Abstract
Purpose
This study was designed to assess the long-term outcome of selected patients with aortic, aortoiliac, and isolated common iliac aneurysms treated with the GORE EXCLUDER® stent-graft.
Methods
Between December 1998 and June 2010, 121 nonconsecutive patients underwent insertion of a GORE EXCLUDER® stent-graft to treat an aortic (n = 80; 66%), aortoiliac (n = 25; 21%), or isolated common iliac (n = 16; 13%) aneurysm. Procedural and follow-up data were collected prospectively. Primary endpoints are overall survival, intervention-free survival, and freedom from aneurysm rupture. Secondary endpoints are device- and procedure-related complications, including all types of endoleaks or endotension, and reintervention.
Results
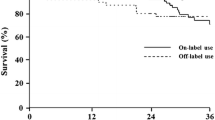
The mean follow-up is 4.98 years (standard deviation, 3.18; median follow-up, 4.05 years). The estimated percentage overall survival (with 95% confidence interval) after respectively 5 and 10 years of follow-up is 74.5% (65.8; 81.3) and 57.8% (47.7; 66.7). The estimated intervention-free survival after respectively 5 and 10 years is 90% (84.3; 96.1) and 77.7% (67; 88.4). There was no aneurysm rupture during follow-up. Early postoperative complications occurred in 16 patients (13%); none were fatal. Late reinterventions were performed in 18 patients (15%). Finally, throughout the follow-up period, endoleaks were identified: type I (n = 4; 3%); type II (n = 39; 32%); type III (n = 0; 0%); endotension was seen in 11 patients (9%).
Conclusions
Aneurysm exclusion with use of the GORE EXCLUDER® stent-graft is durable through a mean follow-up of nearly 5 years. There was no postprocedural aneurysm rupture. Complications occurred throughout the follow-up period, requiring continued clinical and radiological surveillance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prinssen M, Verhoeven EL, Buth J, Cuypers PW, Van Sambeek MR, Balm R et al (2004) A randomized trial comparing conventional and endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med 351:1607–1618
Greenhalgh RM, Brown LC, Kwong GP, Powell JT, EVAR Tompson SG trial participants (2005) Endovascular aneurysm repair versus open repair in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm (EVAR 1): randomised controlled trial. Lancet 365:2179–2186
De Bruin JL, Baas AF, Buth J, Prinssen M, Verhoeven EL, Cuypers PW, van Sambeek MR, Balm R, Grobbee DE, Blankensteijn JD DREAM, Group Study (2010) Long-term outcome of open or endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med 362(20):1881–1889
Leurs LJ, Buth J, Laheij RJ (2007) Long-term results of endovascular abdominal aneurysm treatment with the first generation of commercially available stent-grafts. Arch Surg 142:33–41
Van Herzeele I, Lefevre A, Van Maele G, Maleux G, Nevelsteen A, Vermassen F (2008) Long-term surveillance is paramount after implantation of the Vanguard stent-graft for abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Cardiovasc Surg 49:59–66
Pfammatter T, Mayer D, Pfiffner R, Koehler C, Hechelhammer L, Lachat ML (2003) Repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms with the Excluder bifurcated stent-graft. J Cardiovasc Surg 44:549–552
Sayeed S, Marone LK, Makaroun MS (2006) The GORE EXCLUDER® endograft device for the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Cardiovasc Surg 47:251–260
Kibbe MR, Matsumura JS for the Excluder Investigators (2003) The GORE EXCLUDER® US multi-center trial: analysis of adverse events at 2 years. Sem Vasc Surg 16:144–150
Curci JA, Fillinger MF, Naslund TC, Rubin BG for the Excluder Bifurcated Endoprosthesis Investigators (2007) Ann Vasc Surg 21:328–338
Tanski W, Fillinger M (2007) Outcomes of original and low-permeability GORE EXCLUDER® endoprosthesis for endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 45:243–249
Cartes-Zumelzu F, Lammer J, Hoelzenbein T, Cejna M, Schoder M, Thurnher S, Kretschmer G (2002) Endovascular placement of a Nitinol-ePTFE stent-graft for abdominal aortic aneurysms: initial and midterm results. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13:465–473
Melissano G, Bertoglio L, Esposito G, Civilini E, Setacci F, Chiesa R (2005) Midterm clinical success and behavior of the aneurysm sac after endovascular AAA repair with the Excluder graft. J Vasc Surg 42:1052–1057
Alterman DM, Stevens SL (2008) The Excluder aortic endograft. Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther 20:136–148
Harris PL, Buth J, Mialhe C, Myhre HO, Norgren L (1997) The need for clinical trials of endovascular abdominal aneurysm stent-graft repair: the EUROSTAR project. J Endovasc Surg 4:72–77
Golzarian J, Murgo S, Dussausois L, Guyot S, Said KA, Wautrecht JC, Struyven J (2002) Evaluation of abdominal aortic aneurysm after endoluminal treatment: comparison of color Doppler sonography with biphasic helical CT. Am J Roentgenol 178:623–628
Pintilie M (2006) Competing risks: a practical perspective. Wiley, Chichester
Hussain Q, Maleux G, Heye S, Fourneau I (2008) Endovascular repair of an actively hemorrhaging stab wound injury to the abdominal aorta. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31:1023–1025
Heye S, Nevelsteen A, Maleux G (2005) Internal iliac artery coil embolization in the prevention of potential type 2 endoleak after endovascular repair of abdominal aortoiliac and iliac artery aneurysms: effect of total occlusion versus residual flow. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:235–239
Bos WT, Tielliu F, Van den Dungen JJ, Zeebregts CJ, Sondakh AO, Prins TR, Verhoeven EL (2009) Results of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair with selective use of the Gore Excluder. J Cardiovasc Surg 50:159–164
Nevala T, Biancari F, Manninen H, Aho P-S, Matsi P, Mäkinen K, Roth W-D, Ylönen K, Lepäntalo M, Perälä J (2009) Finnish multicenter study on the midterm results of use of the Zenith stent-graft in the treatment of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20:448–454
Golzarian J, Struyven J, Abada HT, Wery D, Dussausois L, Madani A, Ferreira J, Dereume JP (1997) Endovascular aortic stent-grafts: transcatheter embolization of persistent perigraft leaks. Radiology 202:731–734
Amesur NB, Zajko AB, Orons PD, Makaroun MS (1999) Embolotherapy of persistent endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms with the Ancure-endovascular technologies endograft system. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10:1175–1182
Bandorski D, Brück M, Günther HU, Manke C (2010) Endograft collapse after endovascular treatment for thoracic aortic disease. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33:492–497
Maleux G, Koolen M, Heye S, Nevelsteen A (2008) Limb occlusion after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms with supported endografts. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19:1409–1412
Goodney PP, Fillinger MF (2007) The effect of endograft relining on sac expansion after endovascular aneurysm repair with the original-permeability GORE EXCLUDER® abdominal aortic aneurysm endoprosthesis. J Vasc Surg 45:686–693
Cho JS, Dillavou ED, Rhee RY, Makaroun MS (2004) Late abdominal aortic aneurysm enlargement after endovascular repair with the Excluder device. J Vasc Surg 39:1236–1242
Haider S, Najjar SF, Cho JS, Rhee RY, Eskandari MK, Matsumora JS, Makaroun MS, Morasch MD (2006) Sac behavior after aneurysm treatment with the GORE EXCLUDER® low-permeability aortic endoprosthesis: 12-months comparison to the original Excluder device. J Vasc Surg 44:694–700
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors state that they haven’t received any funding for research from any of the following organizations: National Institutes of Health (NIH), Wellcome Trust, Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maleux, G., Claes, H., Van Holsbeeck, A. et al. Ten Years of Experience with the GORE EXCLUDER® Stent-Graft for the Treatment of Aortic and Iliac Aneurysms: Outcomes from a Single Center Study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35, 498–507 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-011-0235-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-011-0235-6