Abstract
Purpose
We have previously reported the clinical efficacy of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsion containing anticancer agent. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of transcatheter arterial infusion (TAI) of W/O/W emulsion via a cystic artery for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
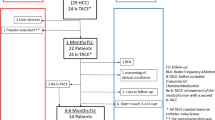
TAI of a W/O/W emulsion was performed at our institute in five patients with Stage III or IV HCC with blood supply from the cystic artery. In all patients, 2–12 ml W/O/W emulsion was infused via a cystic artery. Therapeutic effects and complications were evaluated in these patients.
Results
Of the five patients treated, one achieved a complete response and two achieved a partial response. After treatment, acute cholecystitis or gallbladder ischemia that required treatment was not encountered in any patient.
Conclusions
W/O/W emulsion can be safely infused via a cystic artery without major complications; it is a good therapeutic option for the patients with advanced HCC fed by a cystic artery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Higashi S, Shimizu M, Nakashima T et al (1995) Arterial-injection chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma using monodispersed poppy-seed oil microdroplets containing fine aqueous vesicles of epirubicin. Initial medical application of a membrane-emulsification technique. Cancer 75:1245–1254
Higashi S, Maeda Y, Kai M et al (1996) A case of hepatocellular carcinoma effectively treated with epirubicin aqueous vesicles in monodispersed iodized poppy-seed oil microdroplets. Hepatogastroenterology 43:1427–1430
Higashi S, Tabata N, Kondo KH et al (1999) Size of lipid microdroplets effects results of hepatic arterial chemotherapy with an anticancer agent in water in- oil-in-water emulsion to hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:816–819
Higashi S, Setoguchi T (2000) Hepatic arterial injection chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with epirubicin aqueous solution as numerous vesicles in iodinated poppy-seed oil microdroplets: clinical application of water-in-oil-in-water emulsion prepared using a membrane emulsification technique. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 45:57–64
Ikushima I, Higashi S, Seguchi K et al (2009) Transarterial infusion chemotherapy with epirubicin in water-in-oil-in-water emulsion for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma in the residual liver after hepatectomy. Eur J Radiol 69:114–119
Miyayama S, Matsui O, Nishida H et al (2003) Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma fed by the cystic artery. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:1155–1161
Duffaud F, Therasse P (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. Bull Cancer 87:881–886
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A et al (2003) CTCAE v3.0: Development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol 13:176–181
Kuroda C, Iwasaki M, Tanaka T et al (1983) Gallbladder infarction following hepatic transcatheter arterial embolization. Angiographic study. Radiology 149:85–89
Nakamura H, Kondoh H (1986) Emphysematous cholecystitis: complication of hepatic artery embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 9:152–153
Simons RK, Sinanan MN, Coldwell DM (1992) Gangrenous cholecystitis as a complication of hepatic artery embolization: case report. Surgery 112:106–110
Takayasu K, Moriyama N, Muramatsu Y et al (1985) Gallbladder infarction after hepatic artery embolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol 144:135–138
Sakamoto I, Aso N, Nagaoki K et al (1998) Complications associated with transcatheter arterial embolization for hepatic tumors. Radiographics 18:605–619
Hirota S, Matsumoto S, Fukuda T et al (1999) Solitary hepatocellular carcinoma fed by the cystic artery: limitation of transcatheter arterial embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 22:206–209
Chopra S, Dodd GD III, Chanin MP, Chintapalli KN (2003) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors adjacent to the gallbladder: feasibility and safety. Am J Roentgenol 180:697–701
Sartori S, Tombesi P, Macario F et al (2008) Subcapsular liver tumors treated with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: a prospective comparison with nonsubcapsular liver tumors for safety and effectiveness. Radiology 248:670–679
Kim SW, Rhim H, Park M et al (2009) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas adjacent to the gallbladder with internally cooled electrodes: assessment of safety and therapeutic efficacy. Korean J Radiol 10:366–376
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S et al (1999) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with radio-frequency ablation versus ethanol injection. Radiology 210:655–661
Akahane M, Koga H, Kato NY et al (2005) Complications of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepato-cellular carcinoma: imaging spectrum and management. Radiographics 25(Suppl 1):S57–S68
Llovet JM, Vilana R, Brú C et al (2000) Increased risk of tumor seeding after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 33:1124–1129
Imamura J, Tateishi R, Shiina S et al (2008) Neoplastic seeding after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol 103:3057–3062
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikushima, I., Higashi, S., Ishii, A. et al. Transcatheter Infusion of Epirubicin in Water-in-Oil-in-Water Emulsion via a Cystic Artery for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34, 802–807 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-010-9988-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-010-9988-6