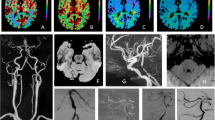
Abstract
Purpose
To determine the safety and efficacy of endovascular therapy for the treatment of basilar artery dissection (BAD).
Methods
Patients with BAD admitted to our hospital from June 2002 to December 2011 were retrospectively reviewed. Strict inclusion and exclusion criteria were made. At enrollment, patients’ manifestations were evaluated. The different devices and techniques used for each patient were recorded and further classified into two groups: the coiling-only group, in which lesions were treated only with coils; and the stented group, in which lesions were treated with only stents or by stent-assisted embolization. Shapes of BAD were described and classified into three types: dilation, pearl-and-string sign, and stenosis. Presentations of BAD were classified as ruptured or unruptured. Digital subtraction angiography results obtained immediately after intervention and at follow-up were evaluated and classified into two groups: stable/improved or recanalized/worsened. Clinical outcome was evaluated by modified Rankin Scale score.
Results
A total of 29 patients were included, and 28 of them were followed up clinically and angiographically. No significant difference of recurrence rate existed between ruptured and unruptured BAD. The coiling-only group demonstrated a significantly higher recurrence rate than the stent-assisted group. In the 22 instances of BAD presenting with dilated shapes, stented cases had better radiological outcome than unstented cases, and initial packing of completely/near completely occluded cases had better radiological follow-up results.
Conclusion
Endovascular therapy proved safe and effective. Stent placement and initial complete occlusion were favorable factors for follow-up stable/improved outcome.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshimoto Y, Hoya K, Tanaka Y, Uchida T (2005) Basilar artery dissection. J Neurosurg 102:476–481
Redekop G, TerBrugge K, Willinsky R (1999) Subarachnoid hemorrhage from vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysm treated with staged bilateral vertebral artery occlusion: the importance of early follow-up angiography: technical case report. Neurosurgery 45:1258–1262
Sakamoto S, Ohba S, Shibukawa M et al (2005) Staged bilateral vertebral artery occlusion for ruptured dissecting aneurysms of the basilar artery: a report of 2 cases. Surg Neurol 64:456–461
Nakahara T, Satoh H, Mizoue T et al (1999) Dissecting aneurysm of basilar artery presenting with recurrent subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurg Rev 22:155–158
van Oel LI, van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M et al (2013) Reconstructive endovascular treatment of fusiform and dissecting basilar trunk aneurysms with flow diverters, stents, and coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:589–595
Alexander CB, Burger PC, Goree JA (1979) Dissecting aneurysms of the basilar artery in 2 patients. Stroke 10:294–299
Diniz-Carneiro DS, Portela LA, De Melo-Souza SE (1992) Intracranial dissecting aneurysms of the posterior circulation: report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 50:351–360
Kim BM, Kim SH, Kim DI et al (2011) Outcomes and prognostic factors of intracranial unruptured vertebrobasilar artery dissection. Neurology 76:1735–1741
Hosoya T, Adachi M, Yamaguchi K et al (1999) Clinical and neuroradiological features of intracranial vertebrobasilar artery dissection. Stroke 30:1083–1090
Schoenberg BS, Mellinger JF, Schoenberg DG (1978) Cerebrovascular disease in infants and children: a study of incidence, clinical features, and survival. Neurology 28:763–768
Nakatomi H, Nagata K, Kawamoto S, Furusho JI (1999) Basilar artery occlusion due to spontaneous basilar artery dissection in a child. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141:99–104
Ruecker M, Furtner M, Knoflach M et al (2010) Basilar artery dissection: series of 12 consecutive cases and review of the literature. Cerebrovasc Dis 30:267–276
Yoshimoto Y, Wakai S (1997) Unruptured intracranial vertebral artery dissection. Clinical course and serial radiographic imagings. Stroke 28:370–374
Pozzati E, Andreoli A, Padovani R, Nuzzo G (1995) Dissecting aneurysms of the basilar artery. Neurosurgery 36:254–258
Masson C, Krespy Y, Masson M, Colombani JM (1993) Magnetic resonance imaging in basilar artery dissection. Stroke 24:1264–1266
Ramgren B, Cronqvist M, Romner B et al (2005) Vertebrobasilar dissection with subarachnoid hemorrhage: a retrospective study of 29 patients. Neuroradiology 47:97–104
Hosoda K, Fujita S, Kawaguchi T et al (1991) Spontaneous dissecting aneurysms of the basilar artery presenting with a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 75:628–633
Kim BM, Suh SH, Park SI et al (2008) Management and clinical outcome of acute basilar artery dissection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1937–1941
Mizutani T (1996) A fatal, chronically growing basilar artery: a new type of dissecting aneurysm. J Neurosurg 84:962–971
Ross GJ, Ferraro F, DeRiggi L, Scotti LN (1994) Spontaneous healing of basilar artery dissection: MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18:292–294
Woimant F, Spelle L (1995) Spontaneous basilar artery dissection: contribution of magnetic resonance imaging to diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 58:540
Patroclo CB, Puglia P Jr, LeiteCda C (2007) Endovascular treatment of a basilar artery dissecting aneurysm. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 65(4A):1012–1014
Pozzati E, Andreoli A, Limoni P, Casmiro M (1994) Dissecting aneurysms of the vertebrobasilar system: study of 16 cases. Surg Neurol 41:119–124
Liu XC, Shi MC, Wang SC (2012) Endovascular treatment for ischemic stroke induced by vertebrobasilar junction artery dissection: 2 case reports. Vasc Endovasc Surg 46:58–61
Farrell MA, Gilbert JJ, Kaufmann JC (1985) Fatal intracranial arterial dissection: clinical pathological correlation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:111–121
Takagi M, Hirata K, Fujitsu K, Yamamoto I (1994) Unusual angiographic changes in a dissecting aneurysm of the basilar artery: case report. Neurosurgery 34:356–358
Berger MS, Wilson CB (1984) Intracranial dissecting aneurysms of the posterior circulation. Report of six cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 61:882–894
Friedman AH, Drake CG (1984) Subarachnoid hemorrhage from intracranial dissecting aneurysm. J Neurosurg 60:325–334
Amin-Hanjani S, Ogilvy CS, Buonanno FS et al (1997) Treatment of dissecting basilar artery aneurysm by flow reversal. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 139:44–51
Ali MJ, Bendok BR, Tella MN et al (2003) Arterial reconstruction by direct surgical clipping of a basilar artery dissecting aneurysm after failed vertebral artery occlusion: technical case report and literature review. Neurosurgery 52:1475–1480
Defillo A, Nussbaum ES, Zelensky A, Nussbaum L (2011) Multiple non-branching dissecting aneurysms of the mid-basilar trunk presenting with sequential subarachnoid hemorrhages. Surg Neurol Int 2:127
Kai Y, Hamada J, Morioka M et al (2004) Successful treatment of a ruptured dissecting basilar artery aneurysm. Case report. J Neurosurg 100:1072–1075
Mizutani T, Aruga T, Kirino T et al (1995) Recurrent subarachnoid hemorrhage from untreated ruptured vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms. Neurosurgery 36:905–911
Kitanaka C, Tanaka J, Kuwahara M et al (1994) Nonsurgical treatment of unruptured intracranial vertebral artery dissection with serial follow-up angiography. J Neurosurg 80:667–674
Hashimoto M, Johkura K, Ichikawa T et al (2008) Conservative treatment of ruptured vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysm. Neurol Sci 29:241–244
O’Shaughnessy BA, Getch CC, Bendok BR, Batjer HH (2005) Late morphological progression of a dissecting basilar artery aneurysm after staged bilateral vertebral artery occlusion: case report. Surg Neurol 63:236–243
Wenderoth JD, Khangure MS, Phatouros CC, ApSimon HT (2003) Basilar trunk occlusion during endovascular treatment of giant and fusiform aneurysms of the basilar artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1226–1229
Yu J, Xu K, Wang H, Wang B, Luo Q (2012) Endovascular coil embolization of parent artery for giant intracranial basilar artery dissection: a case report. Turk Neurosurg 22:483–488
Hamada J, Kai Y, Morioka M et al (2003) Multimodal treatment of ruptured dissecting aneurysms of the vertebral artery during the acute stage. J Neurosurg 99:960–966
Park SI, Kim BM, Kim DI et al (2009) Clinical and angiographic follow-up of stent-only therapy for acute intracranial vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1351–1356
Liu L, Jiang C, He H et al (2010) Delayed thrombosis of the basilar artery after stenting for a basilar trunk dissection aneurysm. A case report and review of the literature. Interv Neuroradiol 16:77–82
Doerfler A, Wanke I, Egelhof T et al (2004) Double-stent method: therapeutic alternative for small wide-necked aneurysms. Technical note. J Neurosurg 100:150–154
Benndorf G, Herbon U, Sollmann WP, Campi A (2001) Treatment of a ruptured dissecting vertebral artery aneurysm with double stent placement: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1844–1848
Lylyk P, Cohen JE, Ceratto R et al (2002) Endovascular reconstruction of intracranial arteries by stent placement and combined techniques. J Neurosurg 97:1306–1313
Komiyama M, Yoshimura M, Honnda Y et al (2005) Acute basilar artery dissection treated by emergency stenting in a 13-year-old boy. Pediatr Neurosurg 41:318–322
Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Deshmukh VR et al (2006) Endovascular reconstruction with the neuroform stent as monotherapy for the treatment of uncoilable intradural pseudoaneurysms. Neurosurgery 59:291–300
Phillips TJ, Wenderoth JD, Phatouros CC et al (2012) Safety of the pipeline embolization device in treatment of posterior circulation aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1225–1231
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Che Jiang and Qiang Li should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, C., Li, Q., Liu, JM. et al. Endovascular Treatment for the Basilar Artery Dissection. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37, 646–656 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0737-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0737-5