Abstract
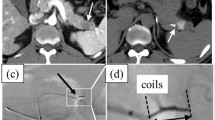
CyberKnife frameless image-guided radiosurgery has become a widely used system for parenchymal extracranial lesions. Gold fiducials are required for the planning and aiming of CyberKnife therapy. We report our initial experience and describe the technique of positioning tumor markers, under CT guidance. We conducted a retrospective review of 105 patients who were referred for CyberKnife stereotactic radiosurgery at Iatropolis CyberKnife Center in Athens. All patients underwent percutaneous fiducial placement via CT guidance. At the desired location, the 18-G needle was advanced into or near the tumor. Data collected included number and locations of fiducials placed and complications experienced to date. One hundred five patients underwent fiducial placement under CT guidance and a total number of 319 gold seeds were implanted. We experienced one episode of pneumothorax that required drainage, one mild pneumothorax, and three episodes of perifocal pulmonary hemorrhage. In conclusion, fiducial implantation under CT guidance appears to be a safe and efficient procedure, as long as it is performed by an experienced interventional radiologist.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casamassima F, Cavedon C, Francescon P et al (2006) Use of motion tracking in stereotactic body radiotherapy: evaluation of uncertainty in off-target dose distribution and optimization strategies. Acta Oncol 45:943–947
Adler JR Jr, Chang SD, Murphy MJ et al (1997) The Cyberknife: a frameless robotic system for radiosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 69:124–128
Kuo JS, Yu C, Petrovich Z et al (2003) The CyberKnife stereotactic radiosurgery system: description, installation, and an initial evaluation of use and functionality. Neurosurgery 53:1235–1239 (discussion 1239)
Quinn AM (2002) CyberKnife: a robotic radiosurgery system. Clin J Oncol Nurs 6:149–156
Gerszten PC, Burton SA, Ozhasoglu C et al (2005) Stereotactic radiosurgery for spinal metastases from renal cell carcinoma. J Neurosurg Spine 3:288–295
Chang SD, Murphy M, Geis P et al (1998) Clinical experience with image-guided robotic radiosurgery (the Cyberknife) in the treatment of brain and spinal cord tumors. Neurol Med Chir 38:780–783
Whyte RI, Crownover R, Murphy MJ et al (2003) Stereotactic radiosurgery for lung tumors: preliminary report of a phase I trial. Ann Thorac Surg 75:1097–1101
Koong AC, Christofferson E, Le QT et al (2005) Phase II study to assess the efficacy of conventionally fractionated radiotherapy followed by a stereotactic radiosurgery boost in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:320–323
Koong AC, Le QT, Ho A et al (2004) Phase I study of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:1017–1021
King CR, Lehmann J, Adler JR et al (2003) CyberKnife radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer: rationale and technical feasibility. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2:25–30
Blomgren H, Lax I, Naslund I et al (1995) Stereotactic high dose fraction radiation therapy of extracranial tumors using an accelerator. Clinical experience of the first thirty-one patients. Acta Oncol 34:861–870
Herfarth KK, Debus J, Lohr F et al (2001) Stereotactic single-dose radiation therapy of liver tumors: results of a phase I/II trial. J Clin Oncol 19:164–170
Wulf J, Hadinger U, Oppitz U et al (2001) Stereotactic radiotherapy of targets in the lung and liver. Strahlenther Onkol 177:645–655
Yu C, Main W, Taylor D et al (2004) An anthropomorphic phantom study of the accuracy of CyberKknife spinal radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 55:1138–1149
Ryu SI, Chang SD, Kim DH et al (2001) Image-guided hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery to spinal lesions. Neurosurgery 49:838–846
Berbeco RI, Nishioka S, Shirato H et al (2005) Residual motion of lung tumours in gated radiotherapy with external respiratory surrogates. Phys Med Biol 50:3655–3667
Shirato H, Shimizu S, Kunieda T et al (2000) Physical aspects of a real-time tumor -tracking system for gated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48:1187–1195
Fu D, Kuduvalli G (2006) Enhancing skeletal features in digitally reconstructed radiographs. In: Reinhardt JM, Pluim JP (eds). Proceedings of SPIE International Society for Optical Engineering 6144:846–851
Fu D, Kuduvalli G, Maurer CR et al (2006) 3D target localization using 2D local displacements of skeletal structures in orthogonal X-ray images for image-guided spinal radiosurgery. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg Suppl 1:198–200
Sinner W (1976) Complications of percutaneous thoracic needle aspiration biopsy. Acta Radiol Diagn 17:813–828
Laurent F, Latrabe V, Vergier B et al (2000) Percutaneous CT-guided biopsy of the lung: comparison between aspiration and automated cutting needles using a coaxial technique. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 23:266–272
Klein JS, Salomon G, Stewart EA (1996) Transthoracic needle biopsy with a coaxially placed 20-gauge automated cutting needle: results in 122 patients. Radiology 198:715–720
Richardson CM, Pointon KS, Manhire AR et al (2002) Percutaneous lung biopsies: a survey of UK practice based on 5444 biopsies. Br J Radiol 75:731–735
Glassberg RM, Sussman SK (1990) Life threatening haemorrhage due to percutaneous thoracic intervention: importance of the internal mammary artery. AJR 154:47–49
Kumaradevan J, Babar S, Watkinson AF (2000) Complications of abdominal biopsy. Imaging 12:226–234
Livraghi T, Damascelli B, Lombardi C et al (1983) Risk in fine-needle abdominal biopsy. J Clin Ultrasound 11(2):77–81
Rosenbaum DA, Frost DB (1990) Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the pancreas complicated by pancreatic ascites. Cancer 65:2537–2538
Frederiksen P, Thommesen P, Skjoldborg H (1976) Pancreatic fistula and hematoma (one each). Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the pancreas. Scand J Gastroenterol 1(1):785–791
Shirato H, Harada T, Harabayashi T et al (2004) Feasibility of insertion/implantation of 2.0-mm-diameter gold internal fiducial markers for precise set up and real-time tumor tracking in radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60:329–334
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sotiropoulou, E., Stathochristopoulou, Ι., Stathopoulos, K. et al. CT-Guided Fiducial Placement for CyberKnife Stereotactic Radiosurgery: An Initial Experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33, 586–589 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9748-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9748-7