Abstract
Purpose
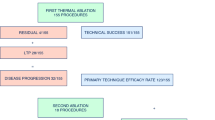
This study evaluated the survival benefit of a combination therapy with radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and intratumoral cisplatin (ITC) administration for lung tumors by using a rabbit VX2 tumor model.
Materials and Methods
Experiments were approved by the institutional animal care committee. VX2 tumor suspension was injected into the lungs of Japanese white rabbits under CT guidance to create a lung tumor model. Thirty-two rabbits bearing a transplanted VX2 lung tumor were randomly assigned to four groups of eight: control (untreated); RFA alone; ITC alone; and RFA with ITC. All treatments were performed one week after tumor transplantation. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were compared by the log-rank test.
Results
The median survival time was 24.5 days (range 17–33 days) in the control group, 40 days (30–80 days) in the RFA alone group, 31.0 days (24–80 days) in the ITC alone group, and not reached (53–80 days) in the RFA with ITC group. The median survival was significantly longer with the RFA/ITC combination compared to the control group (P < 0.001), RFA alone (P = 0.034), and ITC alone (P = 0.004). The survival time after RFA alone was also significantly longer than that of the control group (P < 0.001). There was no significant difference in tumor size or the rate of pneumothorax between each group.
Conclusion
RFA prolonged the survival of rabbits with lung VX2 tumors when combined with ITC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dupuy DE, Zagoria RJ, Akerley W, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of malignancies in the lung. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;174(1):57–9.
Lencioni R, Crocetti L, Cioni R, et al. Response to radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary tumours: a prospective, intention-to-treat, multicentre clinical trial (the RAPTURE study). Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(7):621–8.
Yuan Z, Wang Y, Zhang J, et al. A Meta-analysis of clinical outcomes after radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation for lung cancer and pulmonary metastases. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(3):302–14.
Hiraki T, Sakurai J, Tsuda T, et al. Risk factors for local progression after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors: evaluation based on a preliminary review of 342 tumors. Cancer. 2006;107(12):2873–80.
Okuma T, Matsuoka T, Yamamoto A, et al. Determinants of local progression after computed tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for unresectable lung tumors: 9-year experience in a single institution. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010;33(4):787–93.
Vogl TJ, Wetter A, Lindemayr S, Zangos S. Treatment of unresectable lung metastases with transpulmonary chemoembolization: preliminary experience. Radiology. 2005;234(3):917–22.
Hiraki T, Gobara H, Sakurai J, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of normal lungs after pulmonary artery embolization with use of degradable starch microspheres: results in a porcine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17(12):1991–8.
Gadaleta CD, Solbiati L, Mattioli V, et al. Unresectable lung malignancy: combination therapy with segmental pulmonary arterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting microspheres and radiofrequency ablation in 17 patients. Radiology. 2013;267(2):627–37.
Vogl TJ, Mekkawy AIA, Thabet DB, et al. Transvenous pulmonary chemoembolization (TPCE) for palliative or neoadjuvant treatment of lung metastases. Eur Radiol. 2019;29(4):1939–49.
Hamamoto S, Okuma T, Yamamoto A, et al. Radiofrequency ablation and immunostimulant OK-432: combination therapy enhances systemic antitumor immunity for treatment of VX2 lung tumors in rabbits. Radiology. 2013;267(2):405–13.
Hamamoto S, Okuma T, Yamamoto A, et al. Combination radiofrequency ablation and local injection of the immunostimulant bacillus Calmette-Guerin induces antitumor immunity in the lung and at a distant VX2 tumor in a rabbit model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;26(2):271–8.
Ueki A, Okuma T, Hamamoto S, et al. Therapeutic effects of CT-guided radiofrequency ablation with concurrent platinum-doublet chemotherapy in a rabbit VX2 lung tumor model. Radiology. 2017;283(2):391–8.
Li X, Zhao M, Wang J, et al. Percutaneous CT-guided radiofrequency ablation as supplemental therapy after systemic chemotherapy for selected advanced non–small cell lung cancers. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201(6):1362–7.
Yu NY, Patawaran MB, Chen JY, et al. Influence of treatment sequence on efficacy of fluorouracil and cisplatin intratumoral drug delivery in vivo. Cancer J Sci Am. 1995;1(3):215–21.
Burris HA 3rd, Vogel CL, Castro D, et al. Intratumoral cisplatin/epinephrine-injectable gel as a palliative treatment for accessible solid tumors: a multicenter pilot study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;118(4):496–503.
Werner JA, Kehrl W, Pluzanska A, et al. A phase III placebo-controlled study in advanced head and neck cancer using intratumoural cisplatin/epinephrine gel. Br J Cancer. 2002;87(9):938–44.
Castro DJ, Sridhar KS, Garewal HS, et al. Intratumoral cisplatin/epinephrine gel in advanced head and neck cancer: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, phase III study in North America. Head Neck. 2003;25(9):717–31.
Vogl TJ, Engelmann K, Mack MG, et al. CT-guided intratumoural administration of cisplatin/epinephrine gel for treatment of malignant liver tumours. Br J Cancer. 2002;86(4):524–9.
Yamada R, Nakamura K, Nishida N, et al. New therapy complementary to transcatheter arterial embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 2001;25(3):381–6.
Wu H, Fan ZP, Jiang AN, et al. Combination of intratumoural micellar paclitaxel with radiofrequency ablation: efficacy and toxicity in rodents. Eur Radiol. 2019;29(11):6202–10.
Bie Z, Li Y, Li B, et al. The efficacy of drug-eluting beads bronchial arterial chemoembolization loaded with gemcitabine for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. 2019;10(9):1770–8.
Kitamoto M, Imagawa M, Yamada H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas: comparison of the radiofrequency effect with and without chemoembolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181(4):997–1003.
Morimoto M, Numata K, Kondou M, et al. Midterm outcomes in patients with intermediate-sized hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial for determining the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cancer. 2010;116(23):5452–60.
Yan S, Xu D, Sun B. Combination of radiofrequency ablation with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58(7):2107–13.
Milne EN, Zerhouni EA. Blood supply of pulmonary metastases. J Thorac Imaging. 1987;2(4):15–23.
Yuan X, Zhang J, Ao G, et al. Lung cancer perfusion: can we measure pulmonary and bronchial circulation simultaneously? Eur Radiol. 2012;22(8):1665–71.
Nair AB, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2016;7(2):27–31.
Yoshida K, Sugiura T, Takifuji N, et al. Randomized phase II trial of three intrapleural therapy regimens for the management of malignant pleural effusion in previously untreated non-small cell lung cancer: JCOG 9515. Lung Cancer. 2007;58(3):362–8.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant No JP16K10360.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Informed Consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Consent for Publication
For this type of study consent for publication is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murai, K., Hamamoto, S., Okuma, T. et al. Survival Benefit of Radiofrequency Ablation with Intratumoral Cisplatin Administration in a Rabbit VX2 Lung Tumor Model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 44, 475–481 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02686-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02686-0