Abstract
Purpose
A transcutaneous port (T-port) has been developed allowing easy exchange of a catheter, which was fixed inside the device, using the Seldinger technique. The objective of the study was to test the T-port in patients who had percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD).
Methods
The T-port, made of titanium, was implanted using local anesthesia in 11 patients (mean age 65 years, range 52–85 years) with biliary duct obstruction (7 malignant and 4 benign strictures). The subcutaneous part of the T-port consisted of a flange with several perforations allowing ingrowth of connective tissue. The T-port allowed catheter sizes of 10 and 12 Fr.
Results
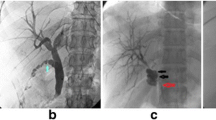
All wounds healed uneventfully and were followed by a stable period without signs of pronounced inflammation or infection. It was easy to open the port and to exchange the drainage tube. The patient’s quality of life was considerably improved even though several patients had problems with repeated bile leakage due to frequent recurrent obstructions of the tubes. The ports were implanted for a mean time of 9 months (range 2–21 months). Histologic examination in four cases showed that the port was well integrated into the soft tissue. Tilting of the T-port in two cases led to perforation of the skin by the subcutaneous part of the ports, which were removed after 7 and 8 months.
Conclusion
The T-port served as an excellent external access to the biliary ducts. The drainage tubes were well fixed within the ports. The quality of life of the patients was considerably improved. Together with improved aesthetic appearance they found it easier to conduct normal daily activities and personal care. However, the problem of recurrent catheter obstruction remained unsolved.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
P Born T Rösch A Tritrap E Frimberger H-D Allescher R Ott (1998) ArticleTitleLong-term results of percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage for benign and malignant bile duct strictures Scand J Gastroenterol 33 344–549
WC Culp TC McCowan RP Lieberman TC Goertzen RF LeVeen TG Heffron (1996) ArticleTitleBiliary strictures in liver transplants recipients: Treatment with metal stents Radiology 199 339–346 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymB3c3ns1I%3D Occurrence Handle8668775
H Oikarinen S Leinonen A Karttunen T Tikkakoski T Hetemaa J Makela M Paivansalo (1999) ArticleTitlePatency and complications of percutaneously inserted metallic stents in malignant biliary obstruction J Vasc Interv Radiol 10 1387–1393 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FkvFemsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10584656
DH Bonnel CL Liguory JF Lefebvre FE Cornud (1997) ArticleTitlePlacement of metallic stents for treatment of postoperative biliary strictures: Long-term outcome in 25 patients AJR Am J Roentgenol 169 1517–1522 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FlsVyltw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9393155
JG Caridii IF Hawkins WE Atkins RS Young (1997) ArticleTitleButton self-retaining drainage catheter Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 20 317–318
JM Friedrich P Schnarkowski KH Link KA Schumacher S Hoch (1992) ArticleTitleFlushable stent-system for internal drainage in occlusive jaundice Eur J Radiol 15 45–48 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyD3M7isVM%3D Occurrence Handle1396789
D Lundgren R Axelsson (1989) ArticleTitleSoft-tissue-anchored percutaneous device for long-term intracorporeal access J Invest Surg 2 17–27 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6C38bhsVM%3D Occurrence Handle2487396
K Donath G Breuner (1982) ArticleTitleA method for study of undecalcified bone and teeth with attached soft tissues J Oral Pathol 11 318–326 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi2B28fjsVY%3D Occurrence Handle6809919
KM Holgers A Ljungh (1999) ArticleTitleCell surface characteristics of microbiological isolates from human percutaneous titanium implants in the head and neck Biomaterials 20 1319–1326 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktVyisrk%3D Occurrence Handle10403050
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nyman, R., Eklöf, H., Eriksson, LG. et al. Soft-Tissue-Anchored Transcutaneous Port for Long-Term Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28, 53–59 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-6500-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-6500-1