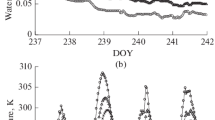
Abstract
The objective of this study was to explore the soil water dynamics under micro-advective conditions. A numerical model was introduced to estimate the airflow turbulence generated by the crop canopy. The vapor pressure and air temperature in the vicinity of the soil surface were estimated from the wind velocity predicted by this model. The energy budget on the soil surface was estimated using wind velocity, vapor pressure, and air temperature simulated by numerical models. The soil water content and temperature were predicted using the simulation model describing the water and heat transfer in soil. Using the energy budget, the accuracy of this model was experimentally verified using a wind tunnel. Spatial changes of the soil water content simulated by this model were reproduced by the experiment. This indicated that the numerical model for estimating the soil water movement under micro-scale advection considering the crop body was satisfactory.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonachela S, Orgaz F, Villalobos FJ, Fereres E (2001) Soil evaporation from drip-irrigated olive orchards. Irrig Sci 20:65–71
Chamberlain AC (1968) Transport of gases to and from surface with bluff and wave-like roughness elements. Q J Roy Met Soc 94:318–332
Daiz-Espejo A, Verhoef A, Knight R (2005) Illustration of micro-scale advection using grid-pattern mini-lysimeters. Agri Forest Meteorol 129:39–52
Harazono Y, Yoshimoto M, Kawamoto T (1996) Photosynthesis rate distribution and light use efficiency within a soybean canopy determined by numerical simulation with the Neo soil-plant-atmosphere model. J Agric Meteoro1 52(4):281–291 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Matthias AD, Salehi R, Warrick AW (1986) Bare soil evaporation near a surface point-source emitter. Agric Water Manag 11:257–277
McKee S, Tomé MF, Ferreira VG, Cuminato JA, Castelo A, Sousa FS, Mangiavacchi N (2008) The MAC method. Comput Fluids 37:907–930
McNaughton KG (1976) Evaporation and advection 1-evaporation from extensive homogeneous surface. Quart J R Met 102:181–191
Ohashi M (2004) A study on analysis of airflow around an individual tree. J Environ Eng AIJ 578:91–96
Philip JR (1959) The theory of local advection 1. Ibid 16:535–547
Raupach MR, Shaw RH (1982) Averaging procedure for flow within vegetation canopies. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 22:79–90
Rider NE, Philip JR, Bradley EF (1963) The horizontal transport of heat and moisture—a micrometeorological study. Quart J Roy Met Soc 89:507–530
Seginer I, Mulhearn PJ, Bradley EF, Finnigan JJ (1976) Turbulent flow in a model plant canopy. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 10:423–453
Wilson NR, Shaw RH (1977) A higher order closure model for canopy flow. J Appl Meteor 16:1197–1205
Yamada T (1982) A numerical model study of turbulent airflow in and above a forest canopy. J Meteol Soc Jpn 60(1):439–453
Young DM (1971) Iterative solution of large linear systems. Academic Press, New York
Yuge K, Haraguchi T, Nakano Y, Kuroda M, Anan M (2005) Quantification of soil surface evaporation under micro-scale advection in drip-irrigated fields. Paddy Water Environ 3(1):5–12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuge, K., Anan, M. & Shinogi, Y. Effects of the micro-scale advection on the soil water movement in micro-irrigated fields. Irrig Sci 32, 159–167 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-013-0413-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-013-0413-1