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 43:1674–1683. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2012.681738
Chang X, Gao Z, Wang S, Chen H (2019) Modelling long-term soil salinity dynamics using SaltMod in Hetao Irrigation District, China. Comput Electron Agric 156:447–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.12.005
Che Z, Wang J, Li J (2021) Determination of threshold soil salinity with consideration of salinity stress alleviation by applying nitrogen in the arid region. Irrig Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-021-00762-y
Chen W, Hou Z, Wu L, Liang Y, Wei C (2010) Effects of salinity and nitrogen on cotton growth in arid environment. Plant Soil 326:61–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9881-0
Dendooven L, Alcántara-Hernández RJ, Valenzuela-Encinas C, Luna-Guido M, Perez-Guevara F, Marsch R (2010) Dynamics of carbon and nitrogen in an extreme alkaline saline soil: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 42:865–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.02.014
Deng C, Zhang G, Pan X (2011) Photosynthetic responses in reed (Phragmites australis (CAV.) TRIN. ex Steud.) seedlings induced by different salinity-alkalinity and nitrogen levels. J Agric Sci Technol 13:687–699
Despotovic M, Nedic V, Despotovic D, Cvetanovic S (2015) Review and statistical analysis of different global solar radiation sunshine models. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 52:1869–1880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.08.035
Dou X, Shi H, Li R, Miao Q, Tian F, Yu D, Zhou L, Wang B (2021) Effects of controlled drainage on the content change and migration of moisture, nutrients, and salts in soil and the yield of oilseed sunflower in the Hetao Irrigation District. Sustainability 13:9835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179835
Feng Z-Z, Wang X-K, Feng Z-W (2005) Soil N and salinity leaching after the autumn irrigation and its impact on groundwater in Hetao Irrigation District, China. Agric Water Manag 71:131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2004.07.001
Feng G, Zhu C, Wu Q, Wang C, Zhang Z, Mwiya RM, Zhang L (2021) Evaluating the impacts of saline water irrigation on soil water-salt and summer maize yield in subsurface drainage condition using coupled HYDRUS and EPIC model. Agric Water Manag 258:107175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107175
He H, Liu L, Li Q, Yan W (2021) Feasibility of using Mg/Al-based layered double hydroxides as an inactivating agent to interrupt phosphorus release from contaminated agricultural drainage ditch sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 223:112599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112599
He H, Liu L, Zhu X (2022) Optimization of extreme learning machine model with biological heuristic algorithms to estimate daily reference evapotranspiration in Hetao Irrigation District of China. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 16:1939–1956. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2022.2125442
Huang Z, Zhang J, Ren D, Hu J, Xia G, Pan B (2022) Modeling and assessing water and nitrogen use and crop growth of peanut in semi-arid areas of Northeast China. Agric Water Manag 267:107621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107621
Lefcheck JS (2016) piecewiseSEM: Piecewise structural equation modelling in r for ecology, evolution, and systematics. Methods Ecol Evol 7:573–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12512
Legates DR, McCabe GJ Jr (1999) Evaluating the use of “goodness-of-fit” Measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour Res 35:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1029/1998WR900018
Liu Y, Li C, Anderson B, Zhang S, Shi X, Zhao S (2017) A modified QWASI model for fate and transport modeling of mercury between the water-ice-sediment in Lake Ulansuhai. Chemosphere 176:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.111
Liu Y, Wang H, Jiang Z, Wang W, Xu R, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Li A, Liang Y, Ou S, Liu X, Cao S, Tong H, Wang Y, Zhou F, Liao H, Hu B, Chu C (2021) Genomic basis of geographical adaptation to soil nitrogen in rice. Nature 590:600–605. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03091-w
Liu M, Shi H, Paredes P, Ramos TB, Dai L, Feng Z, Pereira LS (2022) Estimating and partitioning maize evapotranspiration as affected by salinity using weighing lysimeters and the SIMDualKc model. Agric Water Manag 261:107362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107362
Ma T, Zeng W, Lei G, Wu J, Huang J (2021) Predicting the rooting depth, dynamic root distribution and the yield of sunflower under different soil salinity and nitrogen applications. Ind Crops Prod 170:113749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113749
Ma T, Chen K, He P, Dai Y, Yin Y, Peng S, Ding J, Yu S, Huang J (2022) Sunflower photosynthetic characteristics, nitrogen uptake, and nitrogen use efficiency under different soil salinity and nitrogen applications. Water 14:982. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060982
Munns R (2002) Salinity, growth and phytohormones. In: Läuchli A, Lüttge U (eds) Salinity: environment–plants–molecules. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 271–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-48155-3_13
Pereira LS, Teodoro PR, Rodrigues PN, Teixeira JL (2003) Irrigation scheduling simulation: the model Isareg. In: Rossi G, Cancelliere A, Pereira LS, Oweis T, Shatanawi M, Zairi A (eds) Tools for drought mitigation in Mediterranean regions, 水科学与技术图书馆. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 161–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0129-8_10
Reddy N, Crohn DM (2014) Effects of soil salinity and carbon availability from organic amendments on nitrous oxide emissions. Geoderma 235–236:363–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.07.022
Rietz DN, Haynes RJ (2003) Effects of irrigation-induced salinity and sodicity on soil microbial activity. Soil Biol Biochem 35:845–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00125-1
Risch AC, Zimmermann S, Ochoa-Hueso R, Schütz M, Frey B, Firn JL, Fay PA, Hagedorn F, Borer ET, Seabloom EW, Harpole WS, Knops JMH, McCulley RL, Broadbent AAD, Stevens CJ, Silveira ML, Adler PB, Báez S, Biederman LA, Blair JM, Brown CS, Caldeira MC, Collins SL, Daleo P, di Virgilio A, Ebeling A, Eisenhauer N, Esch E, Eskelinen A, Hagenah N, Hautier Y, Kirkman KP, MacDougall AS, Moore JL, Power SA, Prober SM, Roscher C, Sankaran M, Siebert J, Speziale KL, Tognetti PM, Virtanen R, Yahdjian L, Moser B (2019) Soil net nitrogen mineralisation across global grasslands. Nat Commun 10:4981. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12948-2
Rivett MO, Buss SR, Morgan P, Smith JWN, Bemment CD (2008) Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: a review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res 42:4215–4232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.07.020
Scarlett K, Denman S, Clark DR, Forster J, Vanguelova E, Brown N, Whitby C (2021) Relationships between nitrogen cycling microbial community abundance and composition reveal the indirect effect of soil pH on oak decline. ISME J 15:623–635. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-00801-0
Shenker M, Ben-Gal A, Shani U (2003) Sweet corn response to combined nitrogen and salinity environmental stresses. Plant Soil 256:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026274015858
Slavich PG, Petterson GH (1993) Estimating the electrical conductivity of saturated paste extracts from 1:5 soil, water suspensions and texture. Soil Res 31:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1071/sr9930073
Tamagno S, Eagle AJ, McLellan EL, van Kessel C, Linquist BA, Ladha JK, Pittelkow CM (2022) Quantifying N leaching losses as a function of N balance: a path to sustainable food supply chains. Agric Ecosyst Environ 324:107714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2021.107714
Tripathi SB, Gurumurthi K, Panigrahi AK, Shaw BP (2007) Salinity induced changes in proline and betaine contents and synthesis in two aquatic macrophytes differing in salt tolerance. Biol Plant 51:110–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0022-z
Van Dam JC, Huygen J, Wesseling JG, Feddes RA, Kabat P, Van Walsum PEV, Groenendijk P, Van Diepen CA (1997) Theory of SWAP version 2.0; Simulation of water flow, solute transport and plant growth in the soil-water-atmosphere-plant environment. DLO Winand Staring Centre
Wang Z-H, Li S-X (2019) Chapter three—nitrate N loss by leaching and surface runoff in agricultural land: a global issue (a review). In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in agronomy. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 159–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2019.01.007
Wang T, Wang Z, Zhang J, Ma K (2022) An optimum combination of irrigation amount, irrigation water salinity and nitrogen application rate can improve cotton (for fiber) nitrogen uptake and final yield. Ind Crops Prod 187:115386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115386
Williams JR, Jones CA, Kiniry JR, Spanel DA (1989) The EPIC crop growth model. Trans. ASAE 32, 0497–0511. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.31032
Willmott CJ, Matsuura K (2005) Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim Res 30:79–82. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr030079
Wu ZY, Lu GH, Wen L, Lin CA (2011) Reconstructing and analyzing China’s fifty-nine year (1951–2009) drought history using hydrological model simulation. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:2881–2894. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-2881-2011
Wu Lu, Misselbrook TH, Feng L, Wu L (2020) Assessment of nitrogen uptake and biological nitrogen fixation responses of soybean to nitrogen fertiliser with SPACSYS. Sustainability 12:5921. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12155921
Xu X, Huang G, Sun C, Pereira LS, Ramos TB, Huang Q, Hao Y (2013) Assessing the effects of water table depth on water use, soil salinity and wheat yield: searching for a target depth for irrigated areas in the upper Yellow River basin. Agric Water Manag 125:46–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2013.04.004
Xu X, Sun C, Qu Z, Huang Q, Ramos TB, Huang G (2015) Groundwater recharge and capillary rise in irrigated areas of the upper yellow river basin assessed by an agro-hydrological model. Irrig Drain 64:587–599. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.1928
Xu X, Sun C, Huang G, Mohanty BP (2016) Global sensitivity analysis and calibration of parameters for a physically-based agro-hydrological model. Environ Model Softw 83:88–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2016.05.013
Xu X, Sun C, Neng F, Fu J, Huang G (2018) AHC: an integrated numerical model for simulating agroecosystem processes—model description and application. Ecol Model 390:23–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2018.10.015
Xu M, Wang G, Wang Z, Hu H, Kumar Singh D, Tian S (2022) Temporal and spatial hydrological variations of the Yellow River in the past 60 years. J Hydrol 609:127750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127750
Yan M, Pan G, Lavallee JM, Conant RT (2020) Rethinking sources of nitrogen to cereal crops. Glob Change Biol 26:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14908
Yao R, Li H, Yang J, Zhu W, Yin C, Wang X, Xie W, Zhang X (2022) Combined application of biochar and N fertilizer shifted nitrification rate and amoA gene abundance of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in salt-affected anthropogenic-alluvial soil. Appl Soil Ecol 171:104348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104348
Yuan B-C, Li Z-Z, Liu H, Gao M, Zhang Y-Y (2007) Microbial biomass and activity in salt affected soils under arid conditions. Appl Soil Ecol 35:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2006.07.004
Zeng W-Z, Xu C, Wu J-W, Huang J-S, Ma T (2013) Effect of salinity on soil respiration and nitrogen dynamics. Ecol Chem Eng S 20:519–530. https://doi.org/10.2478/eces-2013-0039
Zhang D, Li W, Xin C, Tang W, Eneji AE, Dong H (2012) Lint yield and nitrogen use efficiency of field-grown cotton vary with soil salinity and nitrogen application rate. Field Crops Res 138:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2012.09.013
Zhao Y, Pang H, Wang J, Huo L, Li Y (2014) Effects of straw mulch and buried straw on soil moisture and salinity in relation to sunflower growth and yield. Field Crops Res 161:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.02.006
Zhu H, Yang J, Yao R, Wang X, Xie W, Zhu W, Liu X, Cao Y, Tao J (2020) Interactive effects of soil amendments (biochar and gypsum) and salinity on ammonia volatilization in coastal saline soil. CATENA 190:104527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104527
Zúñiga GE, Argandoña VH, Corcuera LJ (1989) Distribution of glycine-betaine and proline in water stressed and unstressed barley leaves. Phytochemistry 28:419–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(89)80024-X
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52170160, 51879085).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH: Designed and performed the experiments, Formal analysis, Analyzed the data, Visualization and wrote and edited the manuscript. LL: Designed the experiments, Provided the financial support, Commented the article, Edited, and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this paper and the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Yunkai Li.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Liu, L. Study on irrigation scheme and nitrogen application to sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) in saline farmland in the arid/semi-arid region of Hetao Irrigation District. Irrig Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-024-00928-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-024-00928-4