Abstract
Purpose
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPS) were historically placed using uncovered bare-metal stents. Current practice has now shifted toward the use of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)-covered stents, given the improved primary patency seen with these stents. The aim of this study was to determine whether there is any added value, such as overall survival or stent patency, when using covered stents versus uncovered stents in TIPS placement in a large cohort.
Materials and Methods
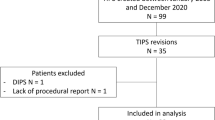
From April 1995 to June 2012, a total of 744 consecutive adult patients underwent de novo TIPS placement (378 receiving uncovered stents, 366 receiving covered stents). Information was obtained on demographics, baseline clinical variables, and outcomes after TIPS placement. Data were collected, compared, and analyzed to assess outcomes including mortality, primary patency (determined via repeat intervention), and secondary patency (determined via ultrasound parameters).
Results
Covered stents were associated with significantly improved primary patency (P < 0.001) and secondary patency (P < 0.001) when compared with uncovered stents in TIPS procedures. Additionally, covered stents were associated with higher estimated overall survival rates and higher survival rates when TIPS was performed emergently and in patients with higher Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) scores. For example, in patients with MELD scores between 11 and 18, there was a predicted survival of 59.2% with covered stents versus 42.8% with uncovered stents at 1 year.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that covered stents offer the additional value of higher estimated overall survival and higher estimated survival in patients undergoing TIPS emergently and in those with higher MELD scores when compared to uncovered stents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nazarian GK, Ferral H, Castañeda-Zúñiga WR, Bjarnason H, Foshager MC, Rank JM, et al. Development of stenoses in transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Radiology. 1994;192(1):231–4.
LaBerge JM, Ferrell LD, Ring EJ, Gordon RL. Histopathologic study of stenotic and occluded transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1993;4(6):779–86.
Thalheimer U, Leandro G, Samonakis DN, Triantos CK, Senzolo M, Fung K, et al. TIPS for refractory ascites: a single-centre experience. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(10):1089–95.
Riggio O, Ridola L, Angeloni S, Cerini F, Pasquale C, Attili AF, et al. Clinical efficacy of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt created with covered stents with different diameters: results of a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2010;53(2):267–72.
Lauermann J, Potthoff A, Mc Cavert M, Marquardt S, Vaske B, Rosenthal H, et al. Comparison of technical and clinical outcome of transjugular portosystemic shunt placement between a bare metal stent and a PTFE-stentgraft device. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2016;39(4):547–56.
Heinzow HS, Lenz P, Köhler M, et al. Clinical outcome and predictors of survival after TIPS insertion in patients with liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(37):5211–8.
Dariushnia SR, Haskal ZJ, Midia M, Martin LG, Walker TG, Kalva SP, et al. Society of interventional radiology standards of practice committee. Quality improvement guidelines for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27(1):1–7.
Luca A, Miraglia R, Maruzzelli L, D’amico M, Tuzzolino F. Early liver failure after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with cirrhosis with model for end-stage liver disease score of 12 or less: incidence, outcome, and prognostic factors. Radiology. 2016;280(2):622–9.
Bureau C, Thabut D, Oberti F, Dharancy S, Carbonell N, Bouvier A, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts with covered stents increase transplant-free survival of patients with cirrhosis and recurrent ascites. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(1):157–63.
Angermayr B, Cejna M, Koenig F, Karnel F, Hackl F, Gangl A, et al. Survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: ePTFE-covered stentgrafts versus bare stents. Hepatology. 2003;38(4):1043–50.
Barrio J, Ripoll C, Bañares R, Echenagusia A, Catalina MV, Camúñez F, et al. Comparison of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt dysfunction in PTFE-covered stent-grafts versus bare stents. Eur J Radiol. 2005;55(1):120–4.
Tripathi D, Ferguson J, Barkell H, Macbeth K, Ireland H, Redhead DN, et al. Improved clinical outcome with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt utilizing polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stents. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;18(3):225–32.
Sommer CM, Gockner TL, Stampfl U, Bellemann N, Sauer P, Ganten T, et al. Technical and clinical outcome of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt: bare metal stents (BMS) versus viatorr stent-grafts (VSG). Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(9):2273–80.
Bureau C, Garcia-Pagan JC, Otal P, Pomier-Layrargues G, Chabbert V, Cortez C, et al. Improved clinical outcome using polytetrafluoroethylene-coated stents for TIPS: results of a randomized study. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(2):469–75.
Bureau C, Pagan JC, Layrargues GP, Metivier S, Bellot P, Perreault P, et al. Patency of stents covered with polytetrafluoroethylene in patients treated by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: long-term results of a randomized multicentre study. Liver Int. 2007;27(6):742–7.
Yang Z, Han G, Wu Q, Ye X, Jin Z, Yin Z, et al. Patency and clinical outcomes of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stents versus bare stents: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25(11):1718–25.
Perarnau JM, Le Gouge A, Nicolas C, d’Alteroche L, Borentain P, Saliba F, et al. STIC-TIPS group. Covered vs. uncovered stents for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2014;60(5):962–8.
Angeloni S, Merli M, Salvatori FM, De Santis A, Fanelli F, Pepino D, et al. Polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent grafts for TIPS procedure: 1-year patency and clinical results. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99(2):280–5.
Hernández-Guerra M, Turnes J, Rubinstein P, Olliff S, Elias E, Bosch J, et al. PTFE-covered stents improve TIPS patency in Budd-Chiari syndrome. Hepatology. 2004;40(5):1197–202.
Jung HS, Kalva SP, Greenfield AJ, Waltman AC, Walker TG, Athanasoulis CA, et al. TIPS: comparison of shunt patency and clinical outcomes between bare stents and expanded polytetrafluoroethylene stent-grafts. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20(2):180–5.
Gaba RC, Omene BO, Podczerwinski ES, Knuttinen MG, Cotler SJ, Kallwitz ER, et al. TIPS for treatment of variceal hemorrhage: clinical outcomes in 128 patients at a single institution over a 12-year period. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23(2):227–35.
Clark W, Golkar F, Luberice K, Toomey P, Paul H, Marcadis A, et al. Uncovering the truth about covered stents: is there a difference between covered versus uncovered stents with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts? Am J Surg. 2011;202(5):561–4.
Bandi JC, Solari J, Rostagno R, Galdame O, Garcia-Monaco R, Gadano AC. Long term follow up of patients treated with coated stents TIPS. J Hepatol. 2010;52(Suppl 1):S328.
Maleux G, Perez-Gutierrez NA, Evrard S, Mroue A, Le Moine O, Laleman W, et al. Covered stents are better than uncovered stents for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites: a retrospective cohort study. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2010;73(3):336–41.
Carbonell N, Pauwels A, Serfaty L, Fourdan O, Lévy VG, Poupon R. Improved survival after variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis over the past two decades. Hepatology. 2004;40(3):652–9.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Megan Griffiths, Scientific/Medical Writer at Cleveland Clinic, for her contributions in editing this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
This is a retrospective study. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A.C., Wang, W., Shah, C. et al. Added Value of Covered Stents in Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt: A Large Single-Center Experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40, 1723–1731 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1694-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1694-1