Abstract
Purpose
To assess prospectively long-term results of doxorubicin-loaded HepaSphere 30–60 μm in consecutive patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) not amenable to curative treatments.
Patients and Methods
Single-center study from June 2011 to December 2015 in 151 patients treated with 75 mg of doxorubicin per HepaSphere vial. Baseline: Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer BCLC A/B was 49.3%/50.7%, and median diameter 6.1 cm (mean 6.7 ± 2.0). Liver function, local response (mRECIST), liver time to progression (LTTP), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS) and adverse events (AEs) were recorded.
Results
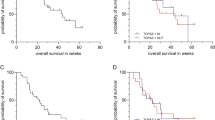
Final analysis included 142 patients with median follow-up of 46.8 months (range 4–72) without grade 4/5 AEs, and 30-day mortality was 0%. Mean number of scheduled treatments was 2.6 (range 1–3) and on demand 3 (range 1–8). Complete response for single tumor ≤ 5 cm was 75.0% and 66.7% for Child A and Child B, while for > 5 cm was 28.6% and 11.8%, respectively. OS was 31.0 months (mean 33.3 ± 15.2; range 8–69), notably for BCLC A 41 months (mean 41.1 ± 15.3; range 13–69) and for BCLC B 26.0 (mean 26.0 ± 10.5; range 8–51). OS at 1, 3 and 5 years: 95.8%, 75.7% and 21.4% for BCLC A, and 94.4%, 36.1% and 2.7% for BCLC B. Median LTTP for BCLC A was 11 months (mean 11.9 ± 4.7; range 3–24) and 7.5 for BCLC B (mean 7.9 ± 2.9). Local response was significant for OS and LTTP (p < 0.0001), while size and lesion number affected LPFS and OS (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
HepaSphere 30–60 μm loaded with doxorubicin provides a safe and effective treatment option for patients with HCC.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DEM:
-
Drug-eluting microsphere
- DEM-TACE:
-
Drug-eluting microsphere transarterial chemoembolization
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- BCLC classification:
-
Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer
- mRECIST:
-
Local response
- LTTP:
-
Time to progression in the liver
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- AEs:
-
Adverse events
- NACT:
-
HCC not amenable to curative treatments
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- CR:
-
Complete response
- PR:
-
Partial response
- SD:
-
Stable disease
- PD:
-
Progressive disease
References
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391(10127):1301–14.
Odisio BC, Ashton A, Yan Y, Wei W, Kaseb A, Wallace MJ, Vauthey JN, Gupta S, Tam AL. Transarterial hepatic chemoembolization with 70–150 µm drug-eluting beads: assessment of clinical safety and liver toxicity profile. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;26(7):965–71.
Aliberti C, Carandina R, Lonardi S, Dadduzio V, Vitale A, Gringeri E, Zanus G, Cillo U. Transarterial chemoembolization with small drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: experience from a cohort of 421 patients at an Italian Center. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017;28(11):1495–502.
Prajapati HJ, Xing M, Spivey JR, Hanish SI, El-Rayes BF, Kauh JS, Chen Z, Kim HS. Survival, efficacy, and safety of small versus large doxorubicin drug-eluting beads TACE chemoembolization in patients with unresectable HCC. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203(6):W706–14.
Richter G, Radeleff B, Stroszczynski C, Pereira P, Helmberger T, Barakat M, Huppert P. Safety and feasibility of chemoembolization with doxorubicin-loaded small calibrated microspheres in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: results of the MIRACLE I prospective multicenter study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018;41(4):587–93.
Malagari K, Kiakidis T, Pomoni M, Moschouris H, Emmanouil E, Spiridopoulos T, Sotirchos V, Tandeles S, Koundouras D, Kelekis A, Filippiadis D, Charokopakis A, Bouma E, Chatziioannou A, Dourakis S, Koskinas J, Karampelas T, Tamvakopoulos K, Kelekis N, Kelekis D. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of chemoembolization with doxorubicin-loaded tightly calibrated small microspheres in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016;39(10):1379–91 (Erratum in: Cardiovasc InterventRadiol. 2016;39(10):1537.).
Osuga K, Khankan AA, Hori S, Okada A, Sugiura T, Maeda M, Nagano H, Yamada A, Murakami T, Nakamura H. Transarterial embolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma with use of superabsorbent polymer microspheres: initial experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13(9 Pt 1):929–34.
Malagari K, Pomoni A, Filippiadis D, et al. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with HepaSphere™. Fut Med. 2015;2(2):147–57.
Malagari K, Pomoni M, Moschouris H, Kelekis A, Charokopakis A, Bouma E, Spyridopoulos T, Chatziioannou A, Sotirchos V, Karampelas T, Tamvakopoulos C, Filippiadis D, Karagiannis E, Marinis A, Koskinas J, Kelekis DA. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with HepaSphere 30–60 μm. Safety and efficacy study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37(1):165–75.
Namur J, Pascale F, Maeda N, Sterba M, Ghegediban SH, Verret V, Paci A, Seck A, Osuga K, Wassef M, Reb P, Laurent A. Safety and efficacy compared between irinotecan-loaded microspheres HepaSphere and DC bead in a model of VX2 liver metastases in the rabbit. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;26(7):1067–75.
Lencioni R, de Baere T, Burrel M, Caridi JG, Lammer J, Malagari K, Martin RC, O’Grady E, Real MI, Vogl TJ, Watkinson A, Geschwind JF. Transcatheter treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with Doxorubicin-loaded DC Bead (DEBDOX): technical recommendations. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2012;35(5):980–5.
Liu DM, Kos S, Buczkowski A, Kee S, Munk PL, Klass D, Wasan E. Optimization of doxorubicin loading for superabsorbent polymer microspheres: in vitro analysis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2012;35(2):391–8.
Kos S, Wasan E, Weir G, Reb P, Cornell C, Ford JA, Liu DM. Elution characteristics of doxorubicin-loaded microspheres differ by drug-loading method and microsphere size. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;22(3):361–8.
Maeda N, Osuga K, Higashihara H, Mikami K, Tomoda K, Hori S, Nakazawa T, Nakamura H. In vitro characterization of cisplatin-loaded superabsorbent polymer microspheres designed for chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(6):877–8.
Varela M, Real MI, Burrel M, Forner A, Sala M, Brunet M, Ayuso C, Castells L, Montañá X, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with drug eluting beads: efficacy and doxorubicin pharmacokinetics. J Hepatol. 2007;46(3):474–81.
Malagari K, Pomoni M, Moschouris H, Bouma E, Koskinas J, Stefaniotou A, Marinis A, Kelekis A, Alexopoulou E, Chatziioannou A, Chatzimichael K, Dourakis S, Kelekis N, Rizos S, Kelekis D. Chemoembolization with doxorubicin-eluting beads for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: five-year survival analysis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2012;35(5):1119–28.
de Baere T, Tselikas L, Deschamps F, Boige V, Ducreux M, Hollebecque A. Advances in transarterial therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: is novel technology leading to better outcomes? Hepat Oncol. 2016;3(2):109–18.
Burrel M, Reig M, Forner A, Barrufet M, de Lope CR, Tremosini S, Ayuso C, Llovet JM, Real MI, Bruix J. Survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) using Drug Eluting Beads. Implications for clinical practice and trial design. J Hepatol. 2012;56(6):1330–5.
Sahin H, Harman M, Cinar C, Bozkaya H, Parildar M, Elmas N. Evaluation of treatment response of chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma with diffusion-weighted imaging on 3.0-T MR imaging. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23(2):241–7.
Lencioni R, Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30(1):52–60.
Dinca H, Pelage JP, Baylatry MT, Ghegediban SH, PascaleF, Manfait M et al. Why do small size doxorubicin-eluting microspheres induce more tissue necrosis than larger ones? A comparative study in healthy pig liver (oral communication 2206-2). CIRSE Annual meeting; 15–19 Sept 2012, Lisbon, Portugal.
Seki A, Hori S, Kobayashi K, Narumiya S. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with epirubicin-loaded superabsorbent polymer microspheres for 135 hepatocellular carcinoma patients: single-center experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2011;34(3):557–65.
Zurstrassen CE, Gireli LPO, Tyng CJ, Bitencourt AGV, Guimarães MD, Barbosa PNV, Santos Cavalcante ACB, Matushita Junior JP, Amoedo MK, Coimbra FJ, Alves RCP, Chojniak R. Safety and efficacy of HepaSphere 50–100 μm in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2017;26(4):212–9.
Bishay VL, Maglione K, Khanna R, Lee KM, Fischman AM, Lookstein RA, Kim E. Chemoembolization with drug-eluting microspheres (DEM-TACE) for hepatocellular carcinoma: single-center review of safety and efficacy. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2014;27(1):187–93.
Golfieri R, Renzulli M, Mosconi C, Forlani L, Giampalma E, Piscaglia F, Trevisani F, Bolondi L. Bologna Liver Oncology Group (BLOG). Hepatocellular carcinoma responding to superselective transarterial chemoembolization: an issue of nodule dimension? J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24(4):509–17.
Lee M, Chung JW, Lee KH, Won JY, Chun HJ, Lee HC, Kim JH, Lee IJ, Hur S, Kim HC, Kim YJ, Kim GM, Joo SM, Oh JS. Korean multicenter registry of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting embolic agents for nodular hepatocellular carcinomas: six-month outcome analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017;28(4):502–12.
Yu CY, Ou HY, Weng CC, Huang TL, Chen TY, Leung-Chit L, Hsu HW, Chen CL, Cheng YF. Drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization as bridge therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma before living-donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(4):1045–8.
Spreafico C, Cascella T, Facciorusso A, Sposito C, Rodolfo L, Morosi C, Civelli EM, Vaiani M, Bhoori S, Pellegrinelli A, Marchianò A, Mazzaferro V. Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with a new generation of beads: clinical-radiological outcomes and safety profile. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38(1):129–34.
Sun JH, Zhou GH, Zhang YL, Nie CH, Zhou TY, Ai J, Zhu TY, Wang WL, Zheng SS. Chemoembolization of liver cancer with drug-loading microsphere 50–100 μm. Oncotarget. 2017;8(3):5392–9.
Miyayama S, Mitsui T, Zen Y, Sudo Y, Yamashiro M, Okuda M, Yoshie Y, Sanada T, Notsumata K, Tanaka N, Matsui O. Histopathological findings after ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 2009;39(4):374–81.
Sakon M, Nagano H, Nakamori S, Dono K, Umeshita K, Murakami T, Nakamura H, Monden M. Intrahepatic recurrences of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: analysis based on tumor hemodynamics. Arch Surg. 2002;137(1):94–9.
Kucukay F, Badem S, Karan A, Ozdemir M, Okten RS, Ozbulbul NI, Kucukay MB, Unlu I, Bostanci EB, Akdogan M. A single-center retrospective comparison of doxorubicin-loaded hepasphere transarterial chemoembolization with conventional transarterial chemoembolization for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;26(11):1622–9.
Covey AM, Maluccio MA, Schubert J, BenPorat L, Brody LA, Sofocleous CT, Getrajdman GI, Fong Y, Brown KT. Particle embolization of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Cancer. 2006;106(10):2181–9.
Gomes AS, Monteleone PA, Sayre JW, Finn RS, Sadeghi S, Tong MJ, Britten CD, Busuttil RW. Comparison of triple-drug transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) with single-drug TACE using doxorubicin-eluting beads: long-term survival in 313 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;209(4):722–32.
Kloeckner R, Weinmann A, Prinz F, Pinto dos Santos D, Ruckes C, Dueber C, Pitton MB. Conventional transarterial chemoembolization versus drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:465.
Chen P, Yuan P, Chen B, Sun J, Shen H, Qian Y. Evaluation of drug-eluting beads versus conventional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2017;41(1):75–85.
Jaeger HJ, Mehring UM, Castañeda F, Hasse F, Blumhardt G, Loehlein D, Mathias KD. Sequential transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1996;19(6):388–96.
Geschwind JF, Ramsey DE, Cleffken B, van der Wal BC, Kobeiter H, Juluru K, Hartnell GG, Choti MA. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of liver tumors: effects of embolization protocol on injectable volume of chemotherapy and subsequent arterial patency. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2003;26(2):111–7.
Erinjeri JP, Salhab HM, Covey AM, Getrajdman GI, Brown KT. Arterial patency after repeated hepatic artery bland particle embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(4):522–6.
Facciorusso A. Drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: current state of the art. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24(2):161–9 (review).
Yang H, Seon J, Sung PS, Oh JS, Lee HL, Jang B, Chun HJ, Jang JW, Bae SH, Choi JY, Yoon SK. Dexamethasone prophylaxis to alleviate postembolization syndrome after transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017;28(11):1503–11.
Sandow TA, Arndt SE, Albar AA, DeVun DA, Kirsch DS, Gimenez JM, et al. Assessment of response to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with doxorubicin-eluting microspheres: tumor biology and hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence in a 5-year transplant cohort. Radiology. 2018;286:1072–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malagari, K., Moschouris, H., Kiakidis, T. et al. Five-Years Outcome Analysis of 142 Consecutive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Doxorubicin Eluting Microspheres 30–60 μm: Results from a Single-Centre Prospective Phase II Trial. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 42, 1551–1562 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02260-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02260-3