Abstract
Purpose
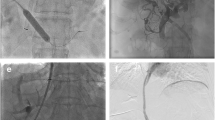
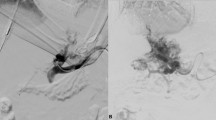
To assess radiofrequency (RF) ablation efficacy, as well as the patency of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPSs), in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Materials and Methods
Retrospective database review of patients with pre-existing TIPS undergoing RF ablation of HCC was conducted over a 159-month period ending in November 2013. TIPS patency pre- and post-RF ablation was assessed by ultrasound, angiography, and/or contrast-enhanced CT or MRI. Patient demographics and immediate post-RF ablation outcomes and complications were also reviewed.
Results
19 patients with 21 lesions undergoing 25 RF ablation sessions were included. Child-Pugh class A, B, and C scores were seen in 1, 13, and 5 patients, respectively. Eleven patients (58 %) ultimately underwent liver transplantation. Immediate technical success was seen in all ablation sessions without residual tumor enhancement (100 %). No patients (0 %) suffered liver failure within 1 month of ablation. Pre-ablation TIPS patency was demonstrated in 22/25 sessions (88 %). Of 22 cases with patent TIPS prior to ablation, post-ablation patency was demonstrated in 22/22 (100 %) at immediate post-ablation imaging and in 21/22 (95 %) at last follow-up (1 patient was incidentally noted to have occlusion 31 months later). No immediate complications were observed.
Conclusion
Ablation efficacy was similar to the cited literature values for patients without TIPS. Furthermore, TIPS patency was preserved in the majority of cases. Patients with both portal hypertension and HCC are not uncommonly encountered, and a pre-existing TIPS does not appear to be a definite contraindication for RF ablation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu DS, Yu NC, Raman SS et al (2005) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma as a bridge to liver transplantation. Hepatology 41:1130–1137
Lau WY, Leung TW, Yu SC, Ho SK (2003) Percutaneous local ablative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a review and look into the future. Ann Surg 237:171–179
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Bartolozzi C (2001) Percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation of liver malignancies: techniques, indications, imaging findings, and clinical results. Abdom Imaging 26:345–360
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Solbiati L, Gazelle GS (1999) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with radio-frequency ablation versus ethanol injection. Radiology 210:655–661
Donahue LA, Kulik L, Baker T et al (2013) Yttrium-90 radioembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. J Vasc Interv Radiol 24:74–80
Pua U, Punamiya S (2012) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt occlusion via modified pringle maneuver for radiofrequency ablation of nearby tumor. J Vasc Interv Radiol 23:563–565
Lu DS, Raman SS, Limanond P et al (2003) Influence of large peritumoral vessels on outcome of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:1267–1274
Otal P, Smayra T, Bureau C et al (2002) Preliminary results of a new expanded-polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent-graft for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178:141–147
Frericks BB, Ritz JP, Albrecht T et al (2008) Influence of intrahepatic vessels on volume and shape of percutaneous thermal ablation zones: in vivo evaluation in a porcine model. Invest Radiol 43:211–218
Kim YJ, Raman SS, Yu NC, Busuttil RW, Tong M, Lu DS (2008) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: can subcapsular tumors be safely ablated? AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:1029–1034
Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Brace C et al (2014) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria—a ten year update. Radiology 273(1):241–260
Lin SM, Lin CJ, Lin CC, Hsu CW, Chen YC (2004) Radiofrequency ablation improves prognosis compared with ethanol injection for hepatocellular carcinoma ≤4 cm. Gastroenterology 127:1714–1723
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M et al (2008) Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology 47:82–89
N’Kontchou G, Mahamoudi A, Aout M et al (2009) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results and prognostic factors in 235 Western patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 50:1475–1483
Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S et al (2005) A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 129:122–130
Cho YK, Rhim H, Noh S (2011) Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection as primary treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma meeting the Milan criteria: a systematic review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:1354–1360
Kohi MP, Fidelman N, Naeger DM, LaBerge JM, Gordon RL, Kerlan RK Jr (2013) Hepatotoxicity after transarterial chemoembolization and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: do two rights make a wrong? J Vasc Interv Radiol 24:68–73
Kang JW, Kim JH, Ko GY, Gwon DI, Yoon HK, Sung KB (2012) Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Acta Radiol 53:545–550
Niessen C, Jung EM, Wohlgemuth WA et al (2013) Irreversible electroporation of a hepatocellular carcinoma lesion adjacent to a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt stent graft. Korean J Radiol 14:797–800
Lee YJ, Lu DS, Osuagwu F, Lassman C (2012) Irreversible electroporation in porcine liver: short- and long-term effect on the hepatic veins and adjacent tissue by CT with pathological correlation. Invest Radiol 47:671–675
Pua U (2014) RE: Irreversible Electroporation of a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Lesion Adjacent to a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Stent Graft. Korean J Radiol 15:181–182
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.K., Al-Tariq, Q.Z., Zaw, T.M. et al. Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38, 1211–1217 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1050-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1050-2