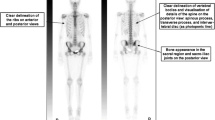
Abstract
Purpose
This study was designed to compare the accuracy of targeting and the radiation dose of bone biopsies performed either under fluoroscopic guidance using a cone-beam CT with real-time 3D image fusion software (FP-CBCT-guidance) or under conventional computed tomography guidance (CT-guidance).
Methods
Sixty-eight consecutive patients with a bone lesion were prospectively included. The bone biopsies were scheduled under FP-CBCT-guidance or under CT-guidance according to operating room availability. Thirty-four patients underwent a bone biopsy under FP-CBCT and 34 under CT-guidance. We prospectively compared the two guidance modalities for their technical success, accuracy, puncture time, and pathological success rate. Patient and physician radiation doses also were compared.
Results
All biopsies were technically successful, with both guidance modalities. Accuracy was significantly better using FP-CBCT-guidance (3 and 5 mm respectively: p = 0.003). There was no significant difference in puncture time (32 and 31 min respectively, p = 0.51) nor in pathological results (88 and 88 % of pathological success respectively, p = 1). Patient radiation doses were significantly lower with FP-CBCT (45 vs. 136 mSv, p < 0.0001). The percentage of operators who received a dose higher than 0.001 mSv (dosimeter detection dose threshold) was lower with FP-CBCT than CT-guidance (27 vs. 59 %, p = 0.01).
Conclusions
FP-CBCT-guidance for bone biopsy is accurate and reduces patient and operator radiation doses compared with CT-guidance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mundy GR (2002) Metastasis to bone: causes, consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 2:584–593
Miller TT (2008) Bone tumors and tumorlike conditions: analysis with conventional radiography. Radiology 246:662–674
Taira AV, Herfkens RJ, Gambhir SS, Quon A (2007) Detection of bone metastases: assessment of integrated FDG PET/CT imaging. Radiology 243:204–211
Wang CK, Li CW, Hsieh TJ, Chien SH, Liu GC, Tsai KB (2004) Characterization of bone and soft-tissue tumors with in vivo 1H MR spectroscopy: initial results. Radiology 232:599–605
Goetz MP, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW et al (2004) Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation of painful metastases involving bone: a multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 22:300–306
Rosenthal D, Callstrom MR (2012) Critical review and state of the art in interventional oncology: benign and metastatic disease involving bone. Radiology 262:765–780
Gianfelice D, Gupta C, Kucharczyk W, Bret P, Havill D, Clemons M (2008) Palliative treatment of painful bone metastases with MR imaging-guided focused ultrasound. Radiology 249:355–363
Ayala AG, Zornosa J (1983) Primary bone tumors: percutaneous needle biopsy. Radiologic–pathologic study of 222 biopsies. Radiology 149:675–679
Jelinek JS, Murphey MD, Welker JA et al (2002) Diagnosis of primary bone tumors with image-guided percutaneous biopsy: experience with 110 tumors. Radiology 223:731–737
Solomon SB, Silverman SG (2010) Imaging in interventional oncology. Radiology 257:624–640
Sarti M, Brehmer WP, Gay SB (2012) Low-dose techniques in CT-guided interventions. Radiographics 32:1109–1119 discussion 1119–1120
Rimondi E, Rossi G, Bartalena T et al (2011) Percutaneous CT-guided biopsy of the musculoskeletal system: results of 2027 cases. Eur J Radiol 77:34–42
Heautot JF, Chabert E, Gandon Y et al (1998) Analysis of cerebrovascular diseases by a new 3-dimensional computerised X-ray angiography system. Neuroradiology 40:203–209
Deschamps F, Solomon SB, Thornton RH et al (2010) Computed analysis of three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography angiography for determination of tumor-feeding vessels during chemoembolization of liver tumor: a pilot study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00270-010-9846-6
Braak SJ, van Strijen MJ, van Leersum M, van Es HW, van Heesewijk JP (2010) Real-Time 3D fluoroscopy guidance during needle interventions: technique, accuracy, and feasibility. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:W445–W451
Descat E, Ferron S, Cornelis F, Palussiere J (2011) Fluoroscopy-guided percutaneous biopsies: value of real-time guidance with image fusion software. J Radiol 92:864–867
Tam AL, Mohamed A, Pfister M et al (2010) C-arm cone beam computed tomography needle path overlay for fluoroscopic guided vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:1095–1099
Pedicelli A, Verdolotti T, Pompucci A et al (2011) Interventional spinal procedures guided and controlled by a 3D rotational angiographic unit. Skelet Radiol 40:1595–1601
Cardella JF, Bakal CW, Bertino RE et al (2003) Quality improvement guidelines for image-guided percutaneous biopsy in adults. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:S227–S230
Racadio JM, Babic D, Homan R et al (2007) Live 3D guidance in the interventional radiology suite. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:W357–W364
Tsalafoutas IA, Tsapaki V, Triantopoulou C, Gorantonaki A, Papailiou J (2007) CT-guided interventional procedures without CT fluoroscopy assistance: patient effective dose and absorbed dose considerations. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:1479–1484
Fazel R, Krumholz HM, Wang Y et al (2009) Exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation from medical imaging procedures. N Engl J Med 361:849–857
Kroeze SG, Huisman M, Verkooijen HM, van Diest PJ, Ruud Bosch JL, van den Bosch MA (2012) Real-time 3D fluoroscopy-guided large core needle biopsy of renal masses: a critical early evaluation according to the IDEAL recommendations. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35:680–685
Braak SJ, van Melick HH, Onaca MG, van Heesewijk JP, van Strijen MJ (2012) 3D cone-beam CT guidance, a novel technique in renal biopsy-results in 41 patients with suspected renal masses. Eur Radiol 22:2547–2552
Braak SJ, Herder GJ, van Heesewijk JP, van Strijen MJ (2012) Pulmonary masses: initial results of cone-beam CT guidance with needle planning software for percutaneous lung biopsy. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35:1414–1421
Busser WM, Hoogeveen YL, Veth RP et al (2011) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteomas with use of real-time needle guidance for accurate needle placement: a pilot study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34:180–183
Morimoto M, Numata K, Kondo M et al (2010) C-arm cone beam CT for hepatic tumor ablation under real-time 3D imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:W452–W454
Braak SJ, van Strijen MJ, van Es HW, Nievelstein RA, van Heesewijk JP (2011) Effective dose during needle interventions: cone-beam CT guidance compared with conventional CT guidance. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22:455–461
Leschka SC, Babic D, El Shikh S, Wossmann C, Schumacher M, Taschner CA (2011) C-arm cone beam computed tomography needle path overlay for image-guided procedures of the spine and pelvis. Neuroradiology. doi:10.1007/s00234-011-0866-y
Strocchi S, Colli V, Conte L (2012) Multidetector CT fluoroscopy and cone-beam CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic biopsy: comparison based on patient doses. Radiat Prot Dosim 151:162–165
Kwok YM, Irani FG, Tay KH, Yang CC, Padre CG, Tan BS (2013) Effective dose estimates for cone beam computed tomography in interventional radiology. Eur Radiol 23:3197–3204
Suzuki S, Furui S, Yamaguchi I et al (2009) Effective dose during abdominal three-dimensional imaging with a flat-panel detector angiography system. Radiology 250:545–550
Abi Jaoudeh N, Kruecker J, Kadoury S et al (2012) Multimodality image fusion-guided procedures: technique, accuracy, and applications. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35:12
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Lorna Saint Ange for editing.
Conflict of interest
L. Tselikas, J. Joskin, G. Farouil, S. Dreuil, A. Hakimé, C. Teriitehau, A. Auperin, T. de Baere, and F. Deschamps have no financial disclosures relative to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tselikas, L., Joskin, J., Roquet, F. et al. Percutaneous Bone Biopsies: Comparison between Flat-Panel Cone-Beam CT and CT-Scan Guidance. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38, 167–176 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0870-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0870-9