Abstract
Purpose
To review outcomes following microwave ablation (MWA) of colorectal cancer pulmonary metastases and assess predictors of oncologic outcomes.
Methods
Technical success, primary and secondary technique efficacy rates were evaluated for 50 patients with 90 colorectal cancer pulmonary metastases at immediate, 4–8 weeks post-MWA and subsequent follow-up CT and/or 18F-FDG PET/CT. Local tumor progression (LTP) rate, LTP-free survival (LTPFS), cancer-specific and overall survivals were assessed. Complications were recorded according to SIR classification.
Results
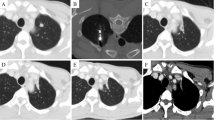
Median follow-up was 25.6 months. Median tumor size was 1 cm (0.3–3.2 cm). Technical success, primary and secondary technique efficacy rates were 99, 90 and 92%, respectively. LTP rate was 10%. One-, 2- and 3-year LTPFS were: 93, 86 and 86%, respectively, with median LTPFS not reached. Median overall survival was 58.6 months, and median cancer-specific survival (CSS) was not reached. One-, 2- and 3-year overall and CSS were 94% and 98, 82 and 90%, 61 and 70%, respectively. On univariate analysis, minimal ablation margin (p < 0.001) and tumor size (p = 0.001) predicted LTPFS, with no LTP for minimal margin ≥ 5 mm and/or tumor size < 1 cm. Pleural-based metastases were associated with increased LTP risk (p = 0.002, SHR = 7.7). Pre-MWA CEA level > 10 ng/ml (p = 0.046) and ≥ 3 prior chemotherapy lines predicted decreased CSS (p = 0.02). There was no 90-day death. Major complications rate was 13%.
Conclusions
MWA with minimal ablation margin ≥ 5 mm is essential for local control of colorectal cancer pulmonary metastases. Pleural-based metastases and larger tumor size were associated with higher risk of LTP. CEA level and pre-MWA chemotherapy impacted CSS.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ, Meester RGS, Barzi A, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(3):177–93.
Cook AD, Single R, McCahill LE. Surgical resection of primary tumors in patients who present with stage IV colorectal cancer: an analysis of surveillance, epidemiology, and end results data, 1988–2000. Ann Surg Oncol. 2005;12(8):637–45.
Kobayashi H, Mochizuki H, Sugihara K, Morita T, Kotake K, Teramoto T, et al. Characteristics of recurrence and surveillance tools after curative resection for colorectal cancer: a multicenter study. Surgery. 2007;141(1):67–75.
Mitry E, Guiu B, Cosconea S, Jooste V, Faivre J, Bouvier AM. Epidemiology, management and prognosis of colorectal cancer with lung metastases: a 30-year population-based study. Gut. 2010;59(10):1383–8.
Siegel R, Desantis C, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(2):104–17.
Fiorentino F, Hunt I, Teoh K, Treasure T, Utley M. Pulmonary metastasectomy in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and quantitative synthesis. J R Soc Med. 2010;103(2):60–6.
Shady W, Petre EN, Gonen M, Erinjeri JP, Brown KT, Covey AM, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of colorectal cancer liver metastases: factors affecting outcomes—a 10-year experience at a single center. Radiology. 2016;278(2):601–11.
Ruers T, Van Coevorden F, Punt CJ, Pierie JE, Borel-Rinkes I, Ledermann JA, et al. Local treatment of unresectable colorectal liver metastases: results of a randomized phase II trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109(9):djx015.
Solbiati L, Ahmed M, Cova L, Ierace T, Brioschi M, Goldberg SN. Small liver colorectal metastases treated with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: local response rate and long-term survival with up to 10-year follow-up. Radiology. 2012;265(3):958–68.
Embun R, Fiorentino F, Treasure T, Rivas JJ, Molins L. Pulmonary metastasectomy in colorectal cancer: a prospective study of demography and clinical characteristics of 543 patients in the Spanish colorectal metastasectomy registry (GECMP-CCR). BMJ Open. 2013;3(5):e002787.
Gonzalez M, Poncet A, Combescure C, Robert J, Ris HB, Gervaz P. Risk factors for survival after lung metastasectomy in colorectal cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(2):572–9.
Rios A, Galindo PJ, Torres J, Roca MJ, Robles R, Lujan JA, et al. Factors causing early relapse after lung metastasis surgery. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2007;16(1):26–32.
Pfannschmidt J, Hoffmann H, Dienemann H. Reported outcome factors for pulmonary resection in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5(6 Suppl 2):S172–8.
Welter S, Jacobs J, Krbek T, Krebs B, Stamatis G. Long-term survival after repeated resection of pulmonary metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84(1):203–10.
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, DiPetrillo TA, Safran HP, Grieco CA, Ng T, et al. Pulmonary radiofrequency ablation: long-term safety and efficacy in 153 patients. Radiology. 2007;243(1):268–75.
Sofocleous CT, May B, Petre EN, Gonen M, Thornton RH, Alago W, et al. Pulmonary thermal ablation in patients with prior pneumonectomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(5):W606–12.
Hess A, Palussiere J, Goyers JF, Guth A, Auperin A, de Baere T. Pulmonary radiofrequency ablation in patients with a single lung: feasibility, efficacy, and tolerance. Radiology. 2011;258(2):635–42.
Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni F, Ierace T, Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases in potential candidates for resection: the “test-of-time approach”. Cancer. 2003;97(12):3027–35.
Hiraki T, Gobara H, Iishi T, Sano Y, Iguchi T, Fujiwara H, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for pulmonary metastases from colorectal cancer: midterm results in 27 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol (JVIR). 2007;18(10):1264–9.
Yamakado K, Hase S, Matsuoka T, Tanigawa N, Nakatsuka A, Takaki H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of unresectable lung metastases in patients with colorectal cancer: a multicenter study in Japan. J Vasc Interv Radiol (JVIR). 2007;18(3):393–8.
de Baere T, Auperin A, Deschamps F, Chevallier P, Gaubert Y, Boige V, et al. Radiofrequency ablation is a valid treatment option for lung metastases: experience in 566 patients with 1037 metastases. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(5):987–91.
Yan TD, King J, Sjarif A, Glenn D, Steinke K, Morris DL. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary metastases from colorectal carcinoma: prognostic determinants for survival. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13(11):1529–37.
Vogl TJ, Naguib NN, Gruber-Rouh T, Koitka K, Lehnert T, Nour-Eldin NE. Microwave ablation therapy: clinical utility in treatment of pulmonary metastases. Radiology. 2011;261(2):643–51.
Egashira Y, Singh S, Bandula S, Illing R. Percutaneous high-energy microwave ablation for the treatment of pulmonary tumors: a retrospective single-center experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol (JVIR). 2016;27(4):474–9.
Petre EN, Jia X, Thornton RH, Sofocleous CT, Alago W, Kemeny NE, et al. Treatment of pulmonary colorectal metastases by radiofrequency ablation. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2013;12(1):37–44.
Belfiore G, Moggio G, Tedeschi E, Greco M, Cioffi R, Cincotti F, et al. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation: a potential complementary therapy for patients with unresectable primary lung cancer—a preliminary report of 33 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183(4):1003–11.
Sacks D, McClenny TE, Cardella JF, Lewis CA. Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines. J Vasc Interv Radiol (JVIR). 2003;14(9 Pt 2):S199–202.
King J, Glenn D, Clark W, Zhao J, Steinke K, Clingan P, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary metastases in patients with colorectal cancer. Br J Surg. 2004;91(2):217–23.
Steinke K, King J, Glenn DW, Morris DL. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors with expandable needle electrodes: tips from preliminary experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183(3):605–11.
Sofocleous CT, Sideras P, Petre EN, Solomon SB. Ablation for the management of pulmonary malignancies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(4):W581–9.
Mouli SK, Kurilova I, Sofocleous CT, Lewandowski RJ. The role of percutaneous image-guided thermal ablation for the treatment of pulmonary malignancies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;209(4):740–51.
Lubner MG, Brace CL, Hinshaw JL, Lee FT Jr. Microwave tumor ablation: mechanism of action, clinical results, and devices. J Vasc Interv Radiol (JVIR). 2010;21(8 Suppl):S192–203.
Vogl TJ, Eckert R, Naguib NN, Beeres M, Gruber-Rouh T, Nour-Eldin NA. Thermal ablation of colorectal lung metastases: retrospective comparison among laser-induced thermotherapy, radiofrequency ablation, and microwave ablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016;207(6):1340–9.
Wolf FJ, Grand DJ, Machan JT, Dipetrillo TA, Mayo-Smith WW, Dupuy DE. Microwave ablation of lung malignancies: effectiveness, CT findings, and safety in 50 patients. Radiology. 2008;247(3):871–9.
Lu Q, Cao W, Huang L, Wan Y, Liu T, Cheng Q, et al. CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of pulmonary malignancies: results in 69 cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2012;10:80.
Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Brace CL, Breen DJ, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria—a 10-year update. Radiology. 2014;273(1):241–60.
Wolf FJ, Aswad B, Ng T, Dupuy DE. Intraoperative microwave ablation of pulmonary malignancies with tumor permittivity feedback control: ablation and resection study in 10 consecutive patients. Radiology. 2012;262(1):353–60.
Giraud P, Antoine M, Larrouy A, Milleron B, Callard P, De Rycke Y, et al. Evaluation of microscopic tumor extension in non-small-cell lung cancer for three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48(4):1015–24.
Sotirchos VS, Petrovic LM, Gonen M, Klimstra DS, Do RK, Petre EN, et al. Colorectal cancer liver metastases: biopsy of the ablation zone and margins can be used to predict oncologic outcome. Radiology. 2016;280(3):949–59.
Steinke K, Glenn D, King J, Clark W, Zhao J, Clingan P, et al. Percutaneous imaging-guided radiofrequency ablation in patients with colorectal pulmonary metastases: 1-year follow-up. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004;11(2):207–12.
Akeboshi M, Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Hataji O, Taguchi O, Takao M, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung neoplasms: initial therapeutic response. J Vasc Interv Radiol (JVIR). 2004;15(5):463–70.
Simon TG, Beland MD, Machan JT, Dipetrillo T, Dupuy DE. Charlson Comorbidity Index predicts patient outcome, in cases of inoperable non-small cell lung cancer treated with radiofrequency ablation. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(12):4167–72.
Lyons NJ, Pathak S, Daniels IR, Spiers A, Smart NJ. Percutaneous management of pulmonary metastases arising from colorectal cancer; a systematic review. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015;41(11):1447–55.
Inoue Y, Miki C, Hiro J, Ojima E, Yamakado K, Takeda K, et al. Improved survival using multi-modality therapy in patients with lung metastases from colorectal cancer: a preliminary study. Oncol Rep. 2005;14(6):1571–6.
Lee JH, Lee SW. The roles of carcinoembryonic antigen in liver metastasis and therapeutic approaches. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017;2017:7521987.
McAfee MK, Allen MS, Trastek VF, Ilstrup DM, Deschamps C, Pairolero PC. Colorectal lung metastases: results of surgical excision. Ann Thorac Surg. 1992;53(5):780–5 (discussion 5–6).
Higashiyama M, Kodama K, Higaki N, Takami K, Murata K, Kameyama M, et al. Surgery for pulmonary metastases from colorectal cancer: the importance of prethoracotomy serum carcinoembryonic antigen as an indicator of prognosis. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;51(7):289–96.
Splatt AM, Steinke K. Major complications of high-energy microwave ablation for percutaneous CT-guided treatment of lung malignancies: single-centre experience after 4 years. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2015;59(5):609–16.
Zheng A, Wang X, Yang X, Wang W, Huang G, Gai Y, et al. Major complications after lung microwave ablation: a single-center experience on 204 sessions. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;98(1):243–8.
Nordholm-Carstensen A, Krarup PM, Jorgensen LN, Wille-Jorgensen PA, Harling H. Occurrence and survival of synchronous pulmonary metastases in colorectal cancer: a nationwide cohort study. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(2):447–56.
Chua TC, Al-Alem I, Zhao J, Glenn D, Liauw W, Morris DL. Radiofrequency ablation of concomitant and recurrent pulmonary metastases after surgery for colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19(1):75–81.
Sofocleous CT, Garg SK, Cohen P, Petre EN, Gonen M, Erinjeri JP, et al. Ki 67 is an independent predictive biomarker of cancer specific and local recurrence-free survival after lung tumor ablation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(Suppl 3):S676–83.
Ziv E, Erinjeri JP, Yarmohammadi H, Boas FE, Petre EN, Gao S, et al. Lung adenocarcinoma: predictive value of KRAS mutation status in assessing local recurrence in patients undergoing image-guided ablation. Radiology. 2017;282(1):251–8.
Shady W, Petre EN, Vakiani E, Ziv E, Gonen M, Brown KT, et al. Kras mutation is a marker of worse oncologic outcomes after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Oncotarget. 2017;8(39):66117–27.
Odisio BC, Yamashita S, Huang SY, Harmoush S, Kopetz SE, Ahrar K, et al. Local tumour progression after percutaneous ablation of colorectal liver metastases according to RAS mutation status. Br J Surg. 2017;104(6):760–8.
Acknowledgements
The research funded by the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Support Grant/Core Grant (P30 CA008748).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
C.T. Sofocleous has received research support from BTG, Ethicon (Neuwave); HS Medical, Angiodynamics; Sota Medical; and is a consultant for Ethicon and GE. S.B. Solomon, shareholder of Johnson & Johnson, has received personal fees from Medtronics, Astra Zeneca, Johnson & Johnson and GE Heathcare. Other authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
IRB waiver of approval was obtained for this retrospective cohort study. The database was HIPAA registered and compliant.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurilova, I., Gonzalez-Aguirre, A., Beets-Tan, R.G. et al. Microwave Ablation in the Management of Colorectal Cancer Pulmonary Metastases. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 41, 1530–1544 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-2000-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-2000-6