Abstract
Purpose
To compare safety, efficacy, radiation exposure and patients comfort in patients of transradial access (TRA) in patients undergoing TARE compared with transfemoral access (TFA) including patient radiation exposure and patient comfort.
Methods
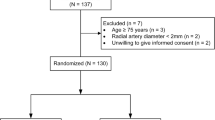
A total of 222 patients undergoing technetium-99 m macro-aggregated albumin and TARE were retrospectively reviewed from 2017 to 2022. We analyzed procedure-related pain, quality of life, recovery time, procedure time, fluoroscopy time (FT), air kerma product and air kerma (AK) to compare the two access for intervention for HCC.
Results
A total of 222 [(TFA (n = 147) and TRA (n = 75)] patients who underwent TARE for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) were included. No significant difference was found regarding FT and DAP in comparison of TRA and TFA. (p = 0.385, p = 0.842). While the mean AK was 892.7 mGy in TFA patients, it was 545.2 mGy in TRA patients and there was statistically significant difference (p = 0.017). Patients who underwent TRA had significantly shorter hospital stays, and recovery times compared to those who underwent TFA (p = 0.001, p = 0.001). In terms of both mental health and physical function, TRA versus TFA has been observed to produce more favorable outcomes (p = 0.044, p = 0.032).
Conclusion
TRA access for TARE procedures significantly enhances patient comfort and satisfaction. The total radiation dose exposed to the patients who underwent TRA access was found to be significantly lower than the patients who underwent TFA access.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sangro B, Salem R, Kennedy A, Coldwell D, Wasan H. Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a review of the evidence and treatment recommendations. Am J Clin Oncol. 2011;34(4):422–31. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e3181df0a50.
Feldman DN, Swaminathan RV, Kaltenbach LA, Baklanov DV, Kim LK, Wong SC, Minutello RM, Messenger JC, Moussa I, Garratt KN, Piana RN, Hillegass WB, Cohen MG, Gilchrist IC, Rao SV. Adoption of radial access and comparison of outcomes to femoral access in percutaneous coronary intervention: an updated report from the national cardiovascular data registry (2007–2012). Circulation. 2013;127(23):2295–306. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.000536.
Valgimigli M, Gagnor A, Calabró P, Frigoli E, Leonardi S, Zaro T, et al. Radial versus femoral access in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing invasive management: a randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2015;385(9986):2465–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60292-6.
Jolly SS, Yusuf S, Cairns J, Niemelä K, Xavier D, Widimsky P, Budaj A, Niemelä M, Valentin V, Lewis BS, Avezum A, Steg PG, Rao SV, Gao P, Afzal R, Joyner CD, Chrolavicius S, Mehta SR. Radial versus femoral access for coronary angiography and intervention in patients with acute coronary syndromes (RIVAL): a randomised, parallel group, multicentre trial. The Lancet. 2011;377(9775):1409–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60404-2.
Romagnoli E, Biondi-Zoccai G, Sciahbasi A, Politi L, Rigattieri S, Pendenza G, et al. Radial versus femoral randomized investigation in ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome: the RIFLE-STEACS (radial versus femoral randomized investigation in ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(24):2481–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.06.017.
Mitchell MD, Hong JA, Lee BY, Umscheid CA, Bartsch SM, Don CW. Systematic review and cost-benefit analysis of radial artery access for coronary angiography and intervention. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012;5(4):454–62. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.112.965269.
Shiozawa S, Tsuchiya A, Endo S, Kato H, Katsube T, Kumazawa K, et al. Transradial approach for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with conventional transfemora l approach. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;37(5):412–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004836-200311000-00013.
Posham R, Biederman DM, Patel RS, Kim E, Tabori NE, Nowakowski FS, Lookstein RA, Fischman AM. Transradial approach for noncoronary interventions: a single-center review of safety and feasibility in the first 1500 cases. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27(2):159–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2015.10.026.
Cowling MG, Buckenham TM, Belli AM. The role of transradial diagnostic angiography. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1997;20(2):103–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002709900115.
Resnick NJ, Kim E, Patel RS, Lookstein RA, Nowakowski FS, Fischman AM. Uterine artery embolization using a transradial approach: initial experience and technique. J Vasc Inte rv Radiol. 2014;25(3):443–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2013.11.010.
Ruzsa Z, Tóth K, Jambrik Z, Kovács N, Nardai S, Nemes B, Hüttl K, Merkely B. Transradial access for renal artery intervention. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2014;6(3):97–103. https://doi.org/10.1556/IMAS.6.2014.3.1.
Bhatia S, Harward SH, Sinha VK, Narayanan G. Prostate artery embolization via transradial or transulnar versus transfemoral arterial access: technical results. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017;28(6):898–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2017.02.029.
Yamada R, Bracewell S, Bassaco B, Camacho J, Anderson MB, Conrad A, Lynn C, Burns P, Collins H, Guimaraes M. Transradial versus transfemoral arterial access in liver cancer embolization: randomized trial to assess patient satisfaction. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018;29(1):38–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2017.08.024.
Lezzi R, Posa A, Merlino B, Pompili M, Annicchiarico E, Rodolfino E, Basso M, Cassano A, Gasbarrini A, Manfredi R. Operator learning curve for transradial liver cancer embolization: implications for the initiation of a transradial access program. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019;25(5):368–74. https://doi.org/10.5152/dir.2019.18437.
Kis B, Mills M, Hoffe SE. Hepatic radioembolization from transradial access: initial experience and comparison to transfemoral access. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2016;22(5):444–9. https://doi.org/10.5152/dir.2016.15571.
Loewenstern J, Welch C, Lekperic S, Bishay V, Ranade M, Patel RS, et al. Patient radiation exposure in transradial versus transfemoral yttrium-90 radioembolization: a retrospective propensity score-matched analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018;29(7):936–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2018.02.011.
Chen YY, Liu P, Wu YS, Lin H, Chen X. Transradial versus transfemoral access in patients with hepatic malignancy and undergoing hepatic interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(52):e13926. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000013926.
Liu LB, Cedillo MA, Bishay V, Ranade M, Patel RS, Kim E, et al. Patient experience and preference in transradial versus transfemoral access during transarterial radioembolization: a randomized single -center trial. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30(3):414–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2018.10.005.
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Consent for Publication
For this type of study, consent for publication is not required.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yakupoğlu, A., Buturak, Ö.S.U. Transradial Access for Transarterial Radioembolization (TARE) in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Comparison with Transfemoral Access. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 46, 1359–1364 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-023-03542-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-023-03542-7