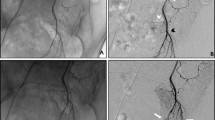
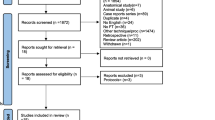
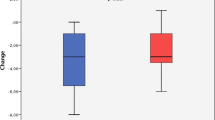
Abstract
Haemorrhoids are abnormally enlarged anal cushions within the lower rectum. They are common, and have potential to significantly impact patients’ quality of life. Superior rectal artery embolisation is a technique which has been discussed in the literature as far back as 40 years ago. More recently, there has been interest in the role of embolisation in the treatment for haemorrhoids, as an alternative to established minimally invasive and conventional surgical techniques. In this review, we discuss the current literature on the topic, with particular focus on technique, clinical outcomes and complications. Emerging procedural and technical considerations are discussed, with further review of the role of coil vs. particle embolisation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tucker H, George E, Barnett D, Longson C. NICE technology appraisal on stapled haemorrhoidopexy for the treatment of haemorrhoids. The Royal College of Surgeons of England. 2008.
Vidal V, Louis G, Bartoli JM, Sielezneff I. Embolization of the hemorrhoidal arteries (the emborrhoid technique): a new concept and challenge for interventional radiology. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2014;95:307–15.
Vidal V, Sapoval M, Sielezneff Y, De Parades V, Tradi F, Louis G, Bartoli JM, Pellerin O. Emborrhoid: a new concept for the treatment of hemorrhoids with arterial embolization: the first 14 cases. CardioVasc Interv Radiol. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-1017-8.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2018) Superior rectal artery embolisation for haemorrhoids—Interventional procedure guidance IPG627. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/IPG627. Accessed 27 Jul 2020.
Hardy A, Chan CLH, Cohen CRG. The surgical management of haemorrhoids—a review. Dig Surg. 2005. https://doi.org/10.1159/000085343.
van Tol RR, Kleijnen J, Watson AJM, Jongen J, Altomare DF, Qvist N, Higuero T, Muris JWM, Breukink SO. European Society of ColoProctology (ESCP) Guideline for Haemorrhoidal Disease. ESCP. 2020.
Mahadevan V. Anatomy of the rectum and anal canal. Surg Oxford. 2017;35:121–5.
Aigner F, Bodner G, Gruber H, Conrad F, Fritsch H, Margreiter R, Bonatti H. The vascular nature of hemorrhoids. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006;10:1044–50.
Bilhim T, Pereira JA, Tinto HR, Fernandes L, Duarte M, O’Neill JE, Pisco JM. Middle rectal artery: myth or reality? Retrospective study with CT angiography and digital subtraction angiography. Surg Radiol Anat. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1068-y.
Sun X, Xu J, Zhang J, Jin Y, Chen Q. Management of rectal bleeding due to internal haemorrhoids with arterial embolisation: a single-centre experience and protocol. Clin Radiol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2018.07.105.
Tradi F, Louis G, Giorgi R, Mege D, Bartoli JM, Sielezneff I, Vidal V. Embolization of the superior rectal arteries for hemorrhoidal disease: prospective results in 25 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2018.01.778.
Cerato MM, Cerato NL, Passos P, Treigue A, Damin DC. Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids: a critical appraisal of the current options. ABCD Arquivos Brasileiros de Cirurgia Digestiva SP. 2014;27:66–70.
Rubbini M, Ascanelli S. Classification and guidelines of hemorrhoidal disease: present and future. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2019;11:117–21.
Giordano P, Overton J, Madeddu F, Zaman S, Gravante G. Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization: a systematic review. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/DCR.0b013e3181af50f4.
Pucher PH, Sodergren MH, Lord AC, Darzi A, Ziprin P. Clinical outcome following Doppler-guided haemorrhoidal artery ligation: a systematic review. Colorectal Dis. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.12205.
Brown SR, Tiernan JP, Watson AJM, Biggs K, Shephard N, Wailoo AJ, Bradburn M, Alshreef A, Hind D. Haemorrhoidal artery ligation versus rubber band ligation for the management of symptomatic second-degree and third-degree haemorrhoids (HubBLe): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30584-0.
Chuang VP, Wallace S, Zornoza J, Davis LJ. Transcatheter arterial occlusion in the management of rectosigmoidal bleeding. Radiology. 1979. https://doi.org/10.1148/133.3.605.
Derodra JK, Reidy JF, Jourdan MH. Embolization of superior haemorrhoidal artery in the management of life-threatening rectal bleeding. Br J Surg. 1992. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.1800790738.
Dobson CC, Nicholson AA. Treatment of rectal hemorrhage by coil embolization. CardioVasc Interv Radiol. 1999. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03035356.
Pichon N, François B, Pichon-Lefièvre F, Mathonnet M, Maubon A, Vignon P. Embolization of rectal arteries: an alternative treatment for hemorrhagic shock induced by traumatic intrarectal hemorrhage. CardioVasc Interv Radiol. 2005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-0168-4.
Berczi V, Gopalan D, Cleveland TJ. Embolization of a hemorrhoid following 18 hours of life-threatening bleeding. CardioVasc Interv Radiol. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-006-0179-4.
Tarazov PG. Arterial embolization of hemorrhoids. CardioVasc Interv Radiol. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1148-6.
Vidal V, Sapoval M, Pellerin O. Arterial embolization of hemorrhoids: reply. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2015;38:1056.
Moussa N, Bonnet B, Pereira H, et al. Mid-term results of superior rectal artery and coils for hemorrhoidal embolization with particles bleeding. CardioVasc Interv Radiol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02441-5.
Moggia E, Talamo G, Gallo G, Bianco A, Barattini M, Salsano G, Zefiro D, Stefanini T, Berti S. Do we have another option to treat bleeding hemorrhoids? The Emborrhoid technique: experience in 16 patients. Reviews on recent clinical trials. 2020.
Zakharchenko A, Kaitoukov Y, Vinnik Y, Tradi F, Sapoval M, Sielezneff I, Galkin E, Vidal V. Safety and efficacy of superior rectal artery embolization with particles and metallic coils for the treatment of hemorrhoids (Emborrhoid technique). Diagn Interv Imaging. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2016.08.002.
Moussa N, Sielezneff I, Sapoval M, et al. Embolization of the superior rectal arteries for chronic bleeding due to haemorrhoidal disease. Colorectal Dis. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.13430.
Huang C-C, Lee C-W, Hsiao J-K, Leung P-C, Liu K-L, Tsang Y-M, Liu H-M. N-butyl cyanoacrylate embolization as the primary treatment of acute hemodynamically unstable lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;22:1594–9.
Lanza E. Transarterial coil embolization of the superior rectal arteries for treatment of stage II hemorrhoids. In: clinicaltrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03805087. Accessed 27 Feb 2020. 2019.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mert Sirakaya contributed to conceptualisation. Mert Sirakaya and Aleem O’Balogun conducted literature review. Mert Sirakaya and Aleem O’Balogun were involved in drafting. Rahil Hussein Kassamali was involved in critical appraisal, revision and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Ethical approval was not necessary.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Consent for Publication
For this type of study, consent for publication was not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirakaya, M., O’Balogun, A. & Kassamali, R.H. Superior Rectal Artery Embolisation for Haemorrhoids: What Do We Know So Far?. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 44, 675–685 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02733-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02733-w