Abstract
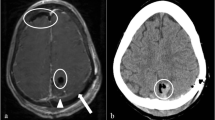
Two children younger than 10 sought care for large, tense pulsatile swelling in the neck after fine-needle aspiration of cervical lymph nodes that resulted in severe respiratory distress. Computed tomographic angiography confirmed the presence of large pseudoaneurysms that caused a mass effect, leading to compression of surrounding vessels and airway. Pseudoaneurysms were successfully treated by coil embolization in one patient and surgical ligation of the internal carotid artery in the other.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubaska SM, Greenberg RK, Clair D et al (2003) Internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysms: treatment with the wallgraft endoprosthesis. J Endovasc Ther 10:182–189
Bush RL, Lin PH, Dodson TF et al (2001) Endoluminal stent placement and coil embolization for the management of carotid artery. J Endovasc Ther 8:53–61
Yasuda H, Kuroda S, Ushikoshi S et al (2005) Combined surgical and endovascular treatment of infected pseudoaneurysm after carotid endarterectomy. Case report. Neurol Med Chir 45:37–40
Bogaerdea MV, Viaeneb P, Vincent T (2007) Iatrogenic perforation of the internal carotid artery by a transarticular screw: an unusual case of repetitive stroke. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 109:466–469
Hertzanu Y, Hirsch M, Tovi F (1987) Pseudoaneurysm of internal carotid artery secondary to tonsillectomy: combined radiologic and surgical treatment. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 10:147–149
Koyanagi M, Nishi S, Hattori I et al (2004) Stent-supported coil embolization for carotid artery pseudoaneurysm as a complication of endovascular surgery. Case report. Neurol Med Chir 44:544–547
Schwartz LB, Clark ET, Gewertz BL (2000) Anastomotic and other pseudoaneurysms. In: Rutherford RB (ed) Vascular surgery, 5th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 752–763
Wai Kl, Clare JR, Vinay AD et al (2001) Pseudoaneurysm of the uterine artery after abdominal hysterectomy: radiologic diagnosis and management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 185:1269–1272
Kwon JH, Kim GS (2002) Obstetric iatrogenic arterial injuries of the uterus: diagnosis with US and treatment with transcatheter arterial embolization. Radiographics 22:35–46
Tanaka H, Patel U, Shrier DA, Coniglio JU (1998) Pseudoaneurysm of the petrous internal carotid artery after skull base infection and prevertebral abscess drainage. Am J Neuroradiol 19:502–504
Bush RL, Lin PH, Dodson TF et al (2001) Endoluminal stent placement and coil embolization for the management of carotid artery pseudoaneurysms. J Endovasc Ther 8:53–61
Reisner A, Marshall GS, Bryant K et al (1999) Endovascular occlusion of a carotid pseudoaneurysm complicating deep neck space infection in a child. J Neurosurg 91:510–514
Perry MO (1993) Complications of missed arterial injuries. J Vasc Surg 17:399–407
Liu AY, Paulsen RD, Marcellus ML et al (1999) Long-term outcomes after carotid stent placement for treatment of carotid artery dissection. Neurosurgery 45:1368–1374
Maras D, Lioupis C, Magoufis G et al (2006) Covered stent-graft treatment of traumatic internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysms: a review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29:958–968
Brega KE, Biffl WL, Offner PJ et al (2000) Treatment of posttraumatic internal carotid arterial pseudoaneurysms with endovascular stents. J Trauma 48:470–472
Haq T, Yaqoob J, Munir K, Usman MU (2004) Endovascular-covered stent treatment of posttraumatic cervical carotid artery pseudoaneurysms. Australas Radiol 48:220–223
Gupta V, Niranjan K, Rawat L, Gupta AK (2008) Stent-graft repair of a large cervical internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm causing dysphagia. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00270-008-9421-6
Lim SP, Duddy MJ (2008) Endovascular treatment of a carotid dissecting pseudoaneurysm in a patient with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV with fatal outcome. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31:201–204
Köroglu M, Arat A, Cekirge S et al (2002) Giant cervical internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in a child: endovascular treatment. Neuroradiology 44:864–867
Raymond KT, Joseph M, Grady MS (1996) Endovascular treatment of a kitchen knife pseudoaneurysm of the cervical internal carotid artery. Am J Roentgenol 166:704
Williams PM, Traquina DN, Wallace RC, Niezgoda JJ (2000) Coil embolization of a ruptured carotid pseudoaneurysm presenting as epistaxis—pediatric otolaryngology: principles and practice. Am J Otolaryngol 21:38–42
Holder R, Hilton D, Martin J, Harris PL et al (2002) Percutaneous thrombin injection of carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. J Endovasc Ther 9:25–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singhal, M., Gupta, V., Singh, P. et al. Iatrogenic Life-Threatening Pseudoaneurysms of Extracranial Internal Carotid Artery After Fine-Needle Aspiration of Cervical Lymph Nodes: Report of Two Cases in Children. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32, 1260–1263 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9506-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9506-x