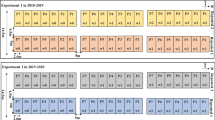
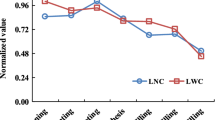
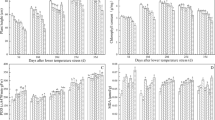
Abstract
The use of spectral data to predict soil water content has gained wide application in agricultural science. However, it is difficult to guarantee crop water status prediction accuracy based on spectral parameters because the physiological indices and crop water status change daily. Therefore, screening representative crop growth indicators could improve the accuracy of the crop water prediction model. In this study, winter wheat was used as the crop of interest. Initially, spectral characteristics proposed by previous studies were selected and screened. Subsequently, soil water content prediction models were constructed based on a combination of crop leaf area index (LAI) and its spectral characteristics and crop growth physiological indices to predict the field soil water content. These models were constructed using three types of parameters, including single spectral characteristics of canopy water content, single spectral characteristics of canopy water content and measured LAI, as well as spectral characteristics of both canopy water content and LAI. The coefficient of determination (R2) that reflects the reliability of the models was 0.31–0.36, 0.57–0.62, and 0.45–0.54, respectively. The model constructed based on measured LAI and spectral characteristics was the most accurate in each growth period and the whole growth period of winter wheat, followed by that based on dual-spectral characteristics, whereas the single spectral characteristics model was the least accurate. The R2 of the model constructed based on measured LAI and characteristic spectral parameters of canopy water content increased by 0.47, 0.16, 0.69, and 0.37 during the entire growth period, respectively, implying that combining LAI with spectral characteristics can improve the accuracy of soil water content prediction models. However, it was difficult to obtain the relevant measured index for the models constructed using measured LAI. Therefore, the dual-spectral characteristics model was recommended as the most appropriate for practical application.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amani M, Mobasheri MR, Mahdavi S (2018) Contemporaneous estimation of leaf area index and soil moisture using the red-NIR spectral space. Remote Sens Lett 9:264–273. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2017.1415472
An M, Han Y, Xu L, Wang X, Ao C, Pang D (2019) KINEROS2-based simulation of total nitrogen loss on slopes under rainfall events. CATENA 177:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.01.039
Babar MA, Reynolds MP, Van Ginkel M, Klatt AR, Raun WR, Stone ML (2006) Spectral reflectance indices as a potential indirect selection criterion for wheat yield under irrigation. Crop Sci 46:578–588. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2005.0059
Blackburn GA (1998) Quantifying chlorophylls and carotenoids at leaf and canopy scales, an evaluation of some hyperspectral approaches. Remote Sens Environ 66:273–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(98)00059-5
Broge NH, Leblanc E (2001) Comparing prediction power and stability of broadband and hyperspectral vegetation indices for estimation of green leaf area index and canopy chlorophyll density. Remote Sens Environ 76:156–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(00)00197-8
Chen M, Willgoose GR, Saco PM (2015) Investigating the impact of leaf area index temporal variability on soil moisture predictions using remote sensing vegetation data. J Hydrol 522:274–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.12.027
Curran PJ, Windham WR, Gholz HL (1995) Exploring the relationship between reflectance red edge and chlorophyll concentration in slash pine leaves. Tree Physiol 15:203–206. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/15.3.203
Cutforth HW, Angadi SV, McConkey BG, Miller PR, Ulrich D, Gulden R, Volkmar K, Entz M, Brandt SA (2013) Comparing rooting characteristics and soil water withdrawal patterns of wheat with alternative oilseed and pulse crops grown in the semiarid Canadian prairie. Can J Soil Sci 93:147–160. https://doi.org/10.4141/CJSS2012-081
Daughtry CST, Hunt JER (2008) Mitigating the effects of soil and residue water contents on remotely sensed estimates of crop residue cove. Remote Sens Environ 124:1647–1657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.08.006
de Fries RS, Townshend JRG (1994) NDVI-derived land cover classifications at a global scale. Int J Remote Sens 15:3567–3586. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169408954345
de Jong SM, Addink EA, Doelman JC (2014) Detecting leaf-water content in Mediterranean trees using high-resolution spectrometry. Int J Appl Earth Obs 27:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2013.09.011
de Neiff AP, Neiff JJ, Casco SL (2006) Leaf litter decomposition in three wetland types of the Paraná River floodplain. Wetlands 26(2):558–566. https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2006)26[558:LLDITW]2.0.CO;2
Dzikiti S, Verreynne JS, Stuckens J, Strever A, Verstraeten WW, Swennen R, Coppin P (2010) Determining the water status of Satsuma mandarin trees [Citrus Unshiu Marcovitch] using spectral indices and by combining hyperspectral and physiological data. Agric For Meteorol 150:369–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2009.12.005
El-Hendawy SE, Al-Suhaibani NA, Elsayed S, Hassan WM, Dewir YH, Refay Y, Abdella KA (2019) Potential of the existing and novel spectral reflectance indices for estimating the leaf water status and grain yield of spring wheat exposed to different irrigation rates. Agric Water Manag 217:356–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.03.006
Elvanidi A, Katsoulas N, Bartzanas T, Ferentinos KP, Kittas C (2017) Crop water status assessment in controlled environment using crop reflectance and temperature measurements. Precis Agric 18:332–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-016-9492-3
Feng R, Zhang Y, Yu W, Hu W, Wu J, Ji R, Wang H, Zhao X (2013) Analysis of the relationship between the spectral characteristics of maize canopy and leaf area index under drought stress. Acta Ecol Sin 33:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2013.09.001
Fischer C, Leimer S, Roscher C, Ravenek J, de Kroon H, Kreutziger Y, Baade J, Beßler H, Eisenhauer N, Weigelt A, Mommer L, Lange M, Gleixner G, Wilcke W, Schröder B, Hildebrandt A (2019) Plant species richness and functional groups have different effects on soil water content in a decade-long grassland experiment. J Ecol 1071:127–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.13046
Gitelson AA, Merzlyak MN, Lichtenthaler HK (1996) Detection of red edge position and chlorophyll content by reflectance measurements near 700 nm. J Plant Physiol 148:501–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0176-1617(96)80285-9
Gupta RK, Vijayan D, Prasad TS (2003) Comparative analysis of red-edge hyperspectral indices. Adv Space Res 32:2217–2222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1177(03)90545-X
Haboudane D, Miller JR, Pattey E, Zarco-Tejada PJ, Strachan IB (2004) Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture. Remote Sens Environ 90:337–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.12.013
Hansen PM, Schjoerring JK (2003) Reflectance measurement of canopy biomass and nitrogen status in wheat crops using normalized difference vegetation indices and partial least squares regression. Remote Sens Environ 86:542–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(03)00131-7
Hatfield JL, Cryder M, Basso B (2020) Remote sensing, advancing the science and the applications to transform agriculture. IT Prof 223:42–45. https://doi.org/10.1109/MITP.2020.2986102
Heppell J, Payvandi S, Zygalakis KC, Smethurst J, Fliege J, Roose T (2014) Validation of a spatial-temporal soil water movement and plant water uptake model. Geotechnique 647:526–539. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.13.P.142
Jiang Z, Huete AR, Didan K, Miura T (2008) Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band. Remote Sens Environ 112:3833–3845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2008.06.006
Jiang J, Zhang Z, Cao Q, Liang Y, Krienke B, Tian Y, Liu X (2020) Use of an active canopy sensor mounted on an unmanned aerial vehicle to monitor the growth and nitrogen status of winter wheat. Remote Sens 12:3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223684
Kanning M, Kühling I, Trautz D, Jarmer T (2018) High-resolution UAV-based hyperspectral imagery for LAI and chlorophyll estimations from wheat for yield prediction. Remote Sens 10:2000. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122000
Lausch A, Pause M, Schmidt A, Salbach C, Gwillym-Margianto S, Merbach I (2013) Temporal hyperspectral monitoring of chlorophyll, LAI, and water content of barley during a growing season. Can J Remote Sens 39:191–207. https://doi.org/10.5589/m13-028
Le Maire G, Francois C, Soudani K, Berveiller D, Pontailler JY, Bréda N, Genet H, Davi H, Dufrene E (2008) Calibration and validation of hyperspectral indices for the estimation of broadleaved forest leaf chlorophyll content, leaf mass per area, leaf area index and leaf canopy biomass. Remote Sens Environ 112:3846–3864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2008.06.005
Li Y, Zhu Y, Dai T, Tian Y, Cao W (2006) Quantitative relationships between leaf area index and canopy reflectance spectra of wheat. Chinese J Appl Ecol 178:1443–1447 (in Chinese)
Li Z, Le Chevalier V, Cournède PH (2009) Towards a continuous approach of functional-structural plant growth. In: Third international symposium on plant growth modeling, simulation, visualization and applications (PMA09), Beijing, China, pp 334–340. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00529351
Liang L, Geng D, Yan J, Qiu S, Di L, Wang S, Xu L, Wang L, Kang JLL (2020) Estimating crop LAI using spectral feature extraction and the hybrid inversion method. Remote Sens-Basel 12:3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213534
Lim H, Cheon E, Lee D, Jeon J, Lee S (2020) Classification of granite soils and prediction of soil water content using hyperspectral visible and near-infrared imaging. Sensors-Basel 20:1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061611
Liu Z (1997) Study on the correction coefficient and leaf area index of winter wheat spring leaf area. J Triticeae Crop 01:42–44 (in Chinese)
Liu F, Liu X, Ding C, Wu L (2015) The dynamic simulation of rice growth parameters under cadmium stress with the assimilation of multi-period spectral indices and crop model. Field Crop Res 183:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.08.004
Luo Y, Chang X, Peng S, Khan S, Wang W, Zheng Q, Cai X (2014) Short-term forecasting of daily reference evapotranspiration using the Hargreaves–Samani model and temperature forecasts. Agric Water Manag 136:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2014.01.006
Malenovský Z, Mishra KB, Zemek F, Rascher U, Nedbal L (2009) Scientific and technical challenges in remote sensing of plant canopy reflectance and fluorescence. J Exp Bot 6011:2987–3004. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp156
Marshak A, Knyazikhin Y, Davis AB, Wiscombe WJ, Pilewskie P (2000) Cloud-vegetation interaction: use of normalized difference cloud index for estimation of cloud optical thickness. Geophys Res Lett 27:1695–1698. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999gl010993
Nguyen HT, Lee BW (2006) Assessment of rice leaf growth and nitrogen status by hyperspectral canopy reflectance and partial least square regression. Eur J Agron 244:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2006.01.001
Pan J, Li T (2013) Extracting desertification from Landsat TM imagery based on spectral mixture analysis and albedo-vegetation feature space. Nat Hazards 682:915–927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0665-3
Penuelas J, Pinol J, Ogaya R, Filella I (1997) Estimation of plant water concentration by the reflectance water index WI R900/R970. Int J Remote Sens 18:2869–2872. https://doi.org/10.1080/014311697217396
Prasad B, Carver BF, Stone ML, Babar MA, Raun WR, Klatt AR (2007) Genetic analysis of indirect selection for winter wheat grain yield using spectral reflectance indices. Crop Sci 47:1416–1425. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.08.0546
Quemada M, Daughtry CST (2016) Spectral indices to improve crop residue cover estimation under varying moisture conditions. Remote Sens-Basel 88:660. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080660
Richardson AJ, Wiegand CL, Anderson GL, Gerbermann AH, Bray M, Summy KR, Sugden EA (1996) Six exemplary applications of GIS technology to subtropical Texas agriculture and natural resources. Geocarto Int 11:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049609354523
Sabater JM, Rüdiger C, Calvet JC, Fritz N, Jarlan L, Kerr Y (2008) Joint assimilation of surface soil moisture and LAI observations into a land surface model. Agric For Meteorol 148:1362–1373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2008.04.003
Sharpe PJH, Walker J, Penridge LK, Wu HI (1985) A physiologically based continuous-time Markov approach to plant growth modelling in semi-arid woodlands. Ecol Model 29(1–4):189–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3800(85)90053-5
Shi BQ, Zhang XL, Bai X, Zhang XX (2015) Chlorophyll estimation model of pinus tabulaeformis based on “Sanbian” parameters. J Northeast for Univ 43:80–83 (in Chinese)
Si Z, Zain M, Mehmood F, Wang G, Gao Y, Duan A (2020) Effects of nitrogen application rate and irrigation regime on growth, yield, and water-nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated winter wheat in the north china plain. Agric Water Manag 231:106002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106002
Sims DA, Gamon JA (2002) Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sens Environ 81:337–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(02)00010-x
Valipour M, Ziatabar-Ahmadi M, Raeini-Sarjaz M, Gholami-Sefidkouhi MA, Shahnazari A, Fazlola R, Darzi-Naftchali A (2015) Agricultural water management in the world during past half century. Arch Agron Soil Sci 615:657–678. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2014.944903
Wang DC, Zhang GL, Rossiter DG, Zhang JH (2016) The prediction of soil texture from visible–near-infrared spectra under varying moisture conditions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 80:420–427. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2015.10.0379
Wang L, Wang X, Chen L, Song NP, Yang XG (2021) Trade-off between soil moisture and species diversity in semi-arid steppes in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci Total Environ 750:141646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141646
Wei S, Yin T, Dissegna MA, Whittle AJ, Ow GLF, Yusof MLM, Lauret N, Gastellu-Etchegorry JP (2020) An assessment study of three indirect methods for estimating leaf area density and leaf area index of individual trees. Agric For Meteorol 292–293:108101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2020.108101
Yuan J, Wang X, Yan C, Wang S, Ju X, Li Y (2019) Soil moisture retrieval model for remote sensing using reflected hyperspectral information. Remote Sens-Basel 11:366. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030366
Yue J, Tian Q, Dong X, Xu N (2020) Using broadband crop residue angle index to estimate the fractional cover of vegetation, crop residue, and bare soil in cropland systems. Remote Sens Environ 237:111538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111538
Zhang Y, Zheng L, Li M, Deng X, Ji R (2015) Predicting apple sugar content based on spectral characteristics of apple tree leaf in different phenological phases. Comput Electron Agric 112:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.01.006
Zhang Z, Zhou XB, Chen YH (2016) Effects of irrigation and precision planting patterns on photosynthetic product of wheat. Agron J 108:2322. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2016.01.0051
Zhang X, Zhang H, Wang C, Tang Y, Zhang B, Wu F, Wang J, Zhang Z (2021) Soil moisture estimation based on the distributed scatterers adaptive filter over the QTP permafrost region using sentinel-1 and high-resolution TerraSAR-X data. Int J Remote Sens 423:902–928. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2020.1820616
Zhu Y, Weindorf DC, Chakraborty S, Haggard B, Johnson S, Bakr N (2010) Characterizing surface soil water with field portable diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. J Hydrol 391:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.07.014
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0407703), The Key R & D projects of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (2018BBF02022), the IWHR Research & Development Support Program (ID0145B082017), Beijing Municipal Education Commission Innovative Transdisciplinary Program “Ecological Restoration Engineering”, and the National Key Laboratory Open Fund (IWHR-SKL-KF201903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA: formal analysis, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. WX: methodology, writing—review and editing. YH: conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, and resource mobilization. QB: result validation and resource mobilization. ZP: result validation and resource mobilization. BZ: result validation and resource mobilization. ZW: result validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, M., Xing, W., Han, Y. et al. The optimal soil water content models based on crop-LAI and hyperspectral data of winter wheat. Irrig Sci 39, 687–701 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-021-00745-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-021-00745-z