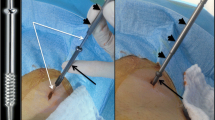
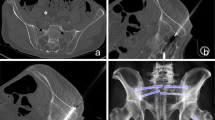
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the feasibility, efficacy and safety of sternal percutaneous fixation by internal cemented screw (FICS) using fluoroscopy and/or CT needle guidance.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective single-center study analyzed 9 consecutive cancer patients managed with percutaneous FICS for sternal fracture fixation or osteolytic metastasis consolidation, from May 2014 to February 2019. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, Numeric Pain Rating Scale (NPRS) and opioid use were studied preoperatively and postoperatively. Sternal images at last follow-up appointment were also collected.
Results
Among the 9 patients, 7 had a sternal fracture with 5 being displaced. The technical feasibility was 100%. Both NPRS score significantly decreased from 5.6/10 ± 2.8 to 1.1/10 ± 1.6, and analgesic consumption was significantly improved (p = 0.03) after intervention. No post-procedural complications requiring surgical correction or screw displacement occurred after a mean imaging follow-up that exceeded 1 year (mean follow-up duration, 401.8 days ± 305.8).
Conclusion
Image-guided sternal percutaneous FICS is feasible and safe. It reduces pain and analgesic consumption related to pathologic fracture of the sternum.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coleman RE. Skeletal complications of malignancy. Cancer. 1997;80(8 Suppl):1588–94.
Aaron AD. Treatment of metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pelvis and the extremities. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1997;79(6):917–32.
Böhm P, Huber J. The surgical treatment of bony metastases of the spine and limbs. J Bone Jt Surg Br. 2002;84(4):521–9.
Mundy GR. Mechanisms of bone metastasis. Cancer. 1997;80(8 Suppl):1546–56.
Hill T, D’Alessandro P, Murray K, Yates P. Prognostic factors following pathological fractures. ANZ J Surg. 2015;85(3):159–63.
Tsuzuki S, Park SH, Eber MR, Peters CM, Shiozawa Y. Skeletal complications in cancer patients with bone metastases. Int J Urol. 2016;23(10):825–32.
Deschamps F, Yevich S, Gravel G, Roux C, Hakime A, de Baère T, et al. Percutaneous fixation by internal cemented screw for the treatment of unstable osseous disease in cancer patients. Semin Interv Radiol. 2018;35(4):238–47.
Anselmetti GC, Marcia S, Saba L, Muto M, Bonaldi G, Carpeggiani P, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: multi-centric results from EVEREST experience in large cohort of patients. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(12):4083–6.
Wang Z, Zhen Y, Wu C, Li H, Yang Y, Shen Z, et al. CT fluoroscopy-guided percutaneous osteoplasty for the treatment of osteolytic lung cancer bone metastases to the spine and pelvis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23(9):1135–42.
Deschamps F, Farouil G, Hakime A, Barah A, Guiu B, Teriitehau C, et al. Cementoplasty of metastases of the proximal femur: is it a safe palliative option? J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23(10):1311–6.
Collinge CA, Crist BD. Combined percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation with sacroplasty using resorbable calcium phosphate cement for osteoporotic pelvic fractures requiring surgery. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(6):e217–22.
Deschamps F, de Baere T, Hakime A, Pearson E, Farouil G, Teriitehau C, et al. Percutaneous osteosynthesis in the pelvis in cancer patients. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(6):1631–9.
Tian Q-H, He C-J, Wu C-G, Li Y-D, Gu Y-F, Wang T, et al. Comparison of percutaneous cementoplasty with and without interventional internal fixation for impending malignant pathological fracture of the proximal femur. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2016;39(1):81–9.
Roux C, Tselikas L, Yevich S, Sandes Solha R, Hakime A, Teriitehau C, et al. Fluoroscopy and cone-beam CT-guided fixation by internal cemented screw for pathologic pelvic fractures. Radiology. 2019;290(2):418–25.
Filippiadis DK, Binkert C, Pellerin O, Hoffmann RT, Krajina A, Pereira PL. Cirse quality assurance document and standards for classification of complications: the cirse classification system. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2017;40(8):1141–6.
Funding
No specific funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
During the past 5 years, TdB has received speaker honorarium from Terumo, Guerbet, BTG, GE and Canon medical; FD has received speaker honorarium from Hypervention, BTG and Guerbet; LT has received research grant from Terumo and speaker honorarium from BTG, Guerbet and GE. The other authors do not declare any conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required, even though this study was IRB approved. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for Publication
This type of study consent for publication is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poussot, B., Deschamps, F., Varin, F. et al. Percutaneous Fixation by Internal Cemented Screws of the Sternum. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 43, 103–109 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02334-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02334-2