Abstract
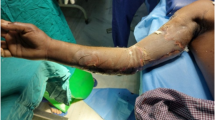
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a colorless corrosive acid used in different industrial branches. Exposure to HF typically results from spills, and most often the hand or fingers are involved. Tissue damage through cutaneous HF exposure occurs through corrosive burns due to the free hydrogen ions and through skin penetration of the fluoride ions, causing a depletion of calcium in the deep tissue layers, ultimately leading to cell death and tissue necrosis. Treatment of HF burns consists of thoroughly flushing the exposed area with water and applying calcium gluconate gel to the skin. If topical treatment does not suffice, subcutaneous injections, as well as intravascular—both intravenous and intra-arterial—calcium gluconate therapy, have been advocated. We report for the first time a case of HF burn of the hand and digits associated with vasospasm. Pain and vasospasm were successfully treated by repeated intra-arterial calcium gluconate injection. We conclude that intra-arterial calcium gluconate injection is a successful and well-tolerated therapy for HF burn associated with Raynaud’s syndrome. Intra-arterial injection allows for well-controlled delivery of therapy as well as assessment of the vascular status.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shewmake SW, Anderson BG (1979) Hydrofluoric acid burns. A report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol 115(5):593–596
Graudins A, Burns MJ, Aaron CK (1997) Regional intravenous infusion of calcium gluconate for hydrofluoric acid burns of the upper extremity. Ann Emerg Med 30(5):604–607
Achinger R, Kohnlein HE, Jacobitz K (1979) A new treatment method of hydrofluoric acid burns of the extremities. Chir Forum Exp Klin Forsch 1979:229–231
Pegg SP, Siu S, Gillett G (1985) Intra-arterial infusions in the treatment of hydrofluoric acid burns. Burns Incl Therm Inj 11(6):440–443
Vance MV, Curry SC, Kunkel DB et al (1986) Digital hydrofluoric acid burns: treatment with intraarterial calcium infusion. Ann Emerg Med 15(8):890–896
Velvart J (1983) Arterial perfusion for hydrofluoric acid burns. Hum Toxicol 2(2):233–238
Nguyen LT, Mohr WJ III, Ahrenholz DH et al (2004) Treatment of hydrofluoric acid burn to the face by carotid artery infusion of calcium gluconate. J Burn Care Rehab 25(5):421–424
Aaron CK, Fudem GM, Hartigan CF et al (1996) Treatment of extremity hydrofluoric acid burns: an in-vivo histopathologic comparison of topical, locally infiltrated, intraarterial, and regional IV calcium gluconate. Acad Emerg Med 5:419
Anderson WJ, Anderson JR (1988) Hydrofluoric acid burns of the hand: mechanism of injury and treatment. J Hand Surg [Am] 13(1):52–57
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, D., Jaeger, U., Sagoschen, I. et al. Intra-Arterial Calcium Gluconate Treatment After Hydrofluoric Acid Burn of the Hand. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32, 155–158 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-008-9361-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-008-9361-1