Abstract
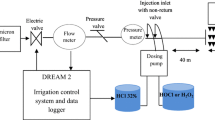
The anti-clogging ability of the emitters depends on their automatic self-cleaning mechanism, the structure and geometry of the flow path, and the type of material carried by irrigation water. Suspended solids in fish farm effluents are mostly organic with a low volumetric mass and high compressibility. In the present study, three types of pressure-compensating emitters, two discharges with three flushing mechanisms of emitter were evaluated. The three emitter flushing mechanisms were: (1) continuous self-cleaning with silicone diaphragm, (2) on–off self-cleaning with silicone diaphragm, and (3) continuous self-cleaning with silicone rubber path. Four drip irrigation units for irrigation with fresh water (control) and effluent of a rainbow trout fish farm were designed and implemented. Two of these units were for control treatment (with and without filtration system) and the other two for effluent treatment (with and without filtration system). A total of 270 pressure compensating emitters of Microflapper, Netafim and Corona brands with discharge of 4 and 8 l h−1 through 24 irrigation events lasting 192 operating hours were evaluated over a period of 10 weeks. The indices of Relative Discharge (Dra), the Christiansen Uniformity Coefficient (CU) and Season Relative Discharge Coefficient of Variation (CV (Dra) S) were used. During the irrigation season, the changes in Dra and CU fluctuated, especially for the Microflapper emitter. The maximum percentage of completely clogged emitters was 83.3% and the lowest Dra was 14% with Microflapper emitters using not filtered effluent. The Dra for these emitters with effluent treatments under no filtration decreased significantly (p < 0.05) compared to control treatment. Without filtration, the type of water, irrigation periods, emitter type and discharge and their interaction affected the relative discharge significantly (p < 0.05). No completely clogged emitter was found under filtration conditions. For both control and effluent treatments, filtration significantly (p < 0.05) increased Dra of 4 and 8 l h−1 Microflapper and 8 l h−1Netafim emitters. Effluent filtration improved Dra of Microflapper emitters by an average of 41%. The 4 l h−1 Netafim emitter performed best in all conditions independently of irrigation water and filtration system, without significant (p < 0.05) differences between them. Overall, the performance of Netafim and Corona emitters was similar and better than Microflapper, which showed the independence of the relative discharge of the emitter to the type of self-cleaning mechanism and its dependence on the type of structure from its self-cleaning mechanism. For each brand, the performance of the emitters with lower discharge (4 l h−1) was better than the higher discharge (with significant difference in some cases).













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adin A, Sacks M (1991) Dripper-clogging factors in wastewater irrigation. J Irrig Drain Eng 117:813–826. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(1991)117:6(813)
Ayers R, Westcot D (1994) Water quality for agriculture. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 29 Rev. 1. FAO, Rome
Bralts VF, Wu I-P, Gitlin HM (1981) Manufacturing variation and drip irrigation uniformity. Trans ASAE 24:113–119. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.34209
Bucks DA, Nakayama F, Gilbert R (1979) Trickle irrigation water quality and preventive maintenance. Agric Water Manag 2:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3774(79)90028-3
Camp C (1998) Subsurface drip irrigation: a review. Trans ASAE 41:1353
Capra A, Scicolone B (1998) Water quality and distribution uniformity in drip/trickle irrigation systems. J Agric Eng Res 70:355–365. https://doi.org/10.1006/jaer.1998.0287
Chen S, Timmons MB, Aneshansley DJ, Bisogni JJ Jr (1993) Suspended solids characteristics from recirculating aquacultural systems and design implications. Aquaculture 112:143–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(93)90440-A
Christiansen J (1941) The uniformity of application of water by sprinkler systems. Agric Eng 22:89–92
Couture I (2004) M. Analyse d’eau pour fin d’irrigation. MAPAQ Montérégie-Est AGRI-VISION, 1–8, Québec, Canada.
Crites R, Tchobanoglous G (1998) Small and decentralized wastewater management systems. vol 628.3 C934s. Mc Graw Hill, London
Enciso-Medina J, Multer W, Lamm F (2011) Management, maintenance, and water quality effects on the long-term performance of subsurface drip irrigation systems. Appl Eng Agric 27:969–978
Gurung TB (2012) Integrated aquaculture within agriculture irrigation for food security and adaptation to climate change. Hydro Nepal. https://doi.org/10.3126/hn.v11i1.7214
Han S, Li Y, Xu F, Sun D, Feng J, Liu Z, Wu R, Wang Zh (2018) Effect of lateral flushing on emitter clogging under drip irrigation with Yellow River water and a suitable method. Irrig Drain 67:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2193
Klontz GW (1991) Fish for the future: concepts and methods of intensive aquaculture. University of Idaho, Moscow
Li N, Kang Y, Li X, Wan S, Zhang C, Wang X (2019) Lateral flushing with fresh water reduced emitter clogging in drip irrigation with treated effluent. Irrig Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-019-00637-3
Liu Z, Xiao Y, Li Y, Zhou B, Feng J, Han S, Muhammad T (2019) Influence of operating pressure on emitter anti-clogging performance of drip irrigation system with high-sediment water. Agric Water Manag 213:174–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.10.017
Manbari N, Maroufpoor E, Aminpour Y, Kamangar BB, Puig-Bargués J (2020) Effect of a combined filtration system and drip irrigation laterals on quality of rainbow trout farm effluent. Irrig Sci 38:131–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-019-00654-2
Maroufpoor E, Aminpour Y, Kamangar BB, Puig-Bargués J (2020) Clogging rate of pressure compensating emitters in irrigation with rainbow trout fish farm effluent. Irrig Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-020-00697-w
Mu NJ (2005) Experimental study on the anti-clogging performance of Labyrinth passage of emitters. China Agricultural University, Beijing (in Chinese)
Mustapha A, Driss B, Khadija E, Mohammed B (2013) Optimization and efficiency in rainbow trout fed diets for reduce the environment impact in Morocco. Univers J Environ Res Technol 3:318–325
Patterson R, Watts K (2003) Micro-particles in recirculating aquaculture systems: particle size analysis of culture water from a commercial Atlantic salmon site. Aquac Eng 28:99–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8609(03)00003-7
Pei Y, Li Y, Liu Y, Zhou B, Shi Z, Jiang Y (2014) Eight emitters clogging characteristics and its suitability under on-site reclaimed water drip irrigation. Irrig Sci 32:141–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-013-0420-2
Pinto MF, Molle B, Alves DG, Ait-Mouheb N, de Camargo AP, Frizzone JA (2017) Flow rate dynamics of pressure-compensating drippers under clogging effect. Revista Brasileira De Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental 21(5):304–309. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-1929/agriambi.v21n5p304-309
Pitts DJ, Haman DZ, Smajstria A (1990) Causes and prevention of emitter plugging in micro irrigation systems. Bulletin-Florida Cooperative Extension Service, University of Florida, Gainesville
Puig-Bargués J, Arbat G, Barragán J, Ramírez de Cartagena F (2005) Hydraulic performance of drip irrigation subunits using WWTP effluents. Agric Water Manag 77:249–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2004.09.032
Puig-Bargués J, Arbat G, Elbana M, Duran-Ros M, Barragán J, Ramírez de Cartagena F, Lamm FR (2010) Effect of flushing frequency on emitter clogging in microirrigation with effluents. Agric Water Manag 97:883–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2010.01.019
Ravina I, Paz E, Sofer Z, Marcu A, Shisha A, Sagi G (1992) Control of emitter clogging in drip irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Irrig Sci 13:129–139
Song P, Li Y, Zhou B, Zhou C, Zhang Z, Li J (2017) Controlling mechanism of chlorination on emitter bio-clogging for drip irrigation using reclaimed water. Agric Water Manag 184:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.12.017
Tchobanoglous G, Schroeder E (1985) Water quality: characteristics, modeling, modification. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL, Stensel HD (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. Metcalf & Eddy Inc McGraw-Hill Inc, USA for Environmental Research Information Cincinnati, New York, p 27
Wang J, Li G, Qiu X, Xu P (2003) Effects of flow passage forms on hydraulic performance of emitters Trans CSAE 21:100–103
Wang DM (2007a) Study on the Hydraulic and Anti-clogging performance of flow-passage form and size for Labyrinth emitters. M.Sc. thesis. China Agriculture University, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wang JD (2007b) Study on the hydraulic and anti-clogging performance of emitters. M.Sc thesis. China Agriculture University, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wei Q, Shi Y, Lu G, Dong W, Huang S (2008) Rapid evaluations of anticlogging performance of drip emitters by laboratorial short-cycle tests. J Irrig Drain Eng 134:298–304. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437
Yao B, Liu Z, Zhang J (2003) Study on the effect of channel path on characteristics parameters of Labyrinth emitters. Water Saving Irrig 5:38–39
Zhou B, Li Y, Song P, Xu Z (2014) Dynamic characteristics and inducing mechanism of emitter clogging in the drip irrigation system using Yellow River water. J Irrig Drain 33:123–128
Zhou B, Li Y, Song P, Xu Z, Bralts V (2016) A kinetic model for biofilm growth inside non-PC emitters under reclaimed water drip irrigation. Agric Water Manag 168:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.01.007
Zhou B, Li Y, Song P, Zhou Y, Yu Y, Bralts V (2017) Anti-clogging evaluation for drip irrigation emitters using reclaimed water. Irrig Sci 35:181–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-016-0530-8
Funding
This study received funding from the Agricultural Jihad Organization of Kurdistan province, Government of Iran under Grant Agreement no. 1/409.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any of the companies with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aminpour, Y., Amiri, P., Maroufpoor, E. et al. Effect of type of emitter self-cleaning mechanism and its structure on the performance of drip irrigation system using effluent of rainbow trout fish. Irrig Sci 40, 163–175 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-022-00767-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-022-00767-1