Abstract
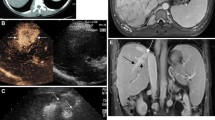
A 73-year-old man with hepatitis-C-related cirrhosis and an elevated alpha-fetoprotein level and tumor in segment 3 of his liver was referred for interventional radiologic treatment. He was not a candidate for surgical resection due to impaired liver function and his personal preferences. On conventional ultrasonography no lesion could be detected, but the tumor was clearly depicted by intra-arterial carbon-dioxide-enhanced ultrasonography. Radiofrequency ablation was performed safely and accurately under the guidance of carbon-dioxide-enhanced ultrasonography. By concomitant performance of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with radiofrequency ablation, extensive necrosis was obtained and adequate tumor volume reduction achieved with only one treatment session.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGhana JP, Dodd GD 3rd (2001) Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: current status. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:3–16
Lin SM, Lin CJ, Lin CC, et al. (2005) Randomised controlled trial comparing percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and percutaneous acetic acid injection to treat hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less. Gut 54:1151–1156
Matsuda Y, Yabuuchi I (1986) Hepatic tumors: US contrast enhancement with CO2 microbubbles. Radiology 161:701–705
Ohmoto K, Tsuzuki M, Yamamoto S (1999) Percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy with intraperitoneal saline infusion for hepatocellular carcinoma in the hepatic dome. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:65–66
Koda M, Ueki M, Maeda T, et al. (2004) Percutaneous sonographically guided radiofrequency ablation with artificial pleural effusion for hepatocellular carcinoma located under the diaphragm. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:583–588
Ohmoto K, Mimura N, Iguchi Y, et al. (2002) CT-guided percutaneous ethanol injection therapy for ultrasonically invisible hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 49:297–299
Minami Y, Kudo M, Kawasaki T, et al. (2004) Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: Usefulness of contrast harmonic sonography for lesions poorly defined with B-mode sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:153–156
Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Koida I, et al. (1994) Imaging diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 20:82–87
Numata K, Tanaka K. Kiba T, et al. (2001) Nonresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Improved percutaneous ethanol injection guided by CO2-enhanced sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:789–798
Chen RC, Liao LY, Wang CS, et al. (2003) Carbon dioxide-enhanced sonographically guided percutaneous ethanol injection: Treatment of patients with viable and recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:1647–1652
Hashimoto M, Watanabe O, Hirano Y, et al. (1997) Use of carbon dioxide microbubble-enhanced sonographic angiography for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169:1307–1310
Kitamoto M, Imagawa M, Yamada H, et al (2003) Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of the radiofrequency effect with and without chemoembolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:997–1003
Veltri A, Moretto P, Doriguzzi A, et al. (2005) Radiofrequency thermal ablation (RFA) after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as a combined therapy for unresectable non-early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Eur Radiol 14:1–9
Ahrar K, Gupta S (2003) Hepatic artery embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Technique, patient selection, and outcomes. Surg Oncol Clin North Am 12:105–126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohmoto, K., Yoshioka, N., Tomiyama, Y. et al. Use of Intra-Arterial Carbon-Dioxide-Enhanced Ultrasonography for Guidance of Radiofrequency Ablation and Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29, 1111–1113 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0285-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0285-8